|
List Of Medical Roots, Suffixes And Prefixes
This is a used in medical terminology, their meanings, and their etymologies. Most of them are combining forms in Neo-Latin and hence international scientific vocabulary. There are a few general rules about how they combine. First, prefixes and suffixes, most of which are derived from ancient Greek or classical Latin, have a droppable vowel, usually -o-. As a general rule, this vowel almost always acts as a joint-stem to connect two consonantal roots (e.g. + + '' -logy'' = '' arthrology''), but generally, the ''-o-'' is dropped when connecting to a vowel-stem (e.g. + '' -itis'' = '' arthritis'', instead of '). Second, medical roots generally go together according to language, i.e., Greek prefixes occur with Greek suffixes and Latin prefixes with Latin suffixes. Although international scientific vocabulary is not stringent about segregating combining forms of different languages, it is advisable when coining new words not to mix different lingual roots. Prefixes and suf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Terminology
Medical terminology is a language used to precisely describe the human body including all its components, processes, conditions affecting it, and procedures performed upon it. Medical terminology is used in the field of medicine. Medical terminology has quite regular morphology, the same prefixes and suffixes are used to add meanings to different roots. The root of a term often refers to an organ, tissue, or condition. For example, in the disorder known as hypertension, the prefix "hyper-" means "high" or "over", and the root word "tension" refers to pressure, so the word "hypertension" refers to abnormally high blood pressure. The roots, prefixes and suffixes are often derived from Greek or Latin, and often quite dissimilar from their English-language variants. This regular morphology means that once a reasonable number of morphemes are learnt it becomes easy to understand very precise terms assembled from these morphemes. Much medical language is anatomical terminology, conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, recent research has suggested that classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants may be considered as an alternative. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing to the substantial risks and high chances of overdose, misuse, and addiction in the absence of medical supervision. Etymology The word ''analgesic'' derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and Visual impairment, problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Signs and symptoms Features that may result from a high level of GH or expanding tumor include: * Headaches * Enlargement of the hands, feet, nose, lips, and ears, and a general thickening of the skin * Soft tissue swelling of internal organs, notably the heart with the attendant weakening of its muscularity, and the kidneys, also the vocal cords resulting in a characteristic thick, deep voice and slowing of speech * Generalized expansion of the skull at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustician
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, craft, science and technology have prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
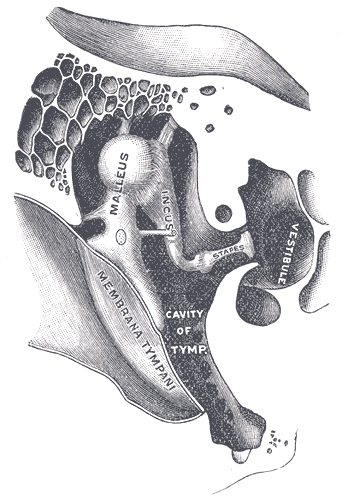
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid Solid is a state of matter where molecules are closely packed and can not slide past each other. Solids resist compression, expansion, or external forces that would alter its shape, with the degree to which they are resisted dependent upon the ..., liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthoma
An acanthoma is a skin neoplasm composed of squamous or epidermal cells. It is located in the prickle cell layer. Types of acanthoma include pilar sheath acanthoma, a benign follicular tumor usually of the upper lip; clear cell acanthoma, a benign tumor found most frequently on the legs; and Degos acanthoma, often confused with but unrelated to Degos disease. History In 2005, "Acanthoma" was added to MeSH as an index term; previous indexing was "Skin Neoplasms" (1965–2004). At that time, PubMed PubMed is an openly accessible, free database which includes primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institute ... indexed only 206 articles with the term "acanthoma" (the term usually in the title or abstract). References External links Rare cancers {{neoplasm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthocyte
Acanthocyte (from the Greek word ἄκανθα ''acantha'', meaning 'thorn'), in biology and medicine, refers to an abnormal form of red blood cell that has a spiked cell membrane, due to thorny projections. A similar term is spur cells. Often they may be confused with echinocytes or schistocytes. Acanthocytes have coarse, irregularly spaced, variably sized crenations, resembling many-pointed stars. They are seen on blood films in abetalipoproteinemia, liver disease, chorea acanthocytosis, McLeod syndrome, and several inherited neurological and other disorders such as neuroacanthocytosis, anorexia nervosa, infantile pyknocytosis, hypothyroidism, idiopathic neonatal hepatitis, alcoholism, congestive splenomegaly, Zieve syndrome, and chronic granulomatous disease. Usage Spur cells may refer synonymously to acanthocytes, or may refer in some sources to a specific subset of 'extreme acanthocytes' that have undergone splenic modification whereby additional cell membrane loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorns, Spines, And Prickles
In plant morphology, thorns, spines, and prickles, and in general spinose structures (sometimes called ''spinose teeth'' or ''spinose apical processes''), are hard, rigid extensions or modifications of leaf, leaves, roots, plant stem, stems, or plant bud, buds with sharp, stiff ends, and generally serve the same function: physically plant defense against herbivory, defending plants against herbivory. Description In common language, the terms are used more or less interchangeably, but in botanical terms, thorns are derived from Shoot (botany), shoots (so that they may or may not be branched, they may or may not have leaves, and they may or may not arise from a bud),Simpson, M. G. 2010. "Plant Morphology". In: ''Plant Systematics, 2nd. edition''. Elsevier Academic Press. Chapter 9.Judd, Campbell, Kellogg, Stevens, Donoghue. 2007. "Structural and Biochemical Characters". In: ''Plant Systematics, a phylogenetic approach, third edition''. Chapter 4. spines are derived from Leaf, leaves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac
Celiac (or coeliac in British English) may refer to: * Coeliac disease * Celiac artery * Celiac lymph nodes * Celiac plexus The celiac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a nerve plexus, complex network of nerves located in the abdomen, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch fro ... {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty or "tummy tuck" is a cosmetic surgery procedure used to make the abdomen thinner and more firm. The surgery involves the removal of excess skin and fat from the middle and lower abdomen in order to tighten the muscle and fascia of the abdominal wall. This type of surgery is usually sought by patients with loose or sagging tissues, that develop after pregnancy or major weight loss. History Modern abdominoplasties were developed starting in the 1960s. Heavier populations have led to increased demand for the surgeries, while technological advancements have improved their quality. Types of Abdominoplasty Surgery Abdominoplasty surgeries vary in scope and are frequently subdivided into categories. Depending on the extent of the surgery, a complete abdominoplasty can take from 1 to 5 hours. A partial abdominoplasty (mini-tuck abdominoplasty) can be completed between 1 and 2 hours. On the other hand a fleur-de-lis abdominoplasty can take up to 7 hours. Complete abd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at the front an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |