|
List Of Battles 1601–1800
Early 17th century (1601–1650) 1601 * Capture of Portobello (1601) 17 January – English expedition assaulted and took Portobello from the Spanish, acquired some booty and then sacked the place. * Battle of Wenden (1601) 7 January – The battle is significant as the first encounter between Swedish reiters and Polish hussars. * Battle of Kokenhausen 23 June – Was the battle opening the Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611) * Siege of Rheinberg 12 June – 2 August – Was the siege of the towns of Rheinberg and Meurs, Rheinberg eventually capitulated on 28 July after a Spanish relief force failed to relieve the city. The town of Meurs surrendered 2 August * Siege of Ostend 5 July – 20 September 1604 was a three-year siege of the city of Ostend during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War. * Battle of Guruslău 3 August – Between the Wallachia, Habsburg Monarchy, & Cossacks against Principality of Transylvania & Moldavia. Wallachian-Austrian victory, Trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Capture Of Portobello (1601)
The Capture of Portobello was a military event during the long ongoing Anglo–Spanish War of 1585-1604, in which an English naval expedition under the command of privateer William Parker (died 1618), of Plymouth, assaulted and took the seaport town of Portobelo at Colon on the eastern / northern coast of Panama / Isthmus of Panama in Central America, from the Spanish, captured some looted booty, and then sacked the place, an important site on the Spanish Main in the then world-wide Spanish Empire.Chartrand p.30 Capture Background The war with the Kingdom of Spain and its then world-wide Spanish Empire, was continuing and English privateers were still roaming the Empire's Spanish Main in the Americas for prizes and attacking ports. In November 1600, English privateer Captain William Parker, sailed from the seaport of Plymouth on the southwest coast of England, facing the English Channel. He was in command of a modest venture consisting of a small fleet of the 100-ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Bantam
The naval Battle of Bantam took place on 27 December 1601 in Bantam Bay (now Banten Bay), Indonesia, when an exploration fleet of five Dutch ships under the command of Wolfert Harmensz and a Portuguese fleet under André Furtado de Mendonça, sent from Goa to restore Portuguese authority, met in the Indonesian archipelago. The battle resulted in Dutch victory and forced the Portuguese to retreat. The outnumbered Dutch fleet took three Portuguese fustas as prizes. Ships involved * Netherlands ** Gelderland (Wolfert Harmensz) ** Zeelandia (Jan Cornelisz) ** Utrecht (Jan Martensz) ** Wachter (yacht) (Gerrit Hendricksz Roobol) ** Duyfken (yacht) (Willem Schouten) * Portugal (André Furtado de Mendonça André Furtado de Mendonça (1558 – 1 April 1611) was a captain and governor of Portuguese India, and a military commander during Portuguese expansion into Ceylon, India, Indonesia and Malacca. Biography He was a son of Afonso Furtado Mendo� ...), 30 vessels total ** 8 galleons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
L'Escalade
''L'Escalade'', or ''Fête de l'Escalade'' (from escalade, the act of scaling defensive walls), is an annual festival in Geneva, Switzerland, held each December commemorating the defeat of an attempt to conquer the Protestant city-state by the Catholic Duchy of Savoy in 1602. The celebrations and other commemorative activities are usually held on 12 December or the closest weekend. Savoyard troops sent by Charles Emmanuel I, Duke of Savoy attempted a surprise attack during the night of 11–12 December 1602, but were repulsed by the Genevese defenders. According to legend, this was possible thanks to individual acts of bravery by Genevese citizens, notably by local resident Catherine Cheynel (also known as ''la Mère Royaume''), who dumped boiling vegetable soup on the invaders and alerted the townsfolk. Background For years, the duke coveted the wealth of Geneva. When Charles Emmanuel came to the throne of the House of Savoy in 1580, he aimed to make Geneva his capital nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of The Narrow Seas
The Battle of the Narrow Seas, also known as the Battle of the Goodwin Sands or Battle of the Dover Straits was a naval engagement that took place on 3–4 October 1602 during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585), Anglo-Spanish War of 1585 and part of the Dutch Revolt. An English fleet under Sir Robert Mansell intercepted and attacked six Spanish galleys under the command of Federico Spinola in the Dover Straits. The battle was fought initially off the coast of England and finally off the Spanish Netherlands. The English were soon joined by a Dutch fleet under Jan Adriaanszoon Cant, and they completed the destruction.Jaques p. 714 Background In 1602 Frederico Spinola, younger brother of Ambrogio Spinola, 1st Marquis of the Balbases, Ambrogio Spinola, had distinguished himself as a soldier in the Army of Flanders and had succeeded in 1599 going through the English Channel and passing the straits of Dover unmolested; this led to a panic called the ''invisible armada'', as it encouraged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
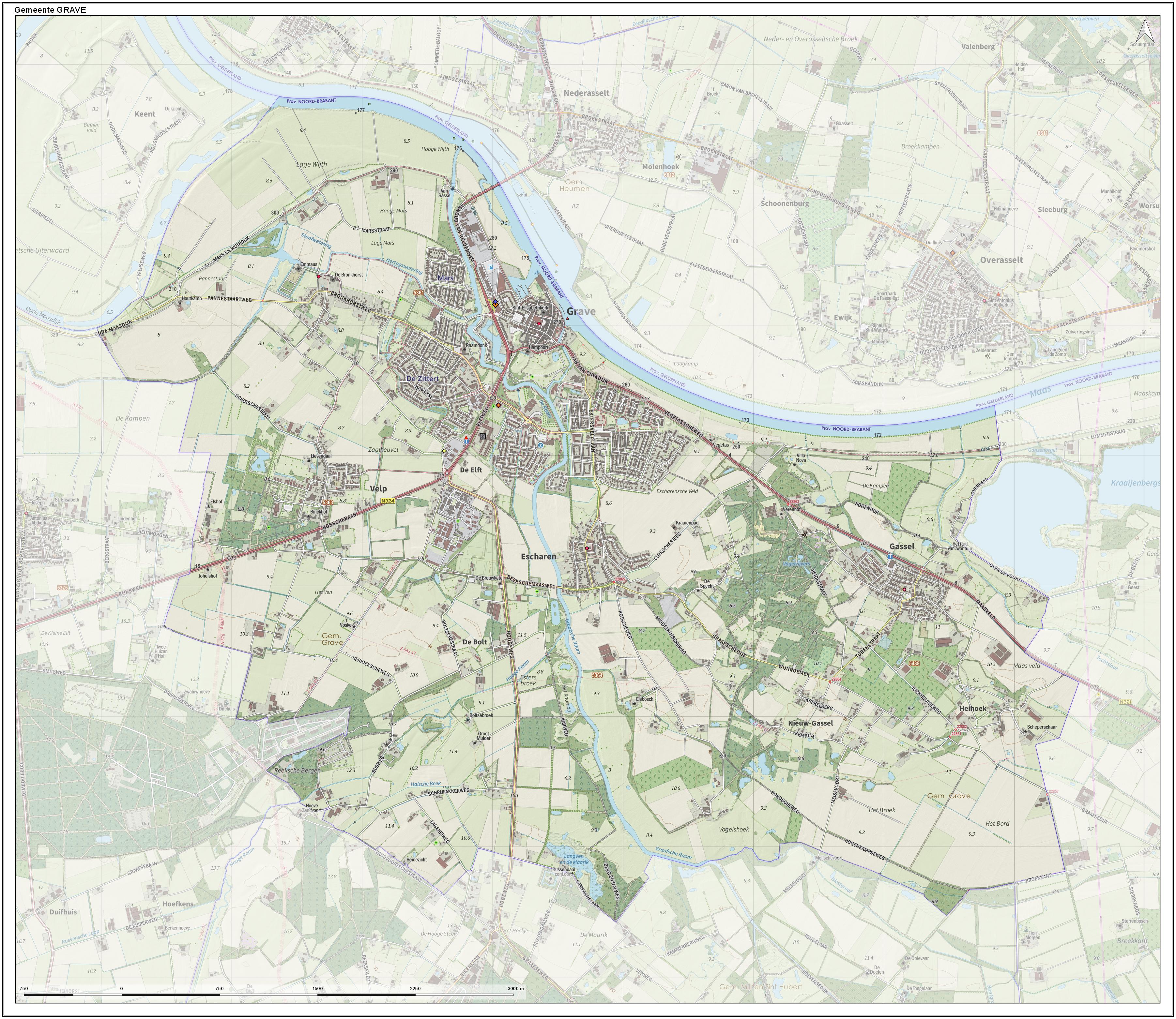
Grave, Netherlands
Grave (; formerly ''De Graaf'') is a city and former municipality in the Dutch province of North Brabant. The former municipality had a population of in . Grave is a member of the Dutch Association of Fortified Cities. The former municipality included the following towns: Grave (capital), Velp, Escharen and Gassel. Grave, Boxmeer, Cuijk, Mill en Sint Hubert, and Sint Anthonis merged into the new municipality of Land van Cuijk on 1 January 2022. History Grave received city rights in 1233. The former municipality of Grave was formed in the Napoleonic era (1810) and coincided with the fortified Grave and immediate surroundings. The history of the town was thus linked to that of the place. This changed in 1942. Then there was a reclassification place where the municipality Grave was expanded with the previously independent municipalities Velp and Escharen. Moreover, in 1994 the neighboring municipality of Beers was abolished and a part thereof, the parish Gassel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Grave (1602)
The siege of Grave was a siege that took place between 18 July and 20 September 1602, as part of the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War. The Spanish-held city of Grave was besieged by a Dutch and English army led by Maurice of Orange and Francis Vere respectively.Markham pp. 338–339 After a siege of nearly two months the city surrendered when a Spanish relief army under Francisco de Mendoza was defeated just outside the city by the besiegers.Wernham pp. 411–412Dalton pp. 93–97 The defeat was severe enough to cause a major mutiny in the Spanish army.Duerloo p. 130 Background Prince Maurice of Orange had been actively campaigning against the Spanish armies in the Southern Netherlands and had successfully made sure that Ostend then under siege by Albert of Austria would be a key distraction while he took the rest of the Spanish garrisons that were still in the Republic.Borman pp. 230–232 Maurice in his first objective successfully besieged and took Rheinberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Dunboy
The siege of Dunboy took place at Dunboy Castle between 5 June and 18 June 1602, during the Nine Years' War in Ireland. It was one of the last battles of the war. An English army of up to 5,000 under Sir George Carew besieged the castle, which was held by a Gaelic Irish force of 143 loyal to Donal Cam O'Sullivan Beare. The English took the castle after eleven days and hanged the majority of captured prisoners. The English also captured a fort on nearby Dursey Island. Background Dunboy Castle is near the town of Castletownbere, on the Beara Peninsula in south-western Ireland. It was a stone tower house, built to control and defend the harbour of Bearhaven, which was a stronghold of Donal Cam O'Sullivan Beare, a Gaelic leader and the 'Chief of Dunboy'. O'Sullivan was part of an alliance of Gaelic leaders who had taken up arms against the English government in Ireland. He was helped by King Philip III of Spain, who sent an invasion force to Kinsale under the command of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Reval (1602)
The Battle of Reval took place on June 30, 1602, during the Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611) near present-day Tallinn in Estonia. The Polish forces were led by Grand Field Hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski who had been sent against Swedish forces gathering by Tallinn by Grand Crown Hetman Jan Zamoyski. Żółkiewski attacked "on the march" with two squadrons of Polish hussars The Polish hussars (; ), alternatively known as the winged hussars, were an elite heavy cavalry formation active in Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Poland and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1503 to 1702. Their epithet is derived fr .... The charge however was not successful. As a result, the Swedish forces put up frisian horses as a protection against further frontal cavalry charges. Żółkiewski then sent light cavalry on a round about flanking maneuver which attacked the Swedes from behind, coinciding with another charge by the hussars. The Swedish lines broke as a result. The Swedes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Sesimbra Bay
The Battle of Sesimbra Bay was a naval engagement that took place on 3 June 1602, during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585), Anglo-Spanish War. It was fought off the coast of Portugal (then within the Iberian Union) between an English naval expeditionary force sent out with orders by Queen Elizabeth I to prevent any further Spanish incursions against Ireland or England itself. The English force under Richard Leveson (admiral), Richard Leveson and William Monson (Royal Navy officer), William Monson met a fleet of Spanish galleys and a large carrack at Sesimbra Municipality, Sesimbra Bay commanded by Álvaro de Bazán, 2nd Marquis of Santa Cruz, Álvaro de Bazán and Federico Spinola. The English were victorious in battle, sinking two galleys, forced the rest to retreat, neutralized the fort, and captured the carrack. It was the last expedition to be sent to Spain by orders of the Queen before her death the following year.Kirsch, p. 63. Background After the defeat of the 4th Spanish Arma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Burning Of Dungannon
The Burning of Dungannon took place in June 1602 when Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone, abandoned and set fire to Dungannon, the traditional capital of the O'Neills. It marked the beginning of the final stage of Tyrone's Rebellion when the Earl became a fugitive, before his sudden reprieve the following year. Following the defeat of his army at the 1601 Battle of Kinsale, Tyrone retreated into his heartland in County Tyrone, Ulster. Courted by the Crown, many of his allied Gaelic lords now changed sides, which turned much of the local population against him. Tyrone was faced with a three-pronged pincer movement with separate forces under Henry Docwra, Arthur Chichester, and Lord Mountjoy advancing on him from Derry, Carrickfergus, and Dundalk respectively. A major tactic of Tyrone's had been to avoid fighting pitched battles, preferring to retreat and ambush. He therefore decided to abandon the town and gave orders to torch it. Soon after his cousin and enemy, Conn MacShane O' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Weissenstein
The siege of Weissenstein took place between 31 May and 30 September 1602, during the Polish–Swedish War of 1600–1611. Two weeks after the capture of Fellin, Grand Crown Hetman Jan Zamoyski led the Polish-Lithuanian army of 2,000 troops to besiege Weissenstein (now known as Paide in Estonia). Weissenstein, a major transportation hub in Estonia, was a site of strategic importance to both Poland and Sweden. Located among the marshes and built during the Teutonic period, the castle had strong artillery and was defended by 700 soldiers, local peasants, and townspeople. Weissenstein was a walled city with 30-meter towers at the corners and high bastions, and thus presented the attacking force with a significant barrier to success, even with siege works. Siege The Polish army began by blockading the fortress. Because the Swedish army was getting relief from Reval Tallinn is the capital and most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Fellin
The siege of Fellin took place between 25 March and 17 May 1602 during the Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611). Polish and Lithuanian forces led by Grand Crown Hetman Jan Zamoyski besieged the Swedish-held town of Fellin (present-day Viljandi in Estonia Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...). The large Polish–Lithuanian army of around 5,000 troops first took the town, while the Swedish defenders, numbering around 800, retreated to the city's castle. After a second frontal attack on the castle, during which the Voivode of Wenden Jerzy Farensbach was killed, the Swedish garrison capitulated, although a group of Finnish soldiers refused to surrender and blew themselves up in the castle's tower. Fellin was later recaptured by the Swedes in a siege in 1608.Sundberg, Ulf: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |