|
List Of Monarchs Of Wessex
This is a list of monarchs of the Wessex, Kingdom of the West Saxons (Wessex) until 886 AD. While the details of the later monarchs are confirmed by a number of sources, the earlier ones are in many cases obscure. The names are given in modern English form followed by the names and titles (as far as is known) in contemporary Old English (Anglo-Saxon) and Latin, the prevalent languages of record at the time in England. This was a period in which spellings varied widely, even within a document. A number of variations of the details below exist. Among these are the preference between the Rune, runic character ''Thorn (letter), thorn'' (Þ, lower-case þ, from the Thorn (rune), rune of the same name) and the letter ''eth'' (Ð or ð), both of which are equivalent to modern ⟨th⟩ and were interchangeable. They were used indiscriminately for Voice (phonetics), voiced and unvoiced ⟨th⟩ sounds, unlike in modern Icelandic orthography, Icelandic. ''Thorn'' tended to be more used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy, kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886. The Anglo-Saxons believed that Wessex was founded by Cerdic and Cynric of the Gewisse, though this is considered by some to be a legend. The two main sources for the history of Wessex are the West Saxon Genealogical Regnal List and the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' (the latter of which drew on and adapted an early version of the List), which sometimes conflict. Wessex became a Christianity, Christian kingdom after Cenwalh () was baptised and was expanded under his rule. Cædwalla later conquered Kingdom of Sussex, Sussex, Kingdom of Kent, Kent and the Isle of Wight. His successor, Ine of Wessex, Ine (), issued one of the oldest surviving English law codes and established a second West Saxon bishopric. The throne subsequently passed to a series of kings wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceawlin Of Wessex
Ceawlin ( ; also spelled Ceaulin, Caelin, Celin, died ''ca.'' 593) was a King of Wessex. He may have been the son of Cynric of Wessex and the grandson of Cerdic of Wessex, whom the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' represents as the leader of the first group of Saxons to come to the land which later became Wessex. Ceawlin was active during the last years of the Anglo-Saxon expansion, with little of southern England remaining in the control of the native Britons by the time of his death. The chronology of Ceawlin's life is highly uncertain. The historical accuracy and dating of many of the events in the later ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' have been called into question, and his reign is variously listed as lasting seven, seventeen, or thirty-two years. The ''Chronicle'' records several battles of Ceawlin's between the years 556 and 592, including the first record of a battle between different groups of Anglo-Saxons, and indicates that under Ceawlin Wessex acquired significant territory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelheard Of Wessex
Æthelheard (meaning roughly "Noble Stern"), also spelled Ethelheard, Edelard or Æþelheard, was King of Wessex from 726 to 740. There is an unreliable record of Æthelheard having been the brother-in-law of his predecessor, Ine, but his ancestry is unknown, perhaps making him the first King of Wessex not to be descended from Cynric by blood. Some sources identify him as the brother of Queen Æthelburg of Wessex, the wife of his predecessor, King Ine. His own successor Cuthred is identified in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' as 'his relative'. When Ine abdicated and went to Rome in 726, he left behind no obvious heir, and according to Bede simply left his kingdom "to younger men". In the wake of his departure, the West Saxon throne was disputed between Æthelheard and a rival claimant, Oswald. Oswald may have had the better claim, as the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' calls him a descendant of the early king Ceawlin, but it was Æthelheard who prevailed. It is possible that his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
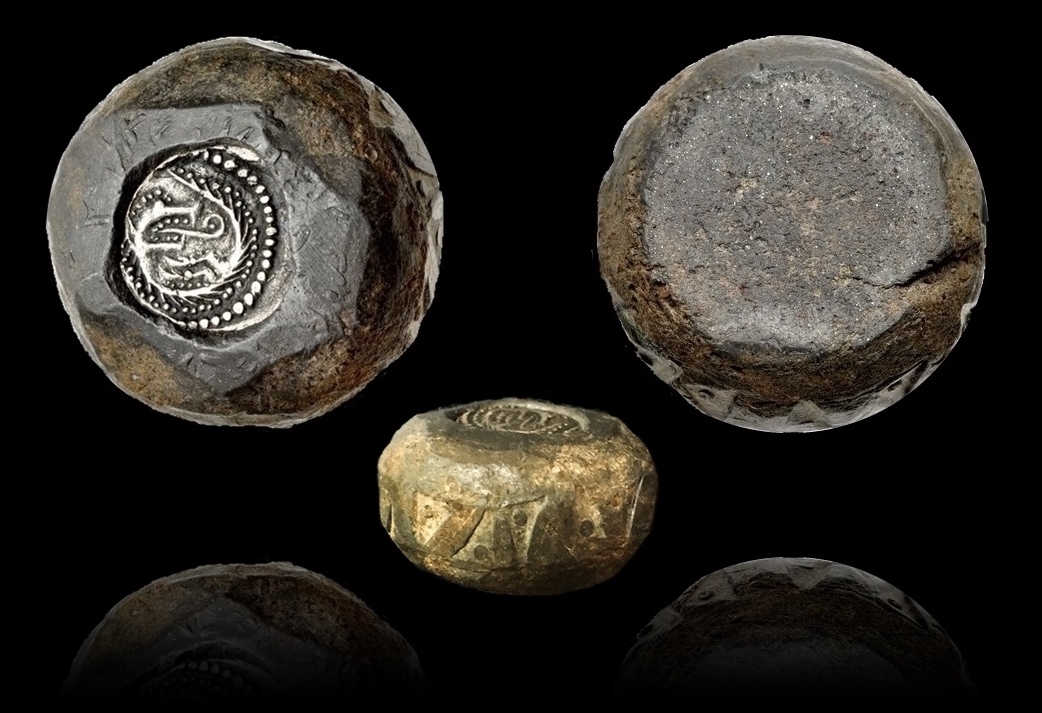
Ine Of Wessex
Ine or Ini (died in or after 726) was King of Wessex from 689 to 726. At Ine's accession, his kingdom dominated much of what is now southern England. However, he was unable to retain the territorial gains of his predecessor, Cædwalla of Wessex, who had expanded West Saxon territory substantially. By the end of Ine's reign, the kingdoms of Kent, Sussex, and Essex were no longer under West Saxon sway; however, Ine maintained control of what is now Hampshire, and consolidated and extended Wessex's territory in the western peninsula. Ine is noted for his code of laws (''Ines asetnessa'' or "laws of Ine"), which he issued in about 694. These laws were the first issued by an Anglo-Saxon king outside Kent. They shed much light on the history of Anglo-Saxon society, and reveal Ine's Christian convictions. Trade increased significantly during Ine's reign, with the town of Hamwic (now Southampton) becoming prominent. It was probably during Ine's reign that the West Saxons began to mint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cædwalla
Cædwalla (; 659 – 20 April 689) was the King of Wessex from approximately 685 until he abdicated in 688. His name is derived from the Welsh Cadwallon. He was exiled from Wessex as a youth and during this period gathered forces and attacked the South Saxons, killing their king, Æthelwealh, in what is now Sussex. Cædwalla was unable to hold the South Saxon territory, however, and was driven out by Æthelwealh's ealdormen. In either 685 or 686, he became King of Wessex. He may have been involved in suppressing rival dynasties at this time, as an early source records that Wessex was ruled by underkings until Cædwalla. After his accession, Cædwalla returned to Sussex and won the territory again. He also conquered the Isle of Wight, gained control of Surrey and the kingdom of Kent, and in 686 he installed his brother Mul as king of Kent. Mul was burned in a Kentish revolt a year later, and Cædwalla returned, possibly ruling Kent directly for a period. Cædwalla was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centwine Of Wessex
Centwine (died after 685) was King of Wessex from c. 676 to 685 or 686, although he was perhaps not the only king of the West Saxons at the time. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' reports that Centwine became king c. 676, succeeding Æscwine. Bede states that after the death of King Cenwalh: "his under-rulers took upon them the kingdom of the people, and dividing it among themselves, held it ten years". Bede's dismissal of Æscwine and Centwine as merely sub-kings may represent the views of the supporters of the King Ine, whose family ruled Wessex in Bede's time. However, if the West Saxon kingdom did fragment following Cenwalh's death, it appears that it was reunited during Centwine's reign. An entry under 682 in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' records that "Centwine drove the Britons to the sea". This is the only event recorded in his reign. The ''Carmina Ecclesiastica'' of Aldhelm, Bishop of Sherborne (died 709), written a generation after Centwine's reign, records that he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æscwine Of Wessex
Æscwine was a King of Wessex from about 674 to 676, but was probably not the only king in Wessex at the time. Bede writes that after the death of King Cenwalh in 672: "his under-rulers took upon them the kingdom of the people, and dividing it among themselves, held it ten years". According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' Cenwalh was succeeded as ruler for about one year by his wife Seaxburh. Æscwine reigned from about 674 to 676. Another source claims that Æscwine's father, Cenfus (), ruled for two years after Seaxburh.Cenfus is not listed in modern king lists, e.g. Yorke, Barbara, ''Kings and Kingdoms of Early Anglo-Saxon England'', pp. 133–134. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' supplies a genealogy, making him a fifth-generation descendant of Cynric. Bede's dismissal of Æscwine as a mere sub-king may represent the views of the supporters of the King Ine of Wessex, whose family ruled Wessex in Bede's time, as Ine's family were ''bona fide'' descendants of Cynric throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaxburh Of Wessex
Seaxburh (; died c. 674) was a queen of Wessex. She is also called Queen of the Gewisse, an early name for the tribe which ruled Wessex. She is said to have ruled Wessex for between one and two years after the death of her husband, Cenwalh, in 672. Her accession to the throne is documented in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle for that year which states that "This year king Kenwalk died, and Sexburga his queen reigned one year after him". It was extremely rare for a woman to reign '' suo jure'' in Anglo-Saxon England, and she was the only woman to appear in a regnal list. She may have reigned for over a year, as the next reign is entered in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' in 674. However, Bede said that after the death of Cenwalh, "sub-kings took upon themselves the government of the kingdom", so the chroniclers may have tidied up a complicated situation. Writing decades after Cenwalh's life, when Bede lists Cenwalh's accession, he mentions Seaxburh as the unnamed second wife whom the k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penda Of Mercia
Penda (died 15 November 655)Manuscript A of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' gives the year as 655. Bede also gives the year as 655 and specifies a date, 15 November. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and History'', 1934) put forward the theory that Bede began his year in September, and consequently November 655 would actually fall in 654; Frank Stenton also dated events accordingly in his ''Anglo-Saxon England'' (1943). 1 Others have accepted Bede's given dates as meaning what they appear to mean, considering Bede's year to have begun on 25 December or 1 January (see S. Wood, 1983: "Bede's Northumbrian dates again"). The historian D. P. Kirby suggested the year 656 as a possibility, alongside 655, in case the dates given by Bede are off by one year (see Kirby's "Bede and Northumbrian Chronology", 1963). The '' Annales Cambriae'' gives the year as 657Annales Cambriae at Fordham University/ref> was a 7th-century king of Mercia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom in what is today the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercian Dynasty
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England. The royal court moved around the kingdom without a fixed capital city. Early in its existence Repton seems to have been the location of an important royal estate. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', it was from Repton in 873–874 that the Great Heathen Army deposed the King of Mercia. Slightly earlier, Offa of Mercia, King Offa seems to have favoured Tamworth, Staffordshire, Tamworth. It was there where he was crowned and spent many a Christmas. For the three centuries between 600 and 900, known as Mercian Supremacy or the "Golden Age of Mercia", having annexed or gained submissions from five of the other six kingdoms of the Heptarchy (Kingdom of East Anglia, East Anglia, Kingdom of Essex, Essex, Kingdom of Kent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenwalh Of Wessex
Cenwalh, also Cenwealh or Coenwalh, was King of Wessex from c. 642 to c. 645 and from c. 648 until his death, according to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', in c. 672. Penda and Anna Bede states that Cenwalh was the son of the King Cynegils baptised by Bishop Birinus. He was also the great-great-grandson of Cerdic.Bede, ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', Book III, chapter 7. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' offers several ancestries for Cynegils, and the relationship of Cynegils and Cenwalh to later kings isn't certain. It has been noted that the name Cenwalh is of British rather than Anglo-Saxon etymology. Although Cynegils is said to have been a convert to Christianity, Bede writes that Cenwalh:refused to embrace the mysteries of the faith, and of the heavenly kingdom; and not long after also he lost the dominion of his earthly kingdom; for he put away the sister of Penda, king of the Mercians, whom he had married, and took another wife; whereupon a war ensuing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cwichelm Of Wessex
Cwichelm ( ; died 636) was an Anglo-Saxon king of the Gewisse, a people in the upper Thames area who later created the kingdom of Wessex. He is usually counted among the Kings of Wessex. Life Cwichelm is first mentioned in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' for 614: "This year Cynegils and Cwichelm fought at ''Beandun'', and slew two thousand and forty-six of the Welsh." Bede records that the attempted assassination of King Edwin of Deira, circa 626, was ordered by the West Saxon King Cwichelm, and does not mention Cynegils. In 628, Cynegils and Cwichelm fought King Penda at Cirencester. The Chronicle could be expected to report a victory, but does not, so it is likely that Penda was the victor. The last mention of Cwichelm is for 636, when the Chronicle records: "This year King Cwichelm was baptized at Dorchester, and died the same year." Cynegils was also baptised at this time, by Bishop Birinus, with Oswald of Bernicia as his godfather. The final entry in the Anglo-Saxon Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |