|
Lituus
The word ''lituus'' originally meant a curved augural staff, or a curved war-trumpet in the ancient Latin language. This Latin word continued in use through the 18th century as an alternative to the vernacular names of various musical instruments. Roman ritual wand The ''lituus'' was a crooked wand (similar in shape to the top part of some Western European crosiers) used as a cult instrument in ancient Roman religion by augurs to mark out a ritual space in the sky (a ''templum''). The passage of birds through this ''templum'' indicated divine favor or disfavor for a given undertaking. The ''lituus'' was also used as a symbol of office for the college of the augurs to mark them out as a priestly group. Music instrument Antiquity The ancient ''lituus'' was an Etruscan high-pitched brass instrument, which was straight but bent at the end, in the shape of a letter J, similar to the Gallic carnyx. It was later used by the Romans, especially for processional music and as a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Templum
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence on later juridical and religious vocabulary in Europe, particularly of the Christian Church. This glossary provides explanations of concepts as they were expressed in Latin pertaining to Religion in ancient Rome, religious practices and beliefs, with links to articles on major topics such as priesthoods, forms of divination, and rituals. For theonyms, or the names and epithets of gods, see List of Roman deities. For public religious holidays, see Roman festivals. For temples see the List of Ancient Roman temples. Individual landmarks of religious Topography of ancient Rome, topography in ancient Rome are not included in this list; see Roman temple. __NOTOC__ Glossary A abominari The verb ''abominari'' ("to avert an omen", from ''ab-'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Tuba
The Roman (plural: ), or trumpet was a military signal instrument used by the ancient Roman military and in religious rituals. They would signal troop movements such as retreating, attacking, or charging, as well as when guards should mount, sleep, or change posts. Thirty-six or thirty-eight ''tubicines'' (tuba players; singular ''tubicen'') were assigned to each Roman legion. The would be blown twice each spring in military, governmental, or religious functions. This ceremony was known as the . It was also used in ancient Roman triumphs. It was considered a symbol of war and battle. The instrument was used by the Etruscans in their funerary rituals. It continued to be used in ancient Roman funerary practices. Roman were usually straight cylindrical instruments with a bell at the end. They were typically made of metals such as silver, bronze, or lead and measured around 4.33 ft or 1.31 meters. Their players, known as the or were well-respected in Roman society. The was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornu (horn)
A ''cornu'' or ''cornum'' (, " horn", sometimes translated misleadingly as " cornet"; : ''cornua'') was an ancient Roman brass instrument about long in the shape of a letter 'G'. The instrument was braced by a crossbar that stiffened the structure and provided a means of supporting its weight on the player's shoulder. Some specimens survive in the archaeological record, two from the ruins of Pompeii. The ''cornu'' may be difficult to distinguish from the '' buccina''. It was used by the Roman army for communicating orders to troops in battle. In Roman art, the ''cornu'' appears among the instruments that accompany games ''( ludi)'' or gladiator combat in the arena, as on the Zliten mosaic. History and usage It was invented by the Etruscans for use in their funeral processions and military. Roman artistic representations of the ''cornu'' are typically realistic. While Etruscan art usually depict the ''cornu'' in use alongside the lituus. It was likely a status symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shawm
The shawm () is a Bore (wind instruments)#Conical bore, conical bore, double-reed woodwind instrument made in Europe from the 13th or possibly 12th century to the present day. It achieved its peak of popularity during the medieval and Renaissance periods, after which it was gradually eclipsed by the oboe family of descendant instruments in classical music. It is likely to have come to Western Europe from the Eastern Mediterranean around the time of the Crusades.The Shawm and Curtal ��from the Diabolus in Musica Guide to Early Instruments Double-reed instruments similar to the shawm were long present in Southern Europe and the East, for instance the Ancient Greek music, ancient Greek, and later Byzantine Empire#Music, Byzantine aulos, the closely related sorna and zurna,A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrianus Junius
Hadrianus Junius (1511–1575), also known as Adriaen de Jonghe, was a Dutch physician, classical scholar, translator, lexicographer, antiquarian, historiographer, emblematist, school rector, and Latin poet. He is not to be confused with several namesakes (including a seventeenth-century Amsterdam school rector). He was not related to Franciscus Junius. Biography Life Youth and education Adriaen de Jonge or Hadrianus Junius, was born in the West Frisian town of Hoorn on 1 July 1511, from a family of local regents. He attended the Latin School in Haarlem. At the relatively advanced age of 23, he went to study in Louvain, where he spent a couple of years. He then embarked on his peregrinatio academica, which led him through Siena, Bologna, Venice and Rome. In his letters, he reports on his visits to the famous legal humanist Andrea Alciato, his attendance at an interrupted Greek-orthodox liturgical service in Venice, and on an experiment with glow-worms in the Bolognese coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornett
The cornett (, ) is a lip-reed wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and Baroque periods, popular from 1500 to 1650. Although smaller and larger sizes were made in both straight and curved forms, surviving cornetts are mostly curved, built in the treble size from in length, usually described as in G. The note sounded with all finger-holes covered is A, which can be lowered a further whole tone to G by slackening the embouchure. The name ''cornett'' comes from the Italian ''cornetto'', meaning "small horn". It was used in performances by professional musicians for both state and liturgical music, especially accompanying choral music. It also featured in popular music in '' alta capella'' or loud wind ensembles. British organologist Anthony Baines wrote that the cornett "was praised in the very terms that were to be bestowed upon the oboe .. it could be sounded as loud as a trumpet and as soft as a recorder, and its tone approached that of the human voice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Praetorius
Michael Praetorius (probably 28 September 1571 – 15 February 1621) was a German composer, organist, and Music theory, music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant Reformation, Protestant hymns. Life Praetorius was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in Creuzburg, in present-day Thuringia. After attending school in Torgau and Zerbst, he studied divinity and philosophy at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). He was fluent in a number of languages. After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He served in the duke's Staatsorchester Braunschweig, State Orchestra, first as organist and later (from 1604) as ''Kapellmeister'' (court music director). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding territories from Muslim rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which culminated in the Siege of Jerusalem (1099), capture of Jerusalem in 1099, these expeditions spanned centuries and became a central aspect of European political, religious, and military history. In 1095, after a Byzantine request for aid,Helen J. Nicholson, ''The Crusades'', (Greenwood Publishing, 2004), 6. Pope Urban II proclaimed the first expedition at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos, AlexiosI Komnenos and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in Western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. Participants came from all over Europe and had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crumhorn
The crumhorn is a double reed , double reed instrument of the woodwind family, most commonly used during the Renaissance music, Renaissance period. In modern times, particularly since the 1960s, there has been a revival of interest in early music, and crumhorns are being played again. It was also spelled krummhorn, krumhorn, krum horn, and cremorne. Terminology The name derives from the German language, German (or or ) meaning ''bent horn''. This relates to the old English language, old English meaning curve, surviving in modern English language, English in 'crumpled' and 'crumpet' (a curved cake). The similar-sounding French term , when used correctly, refers to a woodwind instrument of different design, though the term is often used in error synonymously with that of crumhorn. It is uncertain if the Spanish wind instrument (attested in an inventory of 1559) designates the crumhorn, but it is known that crumhorns were used in Spain in the 16th century, and the identific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalterium (instrument)
:''See Rotte (psaltery) for medieval harp psaltery & Ancient Greek harps for earlier psalterion'' A psaltery () (or sawtry, an archaic form) is a fretboard-less box zither (a simple chordophone) and is considered the archetype of the zither and dulcimer. Plucked keyboard instruments such as the harpsichord were also inspired by it. Its resonance box is usually trapezoidal, rectangular or in the form of a "pig's head" and often richly decorated. Etymology The psaltery of Ancient Greece ('' epigonion'') was a harp-like stringed instrument. The word ''psaltery'' derives from the Ancient Greek ψαλτήριον (''psaltḗrion''), "stringed instrument, psaltery, harp" and that from the verb ψάλλω (''psállō''), "to touch sharply, to pluck, pull, twitch" and in the case of the strings of musical instruments, "to play a stringed instrument with the fingers, and not with the plectrum." The psaltery was originally made from wood, and relied on natural acoustics for sound prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
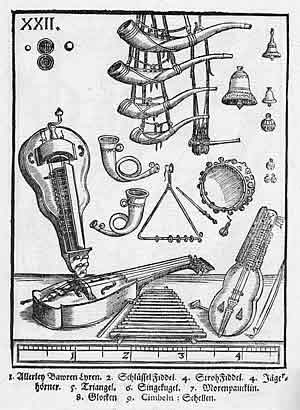
Gittern
The gittern was a relatively small gut-strung, round-backed instrument that first appeared in literature and pictorial representation during the 13th century in Western Europe (Iberian Peninsula, Italy, France, England). It is usually depicted played with a quill plectrum, as can be seen clearly beginning in manuscript illuminations from the thirteenth century. It was also called the in Spain, or in France, the in Italy and in Germany. A popular instrument with court musicians, minstrels, and amateurs, the gittern is considered an ancestor of the modern guitar and other instruments like the mandore, bandurria and gallichon. From the early 16th century, a -shaped (flat-backed) began to appear in Spain, and later in France, existing alongside the gittern. Although the round-backed instrument appears to have lost ground to the new form which gradually developed into the guitar familiar today, the influence of the earlier style continued. Examples of lutes converted into g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |