|
List Of Near-parabolic Comets
The following is a list of comets with a very high eccentricity (generally 0.99 or higher) and a period of over 1,000 years that do not quite have a high enough velocity to escape the Solar System. Often, these comets, due to their extreme semimajor axes and eccentricity, will have small orbital interactions with planets and minor planets, most often ending up with the comets fluctuating significantly in their orbital path. These comets probably come from the Oort cloud, a cloud of comets orbiting the Sun from ~10,000 to roughly 50,000 AU. The actual orbit of these comets significantly differs from the provided coordinates. A Solar System barycentric orbit computed at an epoch when the object is located beyond all the planets is a more accurate measurement of its long-term orbit. List of near-parabolic comets See also * List of comets by type * List of Halley-type comets * List of hyperbolic comets * List of long-period comets * List of numbered comets * List of period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding the nucleus, and sometimes a Comet tail, tail of gas and dust gas blown out from the coma. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the outstreaming solar wind plasma acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently close and bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and can Subtended angle, subtend an arc of up to 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
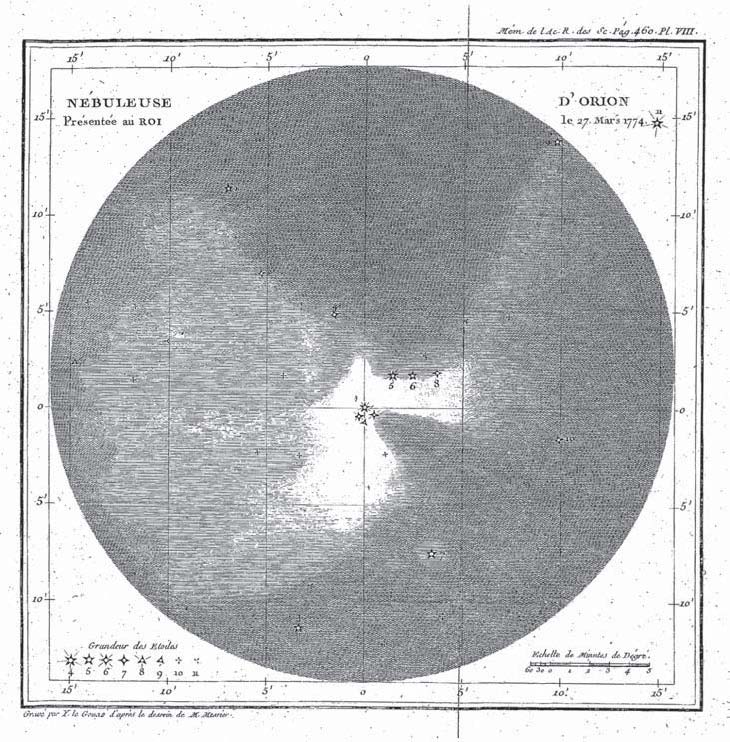
Victor Mauvais
Félix-Victor Mauvais (or Victor Mauvais; March 7, 1809 – March 22, 1854) was a French politician and astronomer. He was born in the small village of Maîche in the department of Doubs and died in Paris. In 1836 he went to the Observatoire de Paris as a student astronomer. He worked at the Bureau des Longitudes from 1843 to 1854, working on meteorology. He was elected to the Académie des Sciences in 1843. He won the Lalande Prize in 1843 for the discovery of comet C/1843 J1. He also discovered comets C/1844 N1 and C/1847 N1. In politics, he served as a leftist member of the National Assembly In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ... from 1848 to 1849. On March 2, 1854, the Observatory and the Bureau des Longitudes were separated, which obliged Mauvais to leave this in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Gottfried Galle
Johann Gottfried Galle (9 June 1812 – 10 July 1910) was a German astronomer from Radis, Germany, at the Berlin Observatory who, on 23 September 1846, with the assistance of student Heinrich Louis d'Arrest, was the first person to view the planet Neptune and know what he was looking at. Urbain Le Verrier had predicted the existence and position of Neptune, and sent the coordinates to Galle, asking him to verify. Galle found Neptune in the same night he received Le Verrier's letter, within 1° of the predicted position. The discovery of Neptune is widely regarded as a dramatic validation of celestial mechanics, and is one of the most remarkable moments of 19th-century science. Early life Galle was born in the Papsthaus (a house in the Pabst wood) 2 km west of Radis in the vicinity of the town of Gräfenhainichen, as the first son of Marie Henriette ''née Pannier'' (1790–1839) and Johann Gottfried Galle (1790–1853), an operator of a tar oven. He attended the Gymn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Félix Adolphe Gambart
Jean-Félix Adolphe Gambart (12 May 1800 – 23 July 1836) was a French astronomer. He was born in Sète in Hérault department, the son of a sea captain. His intelligence was noticed at a young age by Alexis Bouvard, who persuaded him to join the astronomy profession. In 1819 he joined the Marseilles Observatory and became the director in 1822. During his career he recorded a number of observations of the satellites of Jupiter, and discovered a total of 13 comets. In 1832 he observed the transit of Mercury across the Sun, noting that the planet appeared deformed as it approached the edge. He suffered from tuberculosis, and in 1836 died from cholera in Paris, aged 36. The crater Gambart on the moon is named after him.Antonín Rükl: ''Atlas Měsíce'' (Atlas of the Moon), Aventinum (Prague 1991), chapter Stadius, p. 90, Crater Gambart o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/1823 Y1
The Great Comet of 1823, also designated C/1823 Y1 or Comet De Bréauté-Pons, was a bright comet visible from December 1823 to April 1824. Discovery and observations It was independently discovered by Nell de Bréauté at Dieppe on December 29, by Jean-Louis Pons on the morning of December 30, and by Wilhelm von Biela at Prague on the same morning. It was already visible to the naked eye when discovered: Pons initially thought he was seeing smoke from a chimney rising over a hill, but continued observing when he noticed it did not change appearance. He was later to note that the comet was, puzzlingly, more easily visible to the naked eye than through a telescope. Biela also noted that it was noticeably brighter than the Great Comet of 1819 had been. The comet was particularly known at the time for exhibiting two tails, one pointing away from the Sun and the other (termed an "anomalous tail" by Karl Harding and Heinrich Olbers) pointing towards it. Caroline Herschel record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Louis Pons
Jean-Louis Pons (24 December 176114 October 1831) was a French astronomer. Despite humble beginnings and being self-taught, he went on to become the greatest visual comet discoverer of all time: between 1801 and 1827 Pons discovered thirty-seven comets, more than any other person in history. Pons worked at three observatories in his career, Marseille Observatory, where he was also trained, a short-lived observatory at Royal Park La Marlia in Tuscany, and finally at an observatory in Florence. Pons's work supported some famous comet recoveries of the 19th century, including Encke's Comet and Crommelin's Comet. However, most of the comets he discovered had near-parabolic orbits and would not return for a time as long as several millennia. Early life Pons was born in Peyre, Hautes-Alpes, to a poor family; he received little formal education. In 1789, he began working for the Marseille Observatory as a caretaker, and gradually gained some experience in assisting the astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/1811 F1
The Great Comet of 1811, formally designated C/1811 F1, is a comet that was visible to the naked eye for around 260 days, the longest recorded period of visibility until the appearance of Comet Hale–Bopp in 1997. In October 1811, at its brightest, and when it was 1.2 AU from Earth, it displayed an apparent magnitude of 0, with an easily visible coma. Discovery The comet was discovered on March 25, 1811, by Honoré Flaugergues at 2.7 AU from the Sun in the now-defunct constellation of Argo Navis. After being obscured for several days by moonlight, it was also found by Jean-Louis Pons on April 11, while Franz Xaver, Baron Von Zach was able to confirm Flaugergues' discovery the same night.. The first provisional orbit was computed in June by Johann Karl Burckhardt. Based on these calculations, Heinrich Wilhelm Matthäus Olbers predicted that the comet would go on to become extremely bright later that year. Observations From May to August, the comet's position made i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/1807 R1
C/1807 R1, also known as the Great Comet of 1807, is a long-period comet. It was visible to naked-eye observers in the northern hemisphere from early September 1807 to late December, and is ranked among the great comets due to its exceptional brightness. Discovery Its discovery is often credited to the Augustinian friar P. Reggente Parisi at Castrogiovanni in Sicily. He recorded observing the comet very close to the horizon in the early twilight of 9 September 1807, not far from the equally bright star Spica: at that time the planets Venus, Mars and Saturn were also near the comet. Moonlight interfered with observations for the following week and thanks to his favorable southerly location, Parisi might have been able to make his discovery several days before a number of other observers in Europe independently discovered the comet. G. W. Kronk: ''Cometography: A Catalog of Comets, Volume 2. 1800–1899''. Cambridge University Press, 2003, , pp. 10–14. Orbital data points sugg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Méchain
Pierre François André Méchain (; 16 August 1744 – 20 September 1804) was a French astronomer and surveyor who, with Charles Messier, was a major contributor to the early study of deep-sky objects and comets. Life Pierre Méchain was born in Laon in northern France, the son of the ceiling designer and plasterer Pierre François Méchain and Marie–Marguerite Roze. He displayed mental gifts in mathematics and physics but had to give up his studies for lack of money. However, his talents in astronomy were noticed by Jérôme Lalande, for whom he became a friend and proof-reader of the second edition of his book "L'Astronomie". Lalande then secured a position for him as assistant hydrographer with the Naval Depot of Maps and Charts at Versailles, where he worked through the 1770s engaged in hydrographic work and coastline surveying. It was during this time—approximately 1774—that he met Charles Messier, and apparently, they became friends. In the same year, he also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects'', referred to with the letter M and their number between 1 and 110. Messier's purpose for list of Messier objects, the catalogue was to help astronomical observers distinguish between permanent and transient astronomical event, transient visually diffuse astronomical object, objects in the sky. Biography Messier was born in Badonviller in the Lorraine region of Kingdom of France, France, in 1730, the tenth of twelve children of Françoise B. Grandblaise and Nicolas Messier, a Court usher. Six of his brothers and sisters died while young, and his father died in 1741. Charles' interest in astronomy was stimulated by the appearance of the Great Comet of 1744, great six-tailed comet in 1744 and by an annular solar eclipse visible from his hometown on 25 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/1769 P1
C/1769 P1 (Messier) is a long-period comet that was visible to the naked eye at its last apparition in 1769. The comet is classified as a great comet due to its superlative brightness. Discovery and observations At the Naval Observatory in Paris, late in the evening of 8 August 1769 Charles Messier in his routine telescope search for comets saw a small nebulosity just above the horizon in the constellation Aries. On the next evening he saw the nebulosity by unassisted eye and confirmed it to be a comet due to its motion in the sky. On 15 August Messier estimated the length of the comet's tail to be 6°. Giovanni Domenico Maraldi and César François Cassini de Thury saw the comet for the first time on 22 August by telescope and later by unassisted eye. Chinese observers reported a "broom star" appearing on 24 August in the southeastern sky. Jean-François-Marie de Surville observed the comet in the pre-dawn of 26 August from a ship off the Philippines and reported the comet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |