|
Lactobacillus Sakei
''Latilactobacillus sakei'' is the type species of the genus ''Latilactobacillus'' that was previously classified in the genus ''Lactobacillus''. It is homofermentative; hexoses are metabolized via glycolysis to lactic acid as main metabolite; pentoses are fermented via the Phosphoketolase pathway to lactic and acetic acids. Uses Antilisterial strains of ''L. sakei'' are used in Europe for the production of saucisson and can be used for the conservation of fresh meat. ''L. sakei'' strains isolated from traditional dry sausage have a potential use as starter cultures. Inhibition of '' Listeria monocytogenes'' in chicken cold cuts can be obtained by addition of sakacin P and sakacin P-producing ''Lactobacillus sakei''. Strain ''2a'' of the subspecies ''L. sakei subsp. sakei'' can also be isolated from meat products. Research suggests that ''L. sakei'' may play a role in maintaining healthy sinus cavities and preventing sinusitis. Biochemistry Bacteriocins productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0–1
''Latilactobacillus sakei'' is the type species of the genus ''Latilactobacillus'' that was previously classified in the genus ''Lactobacillus''. It is homofermentative; hexoses are metabolized via Glycolysis, glycolysis to lactic acid as main metabolite; pentoses are fermented via the Phosphoketolase pathway to lactic and acetic acids. Uses Antilisterial strains of ''L. sakei'' are used in Europe for the production of saucisson and can be used for the conservation of fresh meat. ''L. sakei'' strains isolated from traditional dry sausage have a potential use as starter cultures. Inhibition of ''Listeria monocytogenes'' in chicken cold Cut of meat, cuts can be obtained by addition of sakacin P and sakacin P-producing ''Lactobacillus sakei''. Strain ''2a'' of the subspecies ''L. sakei subsp. sakei'' can also be isolated from meat products. Research suggests that ''L. sakei'' may play a role in maintaining healthy sinus cavities and preventing sinusitis. Biochemistry Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class II Bacteriocin
Class II bacteriocins are a class of small peptides that inhibit the growth of various bacteria. Many Gram-positive bacteria produce ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides, termed bacteriocins. Bacteriocins for which disulfide bonds are the only modification to the peptide are Class II bacteriocins. Class IIa One important and well studied class of bacteriocins is the class IIa or pediocin-like bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria. All class IIa bacteriocins are produced by food-associated strains, isolated from a variety of food products of industrial and natural origins, including meat products, dairy products and vegetables. Class IIa bacteriocins are all cationic, display anti-''Listeria'' activity, and kill target cells by permeabilizing the cell membrane. Class IIa bacteriocins contain between 37 and 48 residues. Based on their primary structures, the peptide chains of class IIa bacteriocins may be divided roughly into two regions: a hydrophilic, catio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakacin X
Sakacins are bacteriocins produced by ''Lactobacillus sakei''. They are often clustered with the other lactic acid bacteriocins. The best known sakacins are sakacin A, G, K, P, and Q. In particular, sakacin A and P have been well characterized. List of named sakacins * Sakacin A is a small, 41 amino acid (the precursor is 90 aa), heat-stable polypeptide. It has been characterized genetically. The regulation of sakacin A has been shown to be related to pheromones (possibly quorum sensing) and temperature changes. It is identical to curvacin/curvaticin A. * Sakacin B is a heat and pH stable protein. * Sakacin G is a 37 amino acid long (small) polypeptide. * Sakacin K is closely related to Sakacin A (and curvacin A), sharing the first 30 N-terminal amino acids. It has been studied extensively for its industrial applications. * Sakacin M is a heat-resistant protein, MW = 4640. * Sakacin P is a small, heat-stable, ribosomally synthesized polypeptide. Its genetics has been well-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakacin T
Sakacins are bacteriocins produced by ''Lactobacillus sakei''. They are often clustered with the other lactic acid bacteriocins. The best known sakacins are sakacin A, G, K, P, and Q. In particular, sakacin A and P have been well characterized. List of named sakacins * Sakacin A is a small, 41 amino acid (the precursor is 90 aa), heat-stable polypeptide. It has been characterized genetically. The regulation of sakacin A has been shown to be related to pheromones (possibly quorum sensing) and temperature changes. It is identical to curvacin/curvaticin A. * Sakacin B is a heat and pH stable protein. * Sakacin G is a 37 amino acid long (small) polypeptide. * Sakacin K is closely related to Sakacin A (and curvacin A), sharing the first 30 N-terminal amino acids. It has been studied extensively for its industrial applications. * Sakacin M is a heat-resistant protein, MW = 4640. * Sakacin P is a small, heat-stable, ribosomally synthesized polypeptide. Its genetics has been well-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Amplification Of Polymorphic DNA
Random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD), pronounced "rapid", is a type of polymerase chain reaction (PCR), but the segments of DNA that are amplified are random. The scientist performing RAPD creates several arbitrary, short primers (10- 12 nucleotides), then proceeds with the PCR using a large template of genomic DNA, hoping that fragments will amplify. By resolving the resulting patterns, a semi-unique profile can be gleaned from an RAPD reaction. No knowledge of the DNA sequence of the targeted genome is required, as the primers will bind somewhere in the sequence, but it is not certain exactly where. This makes the method popular for comparing the DNA of biological systems that have not had the attention of the scientific community, or in a system in which relatively few DNA sequences are compared (it is not suitable for forming a cDNA databank). Because it relies on a large, intact DNA template sequence, it has some limitations in the use of degraded DNA samples. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCR Primer
PCR or pcr may refer to: Science * Phosphocreatine, a phosphorylated creatine molecule * Principal component regression, a statistical technique Medicine * Polymerase chain reaction ** COVID-19 testing, often performed using the polymerase chain reaction method * Protein/creatinine ratio, in urine * Pathologic complete response (pCR), in neoadjuvant therapy Technology * Passport Carrier Release, telecommunications software * Peak cell rate, on ATM networks * Platform Configuration Register, a Trusted Platform Module component * Program clock reference, in MPEG transport streams * Processor Control Region, a Windows data structure * XM PCR, a satellite receiver Political parties * '' Parti Communiste Réunionnais'' or Communist Party of Réunion * '' Partidul Comunist Român'' or Romanian Communist Party * ''Partido Comunista Revolucionário'' or Revolutionary Communist Party * '' Partido Cívico Renovador'' or Civic Renovation Party, Dominican Republic Other uses * Put/ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugenol
Eugenol is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol, a member of the allylbenzene class of chemical compounds. It is a colorless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, basil and bay leaf. It is present in concentrations of 80–90% in clove bud oil and at 82–88% in clove leaf oil. Eugenol has a pleasant, spicy, clove-like scent. The name is derived from ''Eugenia caryophyllata'', the former Linnean nomenclature term for cloves. The currently accepted name is ''Syzygium aromaticum''. Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of eugenol begins with the amino acid tyrosine. L-tyrosine is converted to ''p''-coumaric acid by the enzyme tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL). From here, ''p''-coumaric acid is converted to caffeic acid by ''p''-coumarate 3-hydroxylase using oxygen and NADPH. ''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) is then used to methylate caffeic acid, forming ferulic acid, which is in turn converted to feruloyl- C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
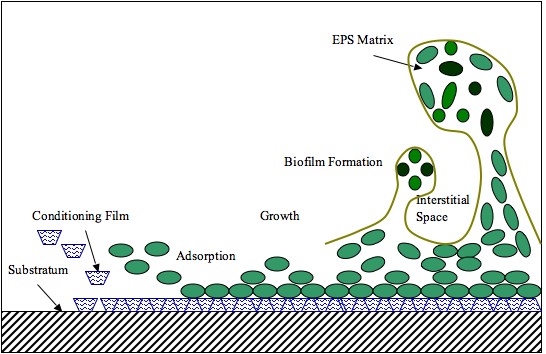
Exopolysaccharide
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physicochemical properties of a biofilm. EPS in the matrix of biofilms provides compositional support and protection of microbial communities from the harsh environments. Components of EPS can be of different classes of polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, Lipopolysaccharides, and minerals. Components EPSs are mostly composed of polysaccharides (exopolysaccharides) and proteins, but include other macromolecules such as DNA, lipids and humic substances. EPSs are the construction material of bacterial settlements and either remain attached to the cell's outer surface, or are secreted into its growth medium. These compounds are important in biofilm formation and cells' attachment to surfaces. EPSs c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakacin K
Sakacins are bacteriocins produced by ''Lactobacillus sakei''. They are often clustered with the other lactic acid bacteriocins. The best known sakacins are sakacin A, G, K, P, and Q. In particular, sakacin A and P have been well characterized. List of named sakacins * Sakacin A is a small, 41 amino acid (the precursor is 90 aa), heat-stable polypeptide. It has been characterized genetically. The regulation of sakacin A has been shown to be related to pheromones (possibly quorum sensing) and temperature changes. It is identical to curvacin/curvaticin A. * Sakacin B is a heat and pH stable protein. * Sakacin G is a 37 amino acid long (small) polypeptide. * Sakacin K is closely related to Sakacin A (and curvacin A), sharing the first 30 N-terminal amino acids. It has been studied extensively for its industrial applications. * Sakacin M is a heat-resistant protein, MW = 4640. * Sakacin P is a small, heat-stable, ribosomally synthesized polypeptide. Its genetics has been well-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |