|
List Of Radioactive Nuclides By Half-life
This is a list of radioactive nuclides (sometimes also called isotopes), ordered by half-life from shortest to longest, in seconds, minutes, hours, days and years. Current methods make it difficult to measure half-lives between approximately 10−19 and 10−10 seconds. 10−24 seconds (yoctoseconds) Twenty-three yoctoseconds is the time needed to traverse a 7- femtometre distance at the speed of light—around the diameter of a large atomic nucleus The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the Department_of_Physics_and_Astronomy,_University_of_Manchester , University of Manchester .... 10−21 seconds (zeptoseconds) 10−18 seconds (attoseconds) 10−12 seconds (picoseconds) 10−9 seconds (nanoseconds) 10−6 seconds (microseconds) 10−3 seconds (milliseconds) 100 seconds 103 seconds (kiloseconds) 106 seconds (megaseconds) 109 seconds (gigasecon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxygen-28
There are three known stable isotopes of oxygen (8O): , , and . Radioactive isotopes ranging from to have also been characterized, all short-lived. The longest-lived radioisotope is with a half-life of , while the shortest-lived isotope is the unbound with a half-life of , though half-lives have not been measured for the unbound heavy isotopes and . List of isotopes , -id=Oxygen-11 , , style="text-align:right" , 8 , style="text-align:right" , 3 , , [] , proton emission, 2p , , (3/2−) , , , -id=Oxygen-12 , , style="text-align:right" , 8 , style="text-align:right" , 4 , , , 2p , , 0+ , , , - , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 8 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 5 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , β+ () , , rowspan=3, (3/2−) , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β+p () , , - , β+p,α ( , - , Can be used in NMR studies of metabolic pathways. , style="text-align:right" , 8 , style="text-align:right" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fluorine-15
Fluorine (9F) has 19 known isotopes ranging from to and two isomers ( and ). Only fluorine-19 is stable and naturally occurring in more than trace quantities; therefore, fluorine is a monoisotopic and mononuclidic element. The longest-lived radioisotope is ; it has a half-life of . All other fluorine isotopes have half-lives of less than a minute, and most of those less than a second. The least stable known isotope is , whose half-life is , corresponding to a resonance width of . List of isotopes , -id=Fluorine-13 , , style="text-align:right" , 9 , style="text-align:right" , 4 , # , , p ?Decay mode shown is energetically allowed, but has not been experimentally observed to occur in this nuclide. , ? , 1/2+# , , -id=Fluorine-14 , , style="text-align:right" , 9 , style="text-align:right" , 5 , , [] , p ?Decay mode shown is energetically allowed, but has not been experimentally observed to occur in this nuclide. , ? , 2− , , -id=Fluorine-15 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beryllium-13
Beryllium (4Be) has 11 known isotopes and 3 known isomers, but only one of these isotopes () is stable and a primordial nuclide. As such, beryllium is considered a monoisotopic element. It is also a mononuclidic element, because its other isotopes have such short half-lives that none are primordial and their abundance is very low (standard atomic weight is ). Beryllium is unique as being the only monoisotopic element with both an even number of protons and an odd number of neutrons. There are 25 other monoisotopic elements but all have odd atomic numbers, and even numbers of neutrons. Of the 10 radioisotopes of beryllium, the most stable are with a half-life of million years and with a half-life of . All other radioisotopes have half-lives under , most under . The least stable isotope is , with a half-life of . The 1:1 neutron–proton ratio seen in stable isotopes of many light elements (up to oxygen, and in elements with even atomic number up to calcium) is prevented in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the Department_of_Physics_and_Astronomy,_University_of_Manchester , University of Manchester based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden experiments, Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Femtometre
The femtometre (American spelling femtometer), symbol fm, (derived from the Danish and Norwegian word 'fifteen', ) is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10−15 metres, which means a quadrillionth of one metre. This distance is sometimes called a fermi and was so named in honour of Italian naturalized to American physicist Enrico Fermi, as it is a typical length-scale of nuclear physics. Definition and equivalents 1000000 zeptometres = 1 femtometre = 1 fermi = 0.000001 nanometre = femtometres = 1 millimetre. For example, the charge radius of a proton is approximately 0.841 femtometres while the radius of a gold nucleus is approximately 8.45 femtometres. 1 barn = 100 fm2 History The femtometre was adopted by the 11th ''Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures'', and added to the SI in 1964, using the Danish word for "15" and the similarity in spelling with ''fermi''. The fermi is named after the It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fluorine-30
Fluorine (9F) has 19 known isotopes ranging from to and two isomers ( and ). Only fluorine-19 is stable and naturally occurring in more than trace quantities; therefore, fluorine is a monoisotopic and mononuclidic element. The longest-lived radioisotope is ; it has a half-life of . All other fluorine isotopes have half-lives of less than a minute, and most of those less than a second. The least stable known isotope is , whose half-life is , corresponding to a resonance width of . List of isotopes , -id=Fluorine-13 , , style="text-align:right" , 9 , style="text-align:right" , 4 , # , , p ?Decay mode shown is energetically allowed, but has not been experimentally observed to occur in this nuclide. , ? , 1/2+# , , -id=Fluorine-14 , , style="text-align:right" , 9 , style="text-align:right" , 5 , , [] , p ?Decay mode shown is energetically allowed, but has not been experimentally observed to occur in this nuclide. , ? , 2− , , -id=Fluorine-15 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isotopes Of Beryllium
Beryllium (4Be) has 11 known Isotope, isotopes and 3 known nuclear isomer, isomers, but only one of these isotopes () is stable and a primordial nuclide. As such, beryllium is considered a monoisotopic element. It is also a mononuclidic element, because its other isotopes have such short half-lives that none are primordial and their abundance is very low (standard atomic weight is ). Beryllium is unique as being the only monoisotopic element with both an even number of protons and an odd number of neutrons. There are 25 other monoisotopic elements but all have odd atomic numbers, and even numbers of neutrons. Of the 10 radionuclide, radioisotopes of beryllium, the most stable are with a half-life of million years and with a half-life of . All other radioisotopes have half-lives under , most under . The least stable isotope is , with a half-life of . The 1:1 neutron–proton ratio seen in stable isotopes of many light elements (up to oxygen, and in elements with even atomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
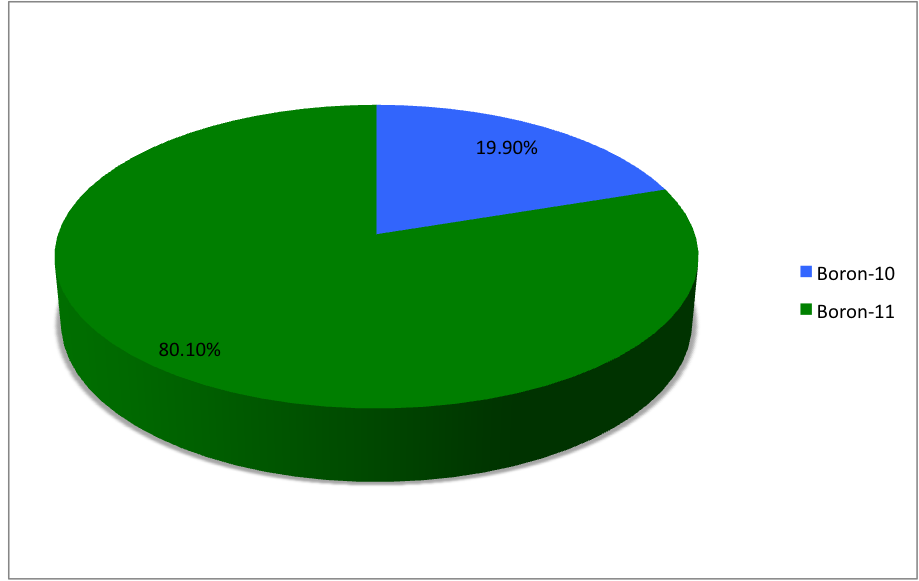
Boron-20
Boron (5B) naturally occurs as isotopes and , the latter of which makes up about 80% of natural boron. There are 13 radioisotopes that have been discovered, with mass numbers from 7 to 21, all with short half-lives, the longest being that of , with a half-life of only and with a half-life of . All other isotopes have half-lives shorter than . Those isotopes with mass below 10 decay into helium (via short-lived isotopes of beryllium for and ) while those with mass above 11 mostly become carbon. List of isotopes , -id=Boron-7 , , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 2 , , [] , p , Subsequently decays by double proton emission to for a net reaction of → + 3 , (3/2−) , , , - , Has 1 halo nucleus, halo protonIntermediate product of Proton–proton chain#The p–p III branch, a branch of proton–proton chain in stellar nucleosynthesis as part of the process converting hydrogen to helium , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beryllium-15
Beryllium (4Be) has 11 known isotopes and 3 known isomers, but only one of these isotopes () is stable and a primordial nuclide. As such, beryllium is considered a monoisotopic element. It is also a mononuclidic element, because its other isotopes have such short half-lives that none are primordial and their abundance is very low (standard atomic weight is ). Beryllium is unique as being the only monoisotopic element with both an even number of protons and an odd number of neutrons. There are 25 other monoisotopic elements but all have odd atomic numbers, and even numbers of neutrons. Of the 10 radioisotopes of beryllium, the most stable are with a half-life of million years and with a half-life of . All other radioisotopes have half-lives under , most under . The least stable isotope is , with a half-life of . The 1:1 neutron–proton ratio seen in stable isotopes of many light elements (up to oxygen, and in elements with even atomic number up to calcium) is prevented in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isotopes Of Neon
Neon (10Ne) possesses three stable isotopes: , , and . In addition, 17 radioactive isotopes have been discovered, ranging from to , all short-lived. The longest-lived is with a half-life of . All others are under a minute, most under a second. The least stable is with a half-life of (). See isotopes of carbon for notes about the measurement. Light radioactive neon isotopes usually decay to fluorine or oxygen, while heavier ones decay to sodium. List of isotopes , -id=Neon-15 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 5 , , [] , proton emission, 2p , , (3/2−) , , , -id=Neon-16 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 6 , , > [ , -id=Neon-21 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 11 , , colspan=3 align=center, Stable , 3/2+ , , ref name="Isotopic Composition of Elements" /> , -id=Neon-22 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 12 , , c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |