|
List Of Battles Of The Spanish–American War
During the Spanish–American War, the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Navy fought 30 significant battles against the Spanish Army and Spanish Navy. Of these, 27 occurred in the Caribbean theater and three in the Pacific theater. The Caribbean theater consisted of two campaigns — the Puerto Rico campaign, which included ten battles, and the Cuba campaign, consisting of 17 battles — while the Pacific theater had one campaign — the Philippine campaign, with two battles — and the capture of Guam. Overview The United States Navy battleship was mysteriously sunk in Havana harbor on 15 February 1898; political pressures from the Democratic Party pushed the administration of Republican President William McKinley into a war that he had wished to avoid. Spain promised multiple times that it would reform the government of Cuba, but never delivered. The United States sent an ultimatum to Spain Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the U.S. acquiring sovereignty over Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines, and establishing a protectorate over Cuba. It represented U.S. intervention in the Cuban War of Independence and Philippine Revolution, with the latter later leading to the Philippine–American War. The Spanish–American War brought an end to almost four centuries of Spanish presence in the Americas, Asia, and the Pacific; the United States meanwhile not only became a major world power, but also gained several island possessions spanning the globe, which provoked rancorous debate over the wisdom of expansionism. The 19th century represented a clear decline for the Spanish Empire, while the United States went from a newly founded country to a rising power. In 1895, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tayacoba
The Battle of Tayacoba, June 30, 1898, (also spelled Tayabacao) was an American special operations effort to land supplies and reinforcements to Cuban rebels fighting for their independence in the Spanish–American War. Background On June 25 the American steamships ''Fanita'' and ''Florida'' accompanied by the gunboat left Key West carrying a cargo of troops, ammunition, supplies and arms (including two dynamite guns, 4,000 Springfield rifles and 200 Mauser rifles), to aid Cuban insurgents under the command of Máximo Gómez. On board were 650 Cubans under General Emilio Núñez, fifty troopers of the Tenth U.S. Cavalry under Carter P. Johnson and Second Lieutenant George P. Ahern, and twenty-five "Rough Riders" under Captain Winthrop Astor Chanler, brother of Captain William Astor Chanler. The first attempt to land took place on June 29 near the port of Cienfuegos, at the mouth of the San Juan River, however as a result of a prior assault on May 11, the position was to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Guam
The Capture of Guam was a bloodless engagement between the United States and Spain during the Spanish–American War. The U.S. Navy sent a single cruiser, , to capture the island of Guam, which was under Spanish control. The Spanish garrison on the island had no knowledge of the war and no real ability to resist the American forces. They surrendered without resistance, and the island passed into American control. The event was the only conflict of the Spanish–American War on Guam. Background Guam had been under Spanish control since 1668.Brief History of Guam /ref> By the time of the war, Guam had been neglected and there was only a small Spanish military presence. The last message the authorities on Guam had received from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo. It is the List of extreme points of the United States#Westernmost points, westernmost point and territory of the United States, as measured from the geographic center of the United States, geographic center of the U.S. In Oceania, Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia. As of 2022, its population was 168,801. Chamorros are its largest ethnic group, but a minority on the multiethnic island. The territory spans and has a population density of . Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamorro people, Chamorro, who are related to the Austronesian peoples, Austronesian peoples of the Malay Archipelago, the Philippines, Taiwanese indigenous peoples, Taiwan, and Polyne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Las Guasimas
The Battle of Las Guasimas of June 24, 1898 was a Spanish rearguard action by Major General Antero Rubín against advancing columns led by Major General Joseph Wheeler, "Fighting Joe" Wheeler and the first land engagement of the Spanish–American War. The battle unfolded from Wheeler's attempt to storm Spanish positions at Las Guasimas de Sevilla, in the jungles surrounding Santiago de Cuba, with the Rough Riders, 1st U.S. Volunteer Cavalry and the 10th Cavalry Regiment (United States), 10th Regular Cavalry. Approaching on June 24, American reports suggested the Spanish Army, Spaniards were digging in with a field gun; however, Cuban Reconnaissance, scouts contradicted these, revealing the Spaniards were preparing to abandon their position. In fact, the Spanish troops had received orders to fall back on Santiago. Wheeler requested the assistance of the attached Cuban forces in an immediate attack, but their commander, Colonel, Col. Gonzales Clavel, refused. Wheeler decided to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guantánamo Bay
Guantánamo Bay (, ) is a bay in Guantánamo Province at the southeastern end of Cuba. It is the largest harbor on the south side of the island and it is surrounded by steep hills which create an enclave that is cut off from its immediate hinterland. The United States assumed territorial control over the southern portion of Guantánamo Bay under the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base#Permanent lease, 1903 Lease. The United States exercises jurisdiction and control over this territory as the home of the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base, while recognizing that Cuba retains ultimate sovereignty. Climate Guantánamo Bay has a hot semi-arid climate according to the Köppen climate classification, with high temperatures throughout the year. Rainfall is rather low, and it is one of the driest regions in Cuba. U.S. control of Guantánamo Bay The United States first seized Guantánamo Bay and established a naval base there in 1898 during the Spanish–American War in the Battle of Guantánamo Bay. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cienfuegos
The Battle of Cienfuegos, also known as the Raid on Cienfuegos, was an engagement of the Spanish–American War, intended by the United States Navy to tighten its blockade of Cuba. Background The Spanish were using undersea cables as a means to communicate with not only the rest of Cuba, but also the Spanish command. These cables had many key junctions, namely, a shore near Cienfuegos. The cables connected to Havana, the port of Santiago, and then branched off to other Caribbean islands such as Jamaica. The cables were run out from an easily located house which contained a critical hub for the undersea cable system. While the house could easily be destroyed, this would only inflict largely superficial damage, and could easily be repaired and functioning in a short period of time. Therefore, command decided to grapple the three cables out of the sea and cut them in several places, disrupting much of the communications between the Spanish and their operations in Cuba. This damage w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Battle Of San Juan (1898)
The Third Battle of San Juan began on 28 June 1898 when an American auxiliary cruiser intercepted a Spanish blockade runner. A Spanish squadron attempted to rescue the blockade runner and succeeded in taking off supplies and her crew but failed to save the ship, which the American warship engaged and forced to run aground. Prelude Puerto Rico had been under attack by US Navy forces under the command of Rear Admiral William T. Sampson since just before the Bombardment of San Juan early on in the war. The only Spanish effort to break the blockading forces had failed on 22 June, and instead of actively engaging the Americans the Spanish forces were bottled up in harbor at the capital of San Juan. Blockade runners had on occasion slipped through the San Juan Blockade, but were often driven away or captured before ever nearing the harbor. The SS ''Antonio Lopez'' was a transport turned blockade runner that had been disarmed and fitted out at Cadiz, Spain and set sail on June 16 fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of San Juan
The Second Battle of San Juan occurred on 22 June 1898 when two Spanish vessels tried to break the American blockade off San Juan. Background San Juan had been under blockade by American forces since April 1898. Most of the time, the blockade consisted of a single auxiliary cruiser which patrolled and pursued blockade runners that were attempting to reach San Juan. By June, the task of blockading San Juan was delegated to the auxiliary cruiser , a former ocean liner commanded by Captain Charles Sigsbee who had formerly commanded the . The Spanish destroyer , originally part of Admiral Cervera's squadron, had mechanical trouble and left the main Spanish fleet eventually reaching San Juan. With ''Terror'' and several other naval vessels at their disposal, the Spanish decided to make an attempt at breaking the blockade. ''Terror'' and the old cruiser set off from San Juan to engage ''St. Paul'' while a crowd of jubilant locals at the harbor cheered them on. Battle Almost as soo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombardment Of San Juan
The Bombardment of San Juan, or the First Battle of San Juan, on 12 May 1898 was an engagement between United States Navy warships and the Spain, Spanish fortifications of San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan, Puerto Rico. It was the first major action of the Puerto Rican Campaign during the Spanish–American War. Background Under the command of Rear Admiral William T. Sampson, a U.S. fleet—consisting of the flagship armored cruiser , battleships and , the unprotected cruisers and , the Monitor (warship), monitors and , the torpedo boat , the auxiliary cruiser , the Collier (ship type), collier , and two unarmed yachts transporting officials and the press,—prepared to attack Puerto Rico. Their mission was to intercept the Spanish Admiral Pascual Cervera y Topete and his fleet steaming from the Cape Verde Islands to the Antilles. American commanders believed the Spanish fleet was steaming for Puerto Rico. With this understanding, Sampson set steam from Key West and lifted an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
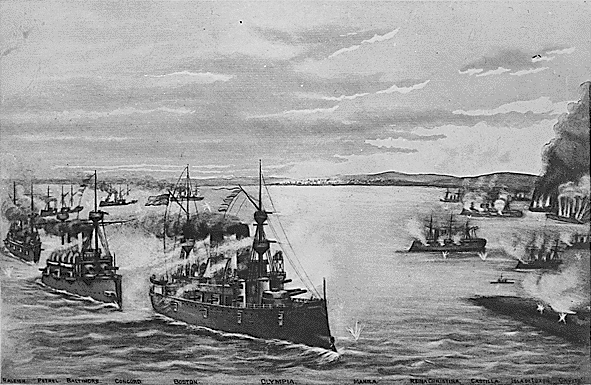
Battle Of Manila Bay
The Battle of Manila Bay (; ), also known as the Battle of Cavite, took place on May 1, 1898, during the Spanish–American War. The American Asiatic Squadron under Commodore George Dewey engaged and destroyed the Spanish Pacific Squadron under ''Contraalmirante'' (Rear admiral) Patricio Montojo. The battle took place in Manila Bay in the Philippines, and was the first major engagement of the Spanish–American War. The battle was one of the most decisive naval battles in history and marked the end of the Spanish colonial period in Philippine history. Tensions between Spain and the United States worsened over the Spanish conduct during their efforts to quell the Cuban War of Independence, with many Americans being agitated by largely falsified reports of Spanish atrocities against the Cuban population. In January 1898, fearing the fate of American interests in Cuba due to the war, the cruiser was dispatched to protect them. Less than a month later, the cruiser explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |