|
List Of Bog Bodies
This is a list of bog body, bog bodies grouped by location of discovery. Bog bodies, or bog people, are the naturally Mummy, preserved corpses of humans and some animals recovered from peat bogs. The bodies have been most commonly found in the northern European countries of Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Ireland. Reports of bog bodies surfaced during the early 18th century. In 1965, the German scientist Alfred Dieck catalogued more than 1,850 bog bodies, but later scholarship revealed much of Dieck's work was erroneous. Hundreds of bog bodies have been recovered and studied, although it is believed that only around 45 remain intact today. How to use this list * There may be more than one name in the "name" category, which may also be used to show alternate spellings for names of the bog body. * The location category shows the city or state in which the bog body was discovered, although some bog bodies are discovered on borders between countries. * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bog Body
A bog body is a human cadaver that has been naturally mummified in a peat bog. Such bodies, sometimes known as bog people, are both geographically and chronologically widespread, having been dated to between 8000 BC and the Second World War. Fischer 1998. p. 237. The unifying factor of the bog bodies is that they have been found in peat and are partially preserved; however, the actual levels of preservation vary widely from perfectly preserved to mere skeletons. Van der Sanden 1996. p. 7. Unlike most ancient human remains, bog bodies often retain their skin and internal organs due to the unusual conditions of the surrounding area. Combined, highly acidic water, low temperature, and a lack of oxygen preserve but severely tan their skin. While the skin is well-preserved, the bones are generally not, due to the dissolution of the calcium phosphate of bone by the peat's acidity. The acidic conditions of these bogs allow for the preservation of materials such as skin, hair, nails, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Denmark
The National Museum of Denmark (Nationalmuseet) in Copenhagen is Denmark, Denmark's largest museum of cultural history, comprising the histories of Danish and foreign cultures, alike. The museum's main building is located a short distance from Strøget at the center of Copenhagen. It contains exhibits from around the world, from Greenland to South America. Additionally, the museum sponsors SILA - The Greenland Research Center at the National Museum of Denmark to further archaeology, archaeological and anthropology, anthropological research in Greenland. The museum has a number of national commitments, particularly within the following key areas: archaeology, ethnology, numismatics, ethnography, natural science, Architectural conservation, conservation, communication, building antiquarian activities in connection with the Church (building), churches of Denmark, as well as the handling of the Danefæ (the National Treasures). Exhibitions The museum covers 14,000 years of Denmark, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunhild
Gunhild (with variants Gundhild, Gunhilda, Gunhilde, Gunhjild, Gunilda, Gunnhild, Gunnhildr, Gunnhildur) is a Germanic languages, Germanic feminine given name composed of two words meaning "war" (gunn and hild/hildr). Notable people with these names include: * , allegedly a Danish queen consort, wife of Harald Bluetooth * Gunhild of Wenden, wife of Sweyn I of Denmark * Gunhild of Wessex, (1055–1097), eldest daughter of Harold Godwinson and Edith the Fair * Gunhild Carling (born 1975), Swedish jazz musician * Gunhild Kyle (1921–2016), Swedish historian * Gunhild Rosén (1855–1928), Swedish ballerina * Gunhilda of Denmark, daughter of Canute the Great and wife of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor * Gunhilde (died 1002), said to have been the sister of Sweyn Forkbeard, King of Denmark * Gunnhild, Mother of Kings, wife of Erik Bloodaxe * Gunnhildr Sveinsdóttir, queen consort of Denmark and Sweden See also * 891 Gunhild, an asteroid in the Asteroid Belt * Gunhild (clothing), a Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haraldskær Woman
The Haraldskær Woman (or Haraldskjaer Woman) is the name given to a bog body of a woman preserved in a bog in Jutland, Denmark, and dating from about 490 BC (pre-Roman Iron Age). Workers found the body in 1835 while excavating peat on the Haraldskær Estate. The anaerobic conditions and acids of the peat bog contributed to the body's excellent preservation. Not only was the intact skeleton found, but so were the skin and internal organs. Scientists settled disputes about the age and identity of this well-preserved body in 1977, when radiocarbon dating determined conclusively that the woman's death occurred around the 5th century BC.Archaeological InstituteHaraldskaer Woman: Bodies of the Bogs, ''Archaeology'', Archaeological Institute of America, December 10, 1997. The Haraldskær Woman's body is on permanent display in a glass-covered sarcophagus inside The Cultural Museum in central Vejle, Denmark. Details Excavators found the body of the Haraldskær Woman in a supine positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It stretches from the Grenen spit in the north to the confluence of the Elbe and the Sude (river), Sude in the southeast. The historic southern border river of Jutland as a cultural-geographical region, which historically also included Southern Schleswig, is the Eider (river), Eider. The peninsula, on the other hand, also comprises areas south of the Eider (river), Eider: Holstein, the Saxe-Lauenburg, former duchy of Lauenburg (district), Lauenburg, and most of Hamburg and Lübeck. Jutland's geography is flat, with comparatively steep hills in the east and a barely noticeable ridge running through the center. West Jutland is characterised by open lands, heaths, plains, and peat bogs, while East Jutland is more fertile with lakes and lush fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
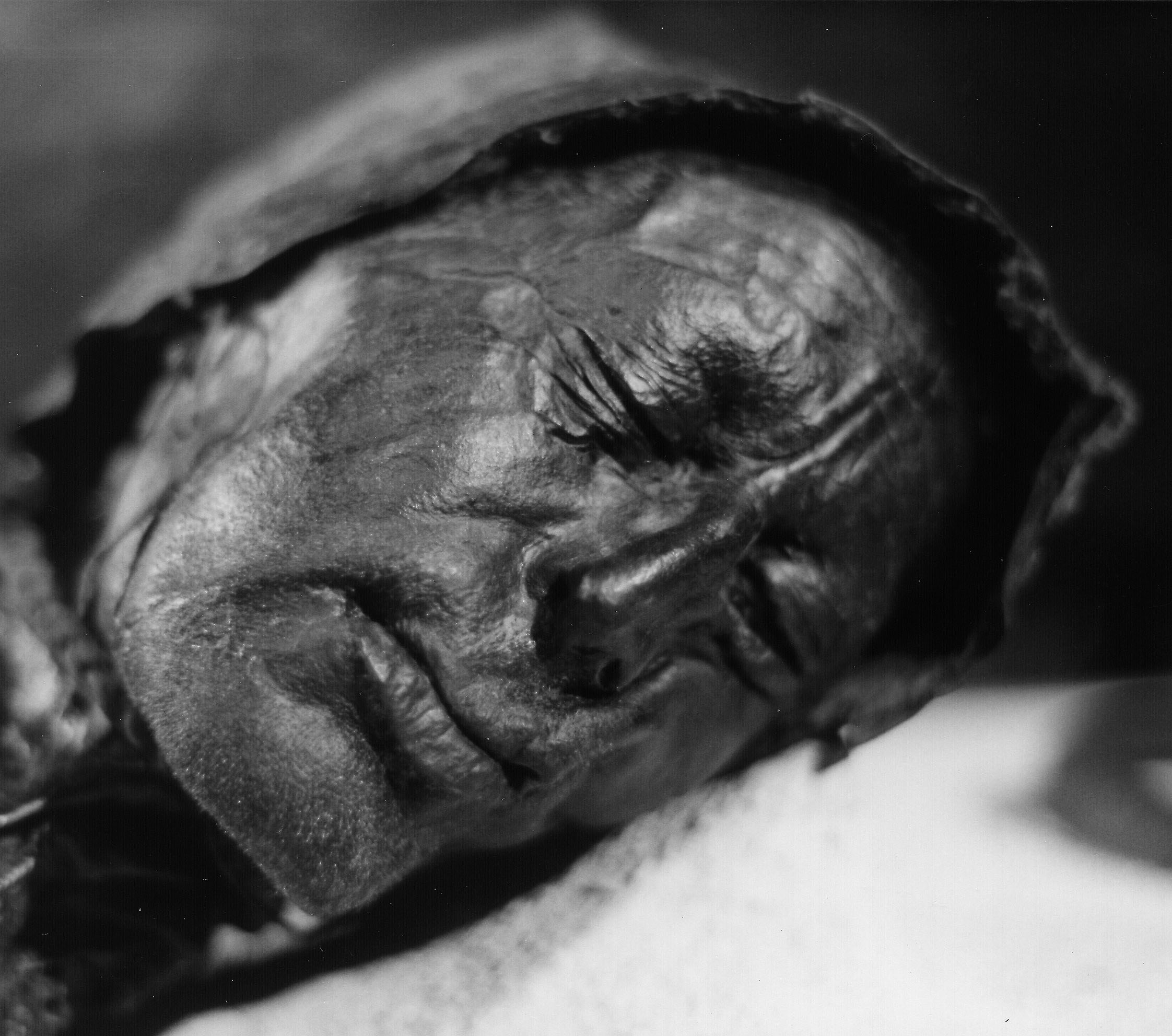
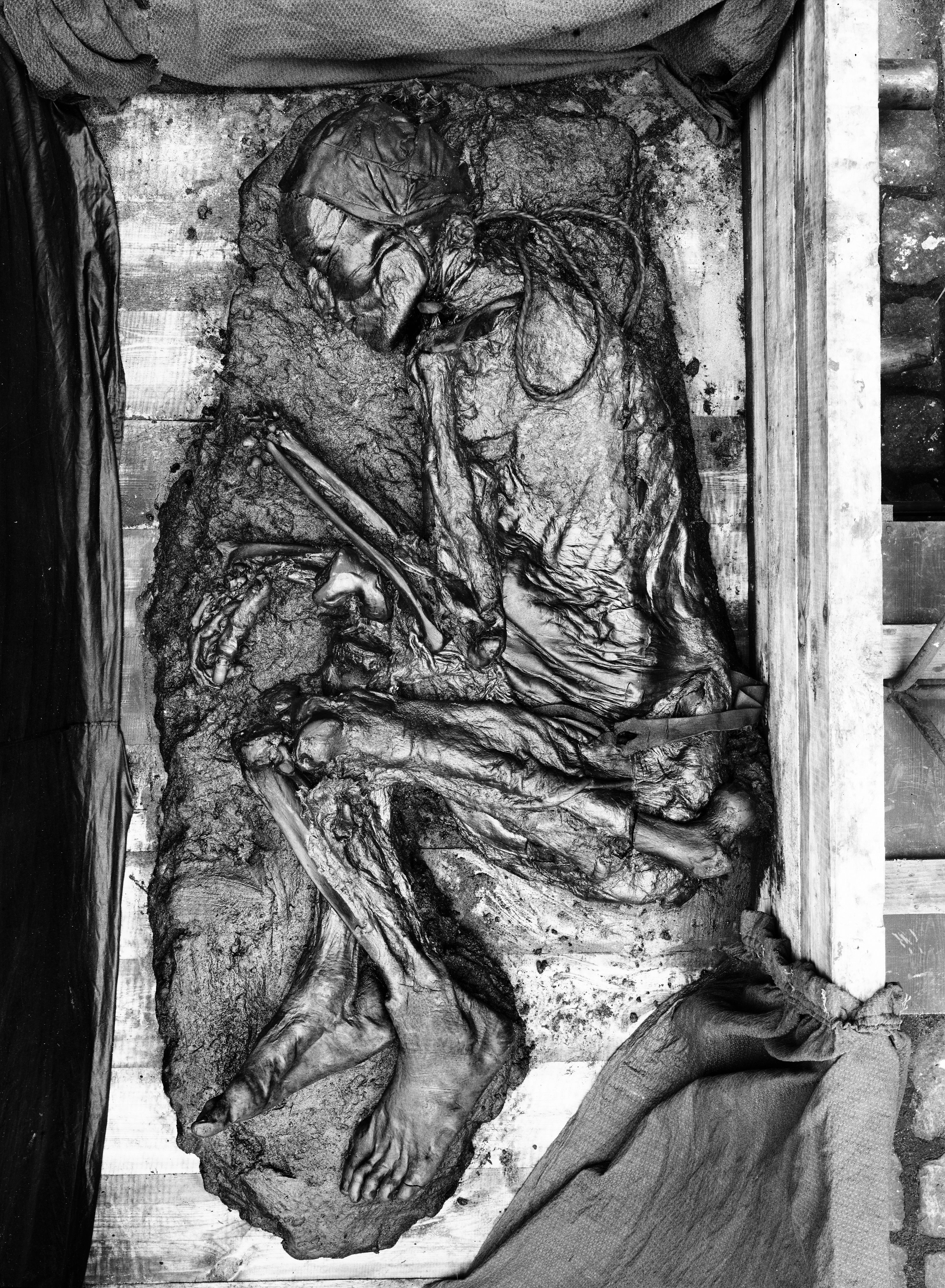
Grauballe Man
The Grauballe Man is a bog body that was uncovered in 1952 from a peat bog near the village of Grauballe in Jutland, Denmark. The body is that of a man dating from the late 3rd century BC, during the early Germanic Iron Age. Based on the evidence of his wounds, he was most likely killed by having his throat slit. His corpse was then deposited in the bog, where his body was naturally preserved for over two millennia. His was not the only bog body to be found in the peat bogs of Jutland. Together with other notable examples, Tollund Man and the Elling Woman, Grauballe Man represents an established tradition at the time. It is commonly thought that these killings, including that of Grauballe Man, were examples of human sacrifice, possibly an important rite in Iron Age Germanic paganism. Grauballe Man has been described as "one of the most spectacular discoveries from Denmark's prehistory" because it is one of the most exceptionally preserved bog bodies in the world. Upon excavation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trepanning
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... from Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is drill">Medieval Latin from Ancient Greek">Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is drilled or scraped into the human skull. The intentional perforation of the cranium exposes the ''dura mater'' to treat health problems related to intracranial diseases or release pressured blood buildup from an injury. It may also refer to any " burr" hole created through other body surfaces, including nail beds. A trephine is an instrument used for cutting out a round piece of skull bone to relieve pressure beneath a surface. Trepanning was sometimes performed on people who were behaving in a manner that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zealand
Zealand ( ) is the largest and most populous islands of Denmark, island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size) at 7,031 km2 (2715 sq. mi.). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020, comprising 40% of the country's population. Zealand is the List of European islands by area, 13th-largest island in Europe by area and the List of European islands by population, 4th most populous. It is connected to Sprogø and Funen by the Great Belt Fixed Link and to Amager by several bridges in Copenhagen. Indirectly, through the island of Amager and the Øresund Bridge, it is also linked to Scania in Sweden. In the south, the Storstrøm Bridge and the Farø Bridges connect it to Falster, and beyond that island to Lolland, from where the Fehmarnbelt Tunnel to Germany is planned. Copenhagen, the capital of Denmark, with a population between 1.3 and 1.4 million people in 2020, is located mostly on the eastern shore of Zeala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tollund Man
The Tollund Man (died 405–384 BC) is a naturally mummified corpse of a man who lived during the 5th century BC, during the period characterised in Scandinavia as the Pre-Roman Iron Age. He was found in 1950, preserved as a bog body near Silkeborg on the Jutland peninsula in Denmark. The man's physical features were so well preserved that he was mistaken for a recent murder victim. Twelve years before his discovery, another bog body, Elling Woman, was found in the same bog. The cause of death has been determined to be by hanging. There is insufficient evidence to determine if the reason for the killing was a ritual sacrifice or a punitive execution. Discovery On 8 May 1950, peat cutters Viggo and Emil Hojgaard discovered a corpse in the peat layer of the Bjældskovdal peat bog, west of Silkeborg, Denmark, which was so well preserved that they at first believed they had discovered a recent murder victim. The Tollund Man lay away from firm ground, buried under of peat, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silkeborg
Silkeborg () is a Denmark, Danish town with a population of 52,571 (1 January 2025).BY3: Population 1. January by urban areas, area and population density The Mobile Statbank from Statistics Denmark Silkeborg is the seat of Silkeborg Municipality, with a population of 101,574 as of 2025. Silkeborg is located in the middle of the Jutlandic peninsula, slightly west of the geographical centre of Denmark. The city is situated on the Gudenå, Gudenå River in the hilly and lush landscape of Søhøjlandet, surrounded by Denmark's largest forest district and a great number of lakes. Silkeborg is also known as Denmark's outdoor capital. The lakes between Silkeborg and Ry, Denmark, Ry that are linked by the Gudenå, are known collectively as ''Silkeborgsøerne'' (the Silkeborg lakes). The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |