|
Lugol's Solution
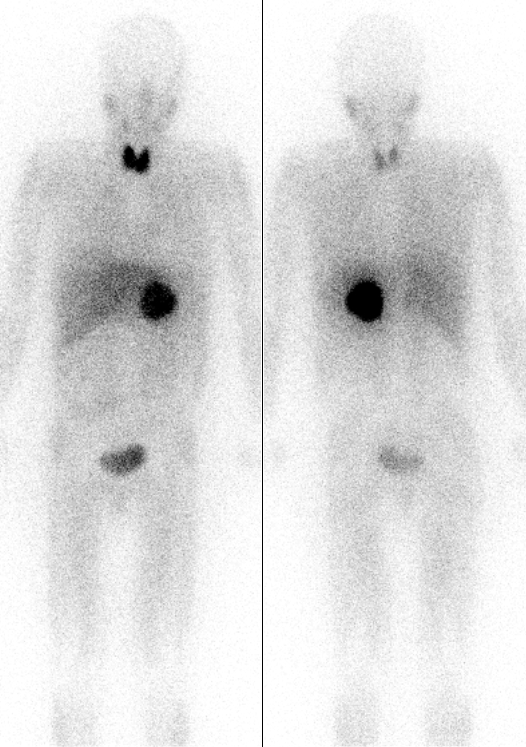
Lugol's iodine, also known as aqueous iodine and strong iodine solution, is a solution of potassium iodide with iodine in water. It is a medication and disinfectant used for a number of purposes. Taken by mouth it is used to treat thyrotoxicosis until surgery can be carried out, protect the thyroid gland from radioactive iodine, and to treat iodine deficiency. When applied to the cervix it is used to help in screening for cervical cancer. As a disinfectant it may be applied to small wounds such as a needle stick injury. A small amount may also be used for emergency disinfection of drinking water. Side effects may include allergic reactions, headache, vomiting, and conjunctivitis. Long term use may result in trouble sleeping and depression (mood), depression. It should not typically be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Lugol's iodine is a liquid made up of two parts potassium iodide for every one part elemental iodine in water. Lugol's iodine was first made in 1829 by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Iodide
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound, medication, and dietary supplement. It is a medication used for treating hyperthyroidism, in radiation emergencies, and for protecting the thyroid gland when certain types of radiopharmaceuticals are used. In the third world it is also used for treating skin sporotrichosis and phycomycosis. It is a supplement used by people with low dietary intake of iodine. It is administered orally. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, and swelling of the salivary glands. Other side effects include allergic reactions, headache, goitre, and depression. While use during pregnancy may harm the baby, its use is still recommended in radiation emergencies. Potassium iodide has the chemical formula K I. Commercially it is made by mixing potassium hydroxide with iodine. Potassium iodide has been used medically since at least 1820. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Potassium iodide is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Guillaume Auguste Lugol
Jean Guillaume Auguste Lugol (18 August 1786 – 16 September 1851) was a French physician. Lugol was born in Montauban. He studied medicine in Paris and graduated MD in 1812. In 1819 he was appointed acting physician at the Hôpital Saint-Louis a post he held until he retired. After his death in 1851 at Neuilly-sur-Seine, his daughter Adele-Augustine, married Paul Broca. Lugol was interested in tuberculosis and presented a paper to the Royal Academy of Science in Paris in which he advocated the use of fresh air, exercise, cold bathing and drugs. He also published four books on scrofulous diseases and their treatment (1829, 1830, 1831, 1834). Members of the Royal Academy visited Lugol's hospital and, observing an improvement in his patients over the course of sixteen months, endorsed his treatment. He suggested that his iodine solution could be used to treat tuberculosis. This assertion attracted much attention at the time. Although not efficacious in treating tuberculosis, Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucogingival Junction
A mucogingival junction is an anatomical feature found on the intraoral mucosa. The mucosa of the cheeks and floor of the mouth are freely moveable and fragile, whereas the mucosa around the teeth and on the palate are firm and keratinized. Where the two tissue types meet is known as a mucogingival junction. There are three mucogingival junctions: on the facial of the maxilla and on both the facial and lingual of the mandible. The palatal gingiva of the maxilla is continuous with the tissue of the palate, which is bound down to the palatal bones. Because the palate is devoid of freely moveable alveolar mucosa, there is no mucogingival junction.Carranza's Clinical Periodontology, W.B. Saunders 2002, page 17. Clinical importance The clinical importance of the mucogingival junction is in measuring the width of attached gingiva. Attached gingiva is important because it is bound very tightly to the underlying alveolar bone and provides protection to the mucosa during functional use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schiller's Test
Schiller's test or Schiller's Iodine test is a medical test in which iodine solution is applied to the cervix in order to diagnose cervical cancer. Procedure Schiller's iodine solution is applied to the cervix under direct vision. Normal cervical mucosa contains glycogen and stains brown, whereas abnormal areas, such as early cervical cancer, do not take up the stain. The abnormal areas can then be biopsied and examined histologically. The composition of Schiller's iodine is the same as Lugol's iodine, the latter being more concentrated. When Schiller's iodine is not available, Lugol's iodine can be used as an alternative. Schiller's test is not specific for cervical cancer, as areas of inflammation, ulceration and keratosis Keratosis (from '' kerat-'' + '' -osis'') is a growth of keratin on the skin or on mucous membranes stemming from keratinocytes, the prominent cell type in the epidermis. More specifically, it can refer to: * actinic keratosis (also known as solar ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hy |