|
Languages Of Estonia
The official language of Estonia is Estonian, a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, which is related to Finnish. It is unrelated to the bordering Russian and Latvian languages, both of which are Indo-European (more specifically East Slavic and Baltic, respectively). Minority languages Võro Võro is a language from the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. It used to be considered a dialect of the South Estonian dialect group of the Estonian language, but nowadays it has its own literary standard and is in search of official recognition as an indigenous regional language of Estonia. Seto dialect Seto is a language from the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. It is sometimes identified as a dialect of either South Estonian (along with Võro, Tartu and Mulgi) or Võro, some linguists also consider Seto and Võro to be dialects from a common language, Võro-Seto, or Seto to be a language on its own, more similar to Medieval Estonian than the current stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Language
Estonian ( ) is a Finnic language, written in the Latin script. It is the official language of Estonia and one of the official languages of the European Union, spoken natively by about 1.1 million people; 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 outside Estonia. Classification Estonian belongs to the Finnic branch of the Uralic language family. The Finnic languages also include Finnish and a few minority languages spoken around the Baltic Sea and in northwestern Russia. Estonian is subclassified as a Southern Finnic language and it is the second-most-spoken language among all the Finnic languages. Alongside Finnish, Hungarian and Maltese, Estonian is one of the four official languages of the European Union that are not of an Indo-European origin. From the typological point of view, Estonian is a predominantly agglutinative language. The loss of word-final sounds is extensive, and this has made its inflectional morphology markedly more fusional, especially with respect to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian Language
Latvian ( ), also known as Lettish, is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family, spoken in the Baltic region. It is the language of Latvians and the official language of Latvia as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 1.3 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and 100,000 abroad. Altogether, 2 million, or 80% of the population of Latvia, speak Latvian. Of those, around 1.16 million or 62% of Latvia's population use it as their primary language at home, however excluding the Latgale Region it is spoken as a native language in villages and towns by over 90% of the population. As a Baltic language, Latvian is most closely related to neighboring Lithuanian (as well as Old Prussian, an extinct Baltic language); however Latvian has followed a more rapid development. In addition, there is some disagreement whether Latgalian and Kursenieki, which are mutually intelligible with Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Võru County
Võru County ( et, Võru maakond or ''Võrumaa''; vro, Võro maakund) is a county in southern Estonia. It is bordered by Valga County and Põlva County and is the only Estonian county bordering two countries - Latvia ( Alūksne Municipality and Ape Municipality) in the south and Russian Federation (Pskov Oblast) in the east. The territory of Võrumaa covers and is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. In January 2013 Võru County had a population of 32,806, 2.5% of the total population in Estonia. The county is subdivided into 12 rural municipalities and one urban municipality, the county capital, Võru. Ethnic Division and Culture In Võru County, there are 95.3% Estonians, 3.3% Russians and 1.4% other nationalities. Two indigenous ethnic groups live in Võru County – the Võro people and the Setos. Both ethnic groups have their own language ( Võro, Seto) and cultural heritage in traditions. Võro People The Võro Institute is established for the preserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched the Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the ''Ninety-five Theses'', divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of northern Europe, especially in northern Germany, Scandinavia and the then-Livonian Order. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state. The split between the Lutherans and the Roman Catholics was made public and clear with the 1521 Edict of Worms: the edicts of the Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagating his ideas, subjecting advocates of Lutheranism to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Võros
Võros ( Võro: ''võrokõsõq,'' pronounced , et, võrukesed, fi, võrolaiset) are inhabitants of historical Võromaa (''Vana Võromaa''), a region in Southeastern Estonia (Võru and Põlva Counties with parts extending into Valga and Tartu Counties). The term is particularly used by proponents of a regional identity. About 70,000 people live in historical Võromaa and many more identify as Võros although they live outside the territory, mostly in Tartu and Tallinn. See also * Võru County (Võrumaa, Võromaa) * Võro language * Võro Institute Võro Institute ( vro, Võro Instituut, et, Võru Instituut) is an Estonian state research and development institution dedicated to the preservation and promotion of the Võro language and culture. History Võro ( vro, võro kiil, links=no ... * Võro language newspaper ''Uma Leht'' External linksInformation about Võros in Eurominority References *Ehala, Martin & Niglas, Katrin (2007): Empirical evaluation of a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via local synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the head of the Roman Catholic Church—the Pope—but the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognized by them as '' primus inter pares'' ("first among equals"), which may be explained as a representative of the church. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played a prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern and Southeastern Europe. The Eastern Orthodox Church officially calls itself the Orthodox Catholic Church. Eastern Orthodox theology is based on holy tradition, which incorporates the dogmatic decrees of the seven ecumenical councils, the Scriptures, and the tea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setomaa
Setomaa (; russian: Сетумаа, seto, Setomaa) is a region south of Lake Peipus and inhabited by the Seto people. The Seto dialect is a variety of South Estonian. The historic range of Setomaa is located in the territories of present-day Estonia and Russia. Estonian Setomaa presently consists of lands in Võru County located in southeastern Estonia and bordering Russia. Petseri (Russian: Pechory) has been the historic and cultural centre for the Setos. Current subdivision Estonian Setomaa consists of: *In Võrumaa county: ** Setomaa Parish (municipality) The Russian part consists of Pechorsky District, part of Pskov Oblast. Between 1918 and 1944, the area was part of Estonia, administered as Petseri County. After Estonia regained its independence from the Soviet Union The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setos
Setos ( seto, setokõsõq, , et, setukesed, ) are an indigenous Finnic peoples and linguistic minority that have historically lived in the borderlands between modern day Estonia and Russia. Setos have historically spoken the Seto language and been Orthodox Christians.Kalkun, A., Kupari, H., & Vuola, E. (2018). ''Coping with Loss of Homeland through Orthodox Christian Processions: Contemporary Practices among Setos, Karelians, and Skolt Sámi in Estonia and Finland''. ''Practical matters'', ''11''. http://practicalmattersjournal.org/2018/06/11/coping-with-loss-of-homeland-2/ The Seto language (like Estonian and Finnish) belongs to the Finnic group of the Uralic language family. Since the early 2000s, the Setos have sought greater recognition, rather than having their language considered a dialect of Estonian. Eastern Orthodox Christianity, with influences from local folk religions is widely practiced by the Seto peoples. The ancestral homes of many Setos can be found to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
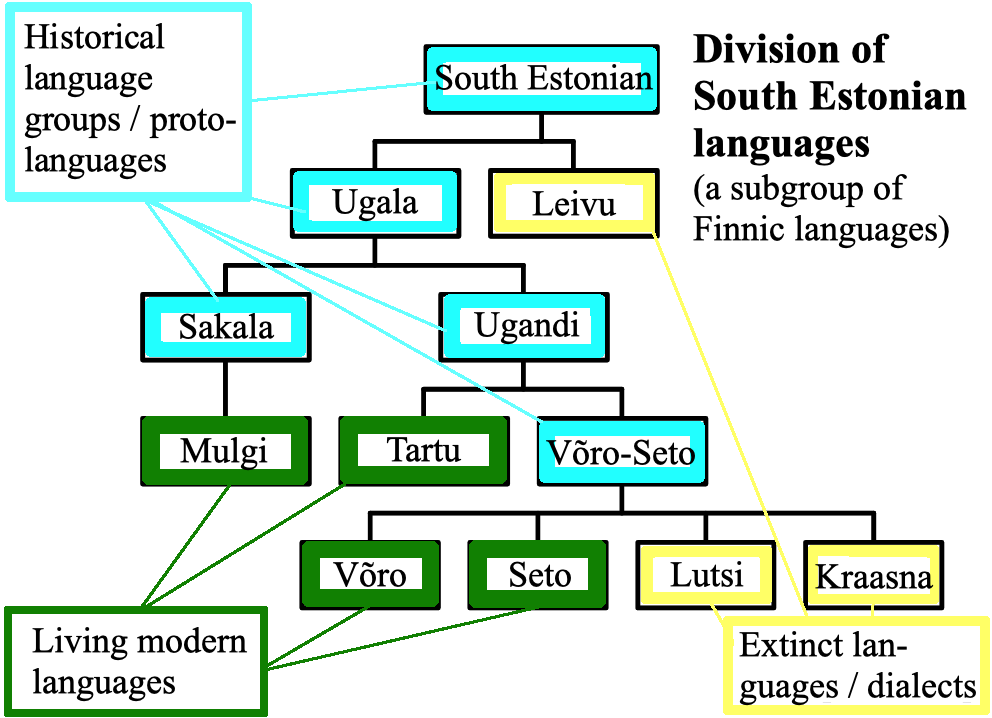
Tartu Language
South Estonian, spoken in south-eastern Estonia, encompasses the Tartu, Mulgi, Võro and Seto varieties. There is no academic consensus on its status, as some linguists consider South Estonian a dialect group of Estonian whereas other linguists consider South Estonian an independent Finnic language. Diachronically speaking, North and South Estonian are separate branches of the Finnic languages. Note that reconstructed *č and *c stand for affricates , . Modern Standard Estonian has evolved on the basis of the dialects of Northern Estonia. However, from the 17th to the 19th centuries in Southern Estonia, literature was published in a standardized form of Southern Tartu and Northern Võro. That usage was called Tartu or literary South Estonian. The written standard was used in the schools, churches and courts of the Võro and Tartu linguistic area but not in the Seto and Mulgi areas. After Estonia gained independence in 1918, the standardized Estonian language policies were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Language
* A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area. Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, "''regional or minority languages''" ''means languages that are:'' #''traditionally used within a given territory of a State by nationals of that State who form a group numerically smaller than the rest of the State's population and'' #''different from the official language(s) of that State'' Recognition of regional or minority languages must not be confused with recognition as an official language. Influence of number of speakers There are many cases when a regional language can claim greater numbers of speakers than certain languages which happen to be official languages of sovereign states. For example, Catalan (a regional language of Spain, Italy and France, albeit the national language of Andorra) has more speakers than Finn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Estonian
South Estonian, spoken in south-eastern Estonia, encompasses the Tartu, Mulgi, Võro and Seto varieties. There is no academic consensus on its status, as some linguists consider South Estonian a dialect group of Estonian whereas other linguists consider South Estonian an independent Finnic language. Diachronically speaking, North and South Estonian are separate branches of the Finnic languages. Note that reconstructed *č and *c stand for affricates , . Modern Standard Estonian has evolved on the basis of the dialects of Northern Estonia. However, from the 17th to the 19th centuries in Southern Estonia, literature was published in a standardized form of Southern Tartu and Northern Võro. That usage was called Tartu or literary South Estonian. The written standard was used in the schools, churches and courts of the Võro and Tartu linguistic area but not in the Seto and Mulgi areas. After Estonia gained independence in 1918, the standardized Estonian language policies were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)