|
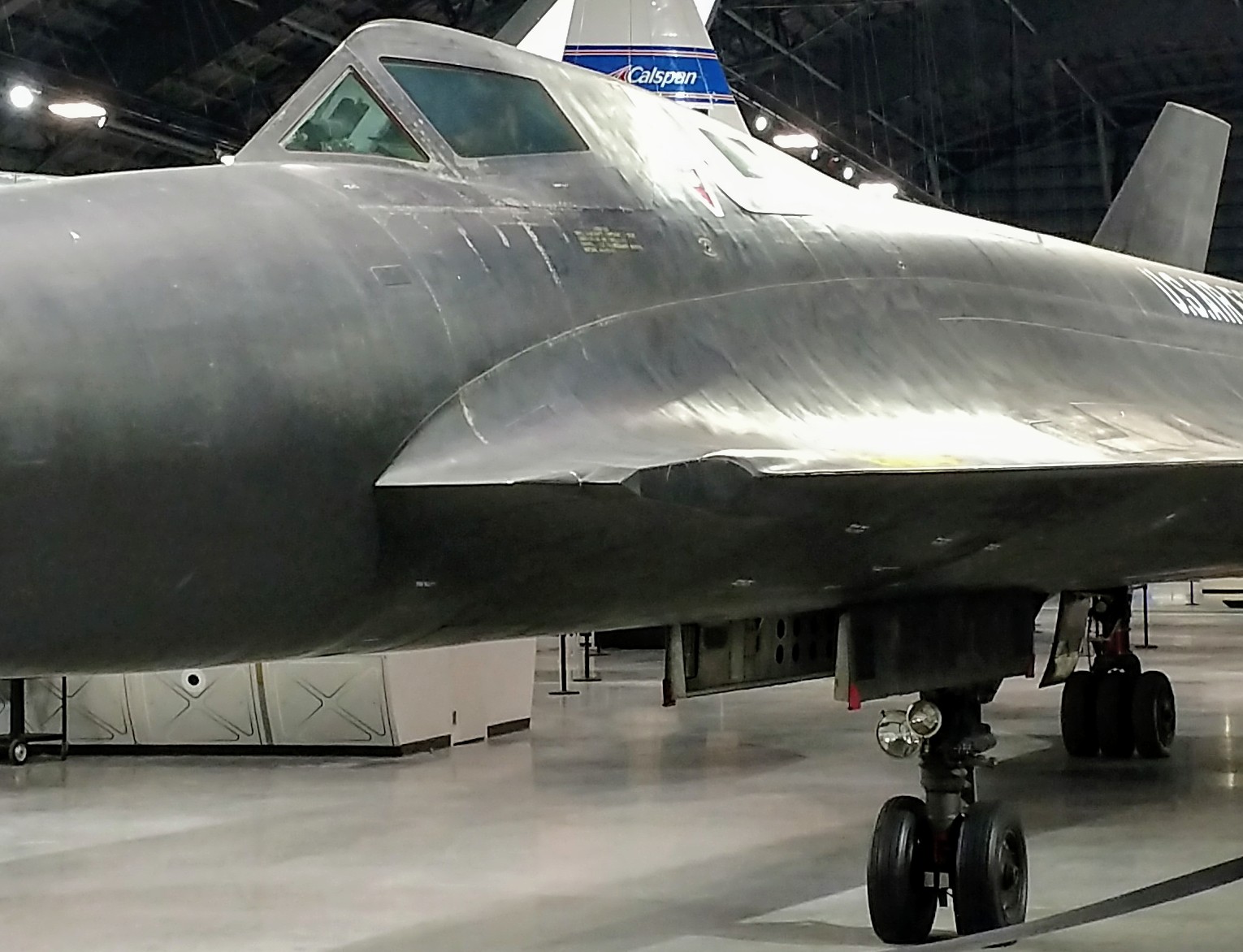
Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird
The Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a retired long-range, high-altitude, Mach 3+ strategic reconnaissance aircraft developed and manufactured by the American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation. Its nicknames include " Blackbird" and " Habu". The SR-71 was developed in the 1960s as a black project by Lockheed's Skunk Works division. American aerospace engineer Clarence "Kelly" Johnson was responsible for many of the SR-71's innovative concepts. Its shape was based on the Lockheed A-12, a pioneer in stealth technology with its reduced radar cross section, but the SR-71 was longer and heavier to carry more fuel and a crew of two in tandem cockpits. The SR-71 was revealed to the public in July 1964 and entered service in the United States Air Force (USAF) in January 1966. During missions, the SR-71 operated at high speeds and altitudes (Mach 3.2 at ), allowing it to evade or outrace threats. If a surface-to-air missile launch was detected, the standard evasive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily in Nevada. The Sierra Nevada is part of the American Cordillera, an almost continuous chain of mountain ranges that forms the western "backbone" of the Americas. The Sierra runs north-south, and its width ranges from to across east–west. Notable features include the General Sherman Tree, the largest tree in the world by volume; Lake Tahoe, the largest alpine lake in North America; Mount Whitney at , the highest point in the contiguous United States; and Yosemite Valley sculpted by glaciers from one-hundred-million-year-old granite, containing high waterfalls. The Sierra is home to three national parks, twenty-six wilderness areas, ten national forests, and two national monuments. These areas include Yosemite, Sequoia, and Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stealth Technology
Stealth technology, also termed low observable technology (LO technology), is a sub-discipline of military tactics and passive and active electronic countermeasures. The term covers a range of military technology, methods used to make personnel, Stealth aircraft, aircraft, Stealth ship, ships, submarines, missiles, satellites, and Stealth ground vehicle, ground vehicles less visible (ideally invisible) to radar, Thermographic camera, infrared, sonar and other detection methods. It corresponds to military camouflage for these parts of the electromagnetic spectrum (i.e., multi-spectral camouflage). Development of modern stealth technologies in the United States began in 1958, where earlier attempts to prevent radar tracking of its Lockheed U-2, U-2 spy planes during the Cold War by the Soviet Union had been unsuccessful. Designers turned to developing a specific shape for planes that tended to reduce detection by redirecting electromagnetic radiation waves from radars. Radiation-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Martin SR-72
The Lockheed Martin SR-72, commonly referred to as "Son of Blackbird," is an American hypersonic concept intended for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR). Proposed privately in 2013 by Lockheed Martin as a successor to the retired Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, the SR-72 was projected by Lockheed Martin executives in 2018 to have a test vehicle fly by 2025 and potentially enter service in the 2030s. Background The SR-71 Blackbird was retired by the United States Air Force in 1998, eliminating a unique and valuable intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capability. Although most fifth-generation jet fighters and planned drones intended for enemy airspace rely on anti-radar stealth technologies, Professor Justin Bronk, a senior research fellow in airpower and technology at the Royal United Services Institute (RUSI), argues that the rise of anti-access/area denial tactics and counter-stealth technologies renders speed more promising than stealth for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Drone Warfare; 2024. e-ISBN (PDF) 978-3-11-074203-9.H. Pan; M. Zahmatkesh; F. Rekabi-Bana; F. Arvin; J. HuT-STAR: Time-Optimal Swarm Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications. These include aerial photography, area coverage,F. Rekabi-Bana; Hu, J.; T. Krajník; Arvin, F.,Unified Robust Path Planning and Optimal Trajectory Generation for Efficient 3D Area Coverage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
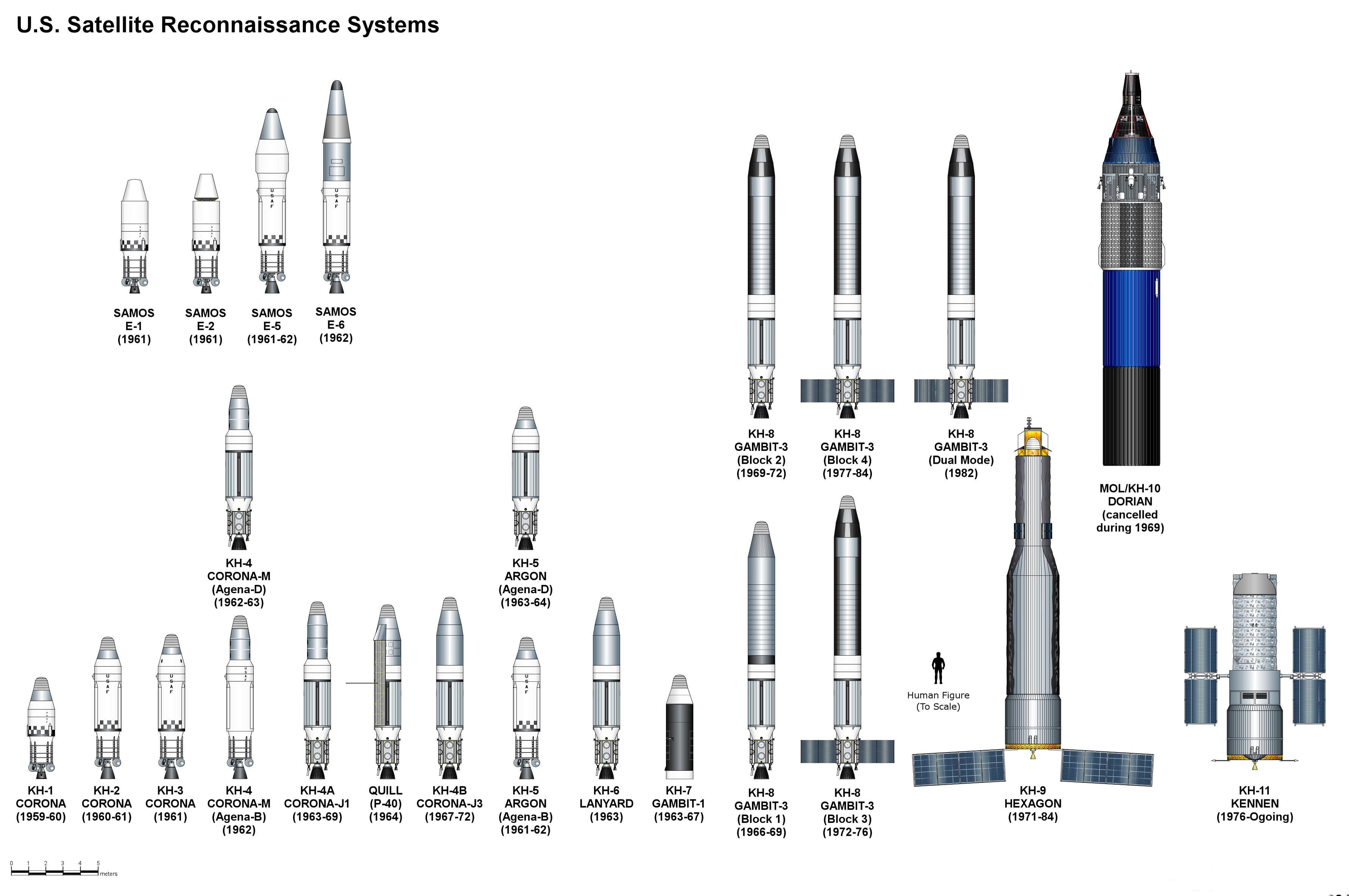
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed YF-12
The Lockheed YF-12 is an American Mach number, Mach 3+ capable, high-altitude interceptor aircraft, interceptor prototype, developed and manufactured by American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation. The interceptor was developed during the late 1950s and early 1960s as a potential replacement for the F-106 Delta Dart interceptor for the United States Air Force (USAF). The YF-12 was a twin-seat version of the then-secret single-seat Lockheed A-12 reconnaissance aircraft operated by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA); unlike the A-12, it was furnished with the Hughes AN/ASG-18 fire-control radar and could be armed with AIM-47 Falcon (GAR-9) air-to-air missiles. Its maiden flight was on 7 August 1963. Its existence was publicly revealed by President Lyndon B. Johnson on 24 February 1964; this move was to provide plausible deniability for the CIA-operated A-12 fleet, which closely resembled the prototype YF-12. During the 1960s, the YF-12 underwent flight evaluations b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Airspeed Record
An air speed record is the highest airspeed attained by an aircraft of a particular class. The rules for all official aviation records are defined by Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI), which also ratifies any claims. Speed records are divided into a number of classes with sub-divisions. There are three classes of aircraft: landplanes, seaplanes, and amphibious aircraft, amphibians, and within these classes there are records for aircraft in a number of weight categories. There are still further subdivisions for Reciprocating engine, piston-engined, turbojet, turboprop, and Rocket engine, rocket-engined aircraft. Within each of these groups, records are defined for speed over a straight course and for closed circuits of various sizes carrying various payloads. Timeline Gray text indicates unofficial records, including unconfirmed or unpublicized war secrets. Official records versus unofficial The Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird holds the official Air Speed Record for a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The National Interest
''The National Interest'' (''TNI'') is an American bimonthly international relations magazine edited by American journalist Jacob Heilbrunn and published by the Center for the National Interest, a public policy think tank based in Washington, D.C., that was established by former U.S. President Richard Nixon in 1994 as the Nixon Center for Peace and Freedom. The magazine is associated with the realist school of international studies. History Founded in 1985 by American columnist and neoconservatism advocate Irving Kristol, the magazine was until 2001 edited by Australian academic Owen Harries. In 2001, The National Interest was acquired by The Center for the National Interest, a public policy think tank based in Washington, D.C., that was established by former U.S. President Richard Nixon on January 20, 1994, as the Nixon Center for Peace and Freedom. In 2005, ten editors of ''The National Interest'' resigned due to different viewpoints regarding the magazine's acqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side-looking Airborne Radar
Side-looking airborne radar (SLAR) is an aircraft, or satellite-mounted imaging radar pointing perpendicular to the direction of flight (hence ''side-looking''). A squinted (nonperpendicular) mode is also possible. SLAR can be fitted with a standard antenna (real aperture radar) or an antenna using synthetic aperture. The platform of the radar moves in direction of the x-axis. The radar "looks" with the looking angle ''θ'' (or so called off-nadir angle). The angle ''α'' between x-axis and the line of sight (LOS) is called cone angle, the angle ''φ'' between the x-axis and the projection of the line of sight to the (x; y)-plane is called azimuth angle. Cone- and azimuth angle are related by cos''α'' = cos''φ'' ∙ cos''ε''. On the earth surface the wave comes in at the (nominal ellipsoidal) incident angle ''β'' with respect to the vertical axis at this point. (In some publications the incident angle is denominated to as ''θi''.) The antenna illuminat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signals-intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication (electronic intelligence—abbreviated to ELINT). As classified and sensitive information is usually encrypted, signals intelligence may necessarily involve cryptanalysis (to decipher the messages). Traffic analysis—the study of who is signaling to whom and in what quantity—is also used to integrate information, and it may complement cryptanalysis. History Origins Electronic interceptions appeared as early as 1900, during the Boer War of 1899–1902. The British Royal Navy had installed wireless sets produced by Marconi on board their ships in the late 1890s, and the British Army used some limited wireless signalling. The Boers captured some wireless sets and used them to make vital transmissions. Since the Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Reconnaissance
Aerial reconnaissance is reconnaissance for a military or Strategy, strategic purpose that is conducted using reconnaissance aircraft. The role of reconnaissance can fulfil a variety of requirements including Artillery observer, artillery spotting, the collection of imagery intelligence, and the observation of enemy maneuvers. History Early developments After the French Revolution, the new rulers became interested in using the balloon (aircraft), balloon to observe enemy manoeuvres and appointed scientist Jean-Marie-Joseph Coutelle, Charles Coutelle to conduct studies using the balloon ''L'Entreprenant'', the first military reconnaissance aircraft. The balloon found its first use in the French Revolutionary Wars: Campaigns of 1794, 1794 conflict with Austria, where in the Battle of Fleurus (1794), Battle of Fleurus they gathered information. Moreover, the presence of the balloon had a demoralizing effect on the Austrian troops, which improved the likelihood of victory for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Approach Warning System
A missile approach warning system (MAW) is part of the avionics package on some military aircraft. A sensor detects attacking missiles. Its automatic warning cues the pilot to make a defensive maneuver and deploy the available countermeasures to disrupt missile tracking. Guided surface-to-air missile (SAM) systems were developed during World War II and began to make their presence felt in the 1950s. In response, electronic countermeasures (ECM) and flying tactics were developed to overcome them. They proved to be quite successful provided that a reliable and timely threat warning was given. The infrared-seeking missile threat Analysis of aircraft losses due to enemy action since the 1960s shows that at least 70% of all losses were attributed to passive heat seeking i.e. infrared (IR) guided missiles. This might be surprising given that radar guided SAM systems have longer engagement ranges, are faster, have higher maneuvering potential, carry larger warheads and are equipped w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |