|
Lithospheric Flexure
In geology, lithospheric flexure (also called regional isostasy) is the process by which the lithosphere (rigid, thin outer layer of the Earth) bends under the action of forces such as the weight of a growing orogeny or changes in ice thickness related to glaciation. The lithosphere rests on the asthenosphere, a viscous layer that in geological time scales behaves like a fluid. Thus, when loaded, the lithosphere progressively reaches an isostatic equilibrium, which represents Archimedes' principle applied to geological settings. This phenomenon was first described in the late 19th century to explain the shorelines uplifted in Scandinavia by the removal of large ice massed during the last glaciation. American geologist G. K. Gilbert used it to explain the uplifted shorelines of Lake Bonneville. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
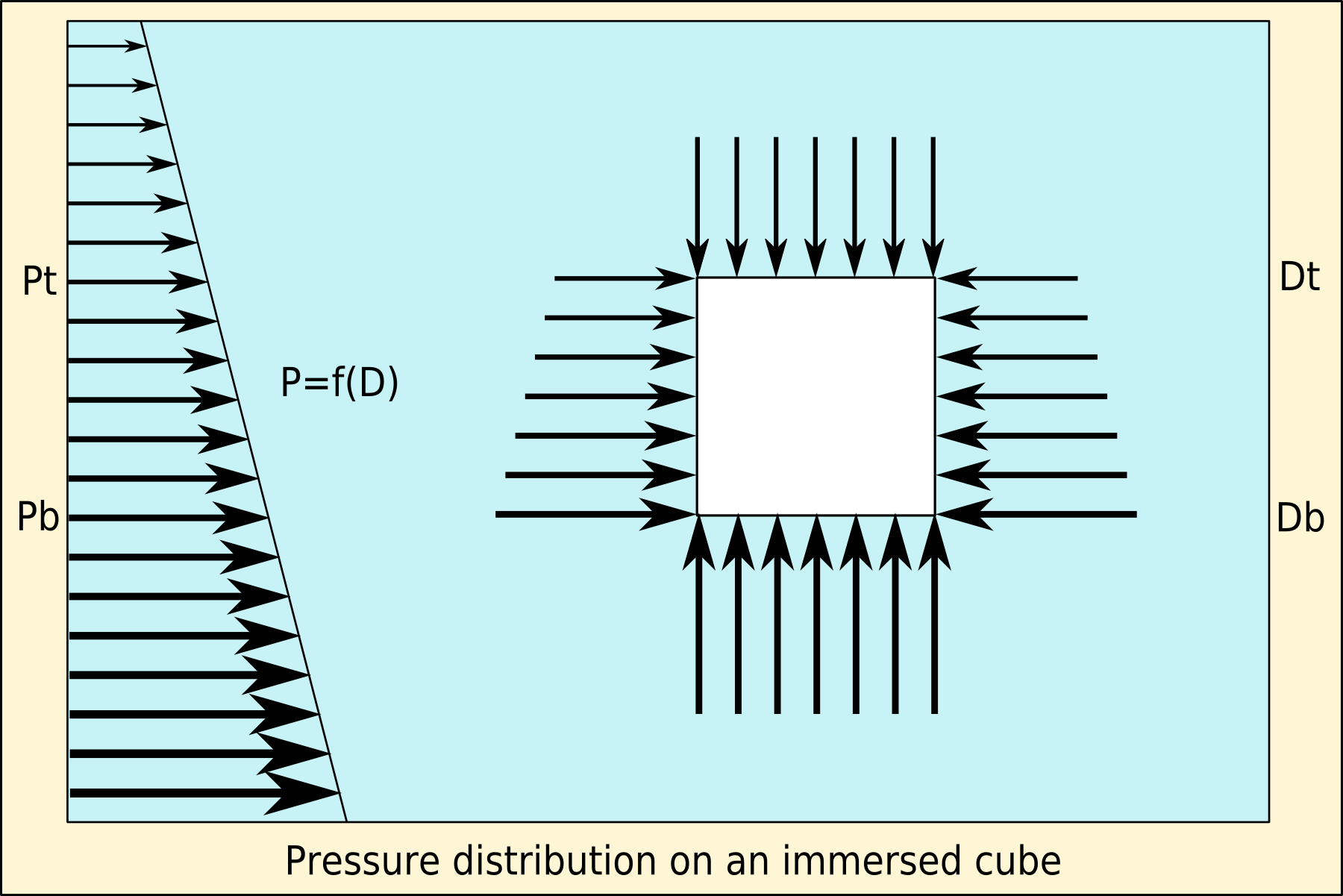
Archimedes' Principle
Archimedes' principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. Archimedes' principle is a law of physics fundamental to fluid mechanics. It was formulated by Archimedes of Syracuse. Explanation In '' On Floating Bodies'', Archimedes suggested that (c. 246 BC): Archimedes' principle allows the buoyancy of any floating object partially or fully immersed in a fluid to be calculated. The downward force on the object is simply its weight. The upward, or buoyant, force on the object is that stated by Archimedes' principle above. Thus, the net force on the object is the difference between the magnitudes of the buoyant force and its weight. If this net force is positive, the object rises; if negative, the object sinks; and if zero, the object is neutrally buoyant—that is, it remains in place without either rising or sinking. In simple words, Archim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler–Bernoulli Beam Theory
Euler–Bernoulli beam theory (also known as engineer's beam theory or classical beam theory) is a simplification of the linear elasticity, linear theory of elasticity which provides a means of calculating the load-carrying and Deflection (engineering), deflection characteristics of Beam (structure), beams. It covers the case corresponding to small deflections of a beam (structure), beam that is subjected to lateral loads only. By ignoring the effects of shear deformation and rotatory inertia, it is thus a special case of Timoshenko–Ehrenfest beam theory. It was first enunciated circa 1750, but was not applied on a large scale until the development of the Eiffel Tower and the Ferris wheel in the late 19th century. Following these successful demonstrations, it quickly became a cornerstone of engineering and an enabler of the Second Industrial Revolution. Additional mathematical models have been developed, such as plate theory, but the simplicity of beam theory makes it an importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Anomaly
The gravity anomaly at a location on the Earth's surface is the difference between the observed value of gravity and the value predicted by a theoretical model. If the Earth were an ideal oblate spheroid of uniform density, then the gravity measured at every point on its surface would be given precisely by a simple algebraic expression. However, the Earth has a rugged surface and non-uniform composition, which distorts its gravitational field. The theoretical value of gravity can be corrected for altitude and the effects of nearby terrain, but it usually still differs slightly from the measured value. This gravity anomaly can reveal the presence of subsurface structures of unusual density. For example, a mass of dense ore below the surface will give a positive anomaly due to the increased gravitational attraction of the ore. Different theoretical models will predict different values of gravity, and so a gravity anomaly is always specified with reference to a particular model. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, elasticity is the ability of a body to resist a distorting influence and to return to its original size and shape when that influence or force is removed. Solid objects will deform when adequate loads are applied to them; if the material is elastic, the object will return to its initial shape and size after removal. This is in contrast to ''plasticity'', in which the object fails to do so and instead remains in its deformed state. The physical reasons for elastic behavior can be quite different for different materials. In metals, the Crystal structure, atomic lattice changes size and shape when forces are applied (energy is added to the system). When forces are removed, the lattice goes back to the original lower energy state. For rubber elasticity, rubbers and other polymers, elasticity is caused by the stretching of polymer chains when forces are applied. Hooke's law states that the force required to deform elastic objects should be Prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Andries Vening Meinesz
Felix Andries Vening Meinesz (30 July 1887 – 10 August 1966) was a Dutch geophysicist and geodesist. He is known for his invention of a precise method for measuring gravity (gravimetry). Thanks to his invention, it became possible to measure gravity at sea, which led him to the discovery of gravity anomalies above the ocean floor. He later attributed these anomalies to continental drift. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society. Biography Vening Meinesz's father, Sjoerd Anne Vening Meinesz, was mayor, first of Rotterdam, then of Amsterdam. Felix was born in The Hague and grew up in a protected environment. In 1910 he graduated in civil engineering in Delft. The same year he started working for the Dutch gravity survey. In 1915 he wrote his dissertation on the defects of the gravimeters used at that time. Vening Meinesz then designed a new gravimeter, which the KNMI (Royal Dutch Meteorological Institute) built. The apparatus has two pendula of the same size hanging in a fram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Bonneville
Lake Bonneville was the largest Late Pleistocene paleolake in the Great Basin of western North America. It was a pluvial lake that formed in response to an increase in precipitation and a decrease in evaporation as a result of cooler temperatures. The lake covered much of what is now western Utah and at its highest level extended into present-day Idaho and Nevada. Many other hydrographically closed basins in the Great Basin contained expanded lakes during the Late Pleistocene, including Lake Lahontan in northwestern Nevada. Geologic description Shorelines of Lake Bonneville are visible above Salt Lake City along the western front of the Wasatch Mountains and on other mountains throughout the Bonneville basin.Gilbert, G.K., 1890. Lake Bonneville. U.S. Geological Survey Monograph 1. 438 pp. These shorelines appear as shelves or benches that protrude from the mountainside above the valley floor, are visible on the ground from long distances and on satellite images, and have both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grove Karl Gilbert
Grove Karl Gilbert (May 6, 1843 – May 1, 1918), known by the abbreviated name G. K. Gilbert in academic literature, was an American geologist. Biography Gilbert was born in Rochester, New York, and graduated from the University of Rochester. During the American Civil War, he was twice listed for the draft, but his name was drawn neither time. In 1871, he joined George M. Wheeler's geographical survey as its first geologist. Rockies geologist Gilbert joined the Powell Survey of the Rocky Mountain Region in 1874, becoming Powell's primary assistant, and stayed with the survey until 1879. During this time he published an important monograph, ''The Geology of the Henry Mountains'' (1877). After the U.S. Geological Survey was created in 1879, he was appointed to the position of Senior Geologist and worked for the USGS until his death (including a term as acting director). Gilbert published a study of the former ancient Lake Bonneville in 1890 (the lake existed during the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes a part of northern Finland). In English usage, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Nordic countries. Iceland and the Faroe Islands are sometimes included in Scandinavia for their Ethnolinguistics, ethnolinguistic relations with Sweden, Norway and Denmark. While Finland differs from other Nordic countries in this respect, some authors call it Scandinavian due to its economic and cultural similarities. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isostasy
Isostasy (Greek ''ísos'' 'equal', ''stásis'' 'standstill') or isostatic equilibrium is the state of gravitational equilibrium between Earth's crust (or lithosphere) and mantle such that the crust "floats" at an elevation that depends on its thickness and density. This concept is invoked to explain how different topographic heights can exist at Earth's surface. Although originally defined in terms of continental crust and mantle, it has subsequently been interpreted in terms of lithosphere and asthenosphere, particularly with respect to oceanic island volcanoes, such as the Hawaiian Islands. Although Earth is a dynamic system that responds to loads in many different ways, isostasy describes the important limiting case in which crust and mantle are in static equilibrium. Certain areas (such as the Himalayas and other convergent margins) are not in isostatic equilibrium and are not well described by isostatic models. The general term ''isostasy'' was coined in 1882 by the Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |