|
Lungless Salamander
Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. With over 500 species, lungless salamanders are by far the largest family of salamanders in terms of their diversity. Most species are native to the Western Hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil. Only two extant genera occur in the Eastern Hemisphere: '' Speleomantes'' (native to Sardinia and mainland Europe south of the Alps) and '' Karsenia'' (native to South Korea). Biology Adult lungless salamanders have four limbs, with four toes on the fore limbs, and usually with five on the hind limbs. Within many species, mating and reproduction occur solely on land. Accordingly, many species also lack an aquatic larval stage, a phenomenon known as direct development in which the offspring hatch as fully-formed, miniature adults. Direct development is correlated with changes in the developmental characteristics of plethodontids compared to other families of salamanders including increases in egg size and durati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Slender Salamander
The California slender salamander (''Batrachoseps attenuatus'') is a lungless salamanderRobert C. Stebbins, Stebbins, Robert C. (2003). ''A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians'', 3rd Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, that is found primarily in coastal mountain areas of Northern California, United States as well as in a limited part of the western foothills of the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada, California, in patches of the northern California Central Valley, Central Valley of California, and in extreme southwestern Oregon. This species resides primarily in a limited range within California as one of a handful quasi-endemic amphibians in the state. In 2001 Elizabeth Jockusch, Elizabeth L. Jockusch and David B. Wake, David Wake used genetic sequencing to find that the California slender salamander, the most common salamander in California, was in fact twenty separate species spread out along the coast from Oregon to Mexico. Presently, the California slender salam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloaca
A cloaca ( ), : cloacae ( or ), or vent, is the rear orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive (rectum), reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles, birds, cartilaginous fish and a few mammals ( monotremes, afrosoricids, and marsupial moles, etc.) have this orifice, from which they excrete both urine and feces; this is in contrast to most placental mammals, which have separate orifices for evacuation and reproduction. Excretory openings with analogous purpose in some invertebrates are also sometimes called cloacae. Mating through the cloaca is called cloacal copulation and cloacal kissing. The cloacal region is also often associated with a secretory organ, the cloacal gland, which has been implicated in the scent-marking behavior of some reptiles, marsupials, amphibians, and monotremes. Etymology The word is from the Latin verb ''cluo'', "(I) cleanse", thus the noun ''cloaca'', " sewer, drain" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps. Much of the world's modern vertebrate diversity originated in a rapid surge of diversification in the early Paleogene, as survivors of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event took advantage of empty ecolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous–Paleogene Boundary
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary, formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) boundary, is a geological signature, usually a thin band of rock containing much more iridium than other bands. The K–Pg boundary marks the end of the Cretaceous Period, the last period of the Mesozoic Era, and marks the beginning of the Paleogene Period, the first period of the Cenozoic Era. Its age is usually estimated at 66 million years, with radiometric dating yielding a more precise age of 66.043 ± 0.043 Ma. The K–Pg boundary is associated with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, a mass extinction which destroyed a majority of the world's Mesozoic species, including all dinosaurs except for some birds. Strong evidence exists that the extinction coincided with a large meteorite impact at the Chicxulub crater and the generally accepted scientific theory is that this impact triggered the extinction event. The word "Cretaceous" is derived from the Latin "creta" ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphiumidae
''Amphiuma'' is a genus of aquatic salamanders from the United States, the only Extant taxon, extant genus within the family (biology), family Amphiumidae . They are colloquially known as amphiumas. They are also known to fishermen as "conger eels" or "Congo snakes", which are zoology, zoologically incorrect designations or misnomers, since amphiumas are actually salamanders (and thus amphibians), and not fish, nor reptiles and are not from Congo Basin, Congo. ''Amphiuma'' exhibits one of the largest complements of DNA in the living world, around 25 times more than a human. Taxonomy Numerous phylogenetic studies have indicated that amphiumas form a clade with the families Torrent salamander, Rhyacotritonidae (torrent salamanders) and Plethodontidae (lungless salamanders), with an especially close relationship to Plethodontidae. Despite this possible relationship, the two families must have still diverged very early on. The genus ''Proamphiuma'' from the Cretaceous is the earlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemoreception
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance (endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemoreceptor is a neuron, or in the form of a neurotransmitter that can activate a nerve fiber if the chemoreceptor is a specialized cell, such as taste receptors, or an internal peripheral chemoreceptor, such as the carotid bodies. In physiology, a chemoreceptor detects changes in the normal environment, such as an increase in blood levels of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia) or a decrease in blood levels of oxygen (hypoxia), and transmits that information to the central nervous system which engages body responses to restore homeostasis. In bacteria, chemoreceptors are essential in the mediation of chemotaxis. Cellular chemoreceptors In prokaryotes Bacteria utilize complex long helical proteins as chemoreceptors, permitting signals to travel long dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surfactant Protein C
Surfactant protein C (SP-C), is one of the pulmonary surfactant proteins. In humans this is encoded by the ''SFTPC'' gene. It is a membrane protein. Structure SFTPC is a 197-residue protein made up of two halves: a unique N-terminal propeptide domain and a C-terminal BRICHOS domain. The around 100-aa long propeptide domain actually contains not only the cleaved part, but also the mature peptide. It can be further broken down into a 23-aa helical transmembrane propeptide proper, the mature secreted SP-C (24-58), and a linker (59-89) that connects to the BRICHOS domain. The propeptide of pulmonary surfactant C has an N-terminal alpha-helical segment whose suggested function was stabilization of the protein structure, since the mature peptide can irreversibly transform from its native alpha-helical structure to beta-sheet aggregates and form amyloid fibrils. The correct intracellular trafficking of proSP-C has also been reported to depend on the propeptide. The structure of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of an adequate oxygen supply at the tissue (biology), tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either ''Generalized hypoxia, generalized'', affecting the whole body, or ''local'', affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise. Hypoxia differs from hypoxemia and anoxemia, in that hypoxia refers to a state in which oxygen present in a tissue or the whole body is insufficient, whereas hypoxemia and anoxemia refer specifically to states that have low or no Oxygen saturation (medicine), oxygen in the blood. Hypoxia in which there is complete absence of oxygen supply is referred to as anoxia. Hypoxia can be due to external causes, when the breathing gas is hypoxic, or internal causes, such as reduced effectiveness of gas transfer in the lung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). In respiratory physiology, the partial pressure of a dissolved gas in liquid (such as oxygen in arterial blood) is also defined as the partial pressure of that gas as it would be undissolved in gas phase yet in equilibrium with the liquid. This concept is also known as blood gas tension. In this sense, the diffusion of a gas liquid is said to be driven by differences in partial pressure (not concentration). In chemistry and thermodynamics, this concept is generalized to non-ideal gases and instead called fugacity. The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of its Thermodynamic activity, thermodynamic activity. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
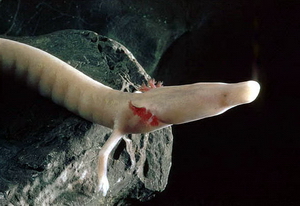
Cave Salamander
A cave salamander is a type of salamander that primarily or exclusively inhabits caves, a group that includes several species. Some of these animals have developed special, even extreme, adaptations to their subterranean environments. Some species have only rudimentary (or even absent) eyes (''blind salamanders''). Others lack pigmentation, rendering them a pale yellowish or pinkish color (e.g., '' Eurycea rathbuni''). With the notable exception of the olm (''Proteus anguinus''), all "cave salamanders" are members of the family Plethodontidae ("lungless salamanders"). Almost all of them are paedomorphic and therefore never undergo metamorphosis, but it is not clear if this happened before or after they adapted to an existence in caves, as some species that don't live in caves are also paedomorphic. History The first dedicated scientific study of a cave animal was focused upon a cave salamander, '' Proteus anguinus''. It was originally identified as a "dragon's larva" by Johann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |