|
List Of Anonymously Published Works
Throughout the history of literature, since the creation of bound texts in the forms of books and codices, various works have been published and written anonymously, often due to their political or controversial nature, or merely for the purposes of the privacy of their authors, among other reasons. This article provides a list of literary works published anonymously, either explicitly attributed to "Anonymous", or published with no specific author's name given. A work that is published anonymously differs from works published under a pseudonym. Not included in this list are works which predate the advent of publishing and general attribution of authorship, such as ancient written inscriptions (such as hieroglyphic or pictographical, transcribed texts), certain historical folklore and myths of oral traditions now published as text, and reference or plain texts (letters, notes, graffiti) recovered archaeologically, which are otherwise unimportant to literary studies. Religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Literature
The history of literature is the historical development of writings in prose or poetry that attempt to provide entertainment or education to the reader, as well as the development of the literary techniques used in the communication of these pieces. Not all writings constitute literature. Some recorded materials, such as compilations of data (e.g., a check register) are not considered literature, and this article relates only to the evolution of the works defined above. Ancient (Bronze Age–5th century) Early literature is derived from stories told in hunter-gatherer bands through oral tradition, including myth and folklore. Storytelling emerged as the human mind evolved to apply causal reasoning and structure events into a narrative and language, allowing early humans to share information with one another. Early storytelling provided opportunity to learn about dangers and social norms while also entertaining listeners. Myth can be expanded to include all use of patterns and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lament For Nippur
The Lament for Nippur, or the Lament for Nibru, is a Sumerian language, Sumerian lament, also known by its incipit tur3 me nun-e ("After the cattle pen..."). It is dated to the Old Babylonian Empire (). It is preserved in Penn Museum on tablet CBS13856. It is one of five known City Lament, Mesopotamian "city laments"—dirges for ruined cities in the voice of the city's tutelary deity, tutelary goddess. Text The Lament is composed of 9 ''kirugu'' (sections, songs) and 8 ''gišgigal'' (antiphons) followed by 3 more ''kirugu''. Numbered by ''kirugu'', the lament is structured as follows: #storm of Enlil; Enlil destroys Nippur #weeping goddess; Nippur addresses Enlil #storm of Enlil; Enlil destroys Nippur #weeping goddess; the poet addresses Nippur #storm of Enlil; Ishme-Dagan recreates Nippur #weeping goddess; the poet addresses Nippur #storm of Enlil; Ishme-Dagan recreates Nippur #storm of Enlil; Enlil recreates Nippur #storm of Enlil; Ishme-Dagan recreates Nippur #storm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
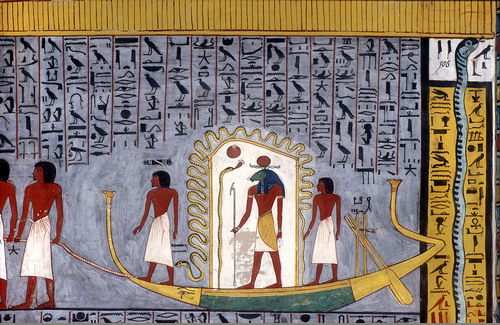
Litany Of Re
The Litany of Re (or more fully "''Book of Praying to Re in the West, Praying to the United One in the West''") is an important ancient Egyptian funerary text of the New Kingdom.Hornung (1999) p.136 Like many funerary texts, it was written on the inside of the tomb for reference by the deceased. Unlike other funerary texts, however, it was reserved only for pharaohs or very favored nobility. It is a two-part composition that in the first part invokes the sun, Ra, in 75 different forms. The second part is a series of prayers in which the pharaoh assumes parts of nature and deities, but mostly of the sun god. Developed in the Eighteenth Dynasty, it also praises the king for his union with the sun god, as well as other deities. The text was used in the entrance of most tombs from the time of Seti I, though we first know of it from the burial chamber of Thutmose III and the tomb of his vizier A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Earth
The Book of the Earth () is an Ancient Egyptian funerary text that has been called many names such as The Creation of the Sun Disk and the Book of Aker. The Book primarily appears on the tombs of Merneptah, Twosret, Ramesses III, Ramesses VI, and Ramesses VII and serves as a counterpart to the Book of Caverns.Book of the Earth by Jimmy Dunn writing as Taylor Ray Ellison The central figures in the story are Osiris, Ra and Ancient Egyptian concept of the soul#Ba, Ba, while the overarching plot is the journey the sun takes through the earth god, Aker (god), Aker. Original sources The scenes were found on all of the walls of the tombs of Ramesses VI and Ramesses VII. There were a few additional scenes found on the walls of other royal tombs extending from the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom to the L ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Caverns
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, mostly of writing and images. Modern books are typically composed of many pages bound together and protected by a cover, what is known as the ''codex'' format; older formats include the scroll and the tablet. As a conceptual object, a ''book'' often refers to a written work of substantial length by one or more authors, which may also be distributed digitally as an electronic book (ebook). These kinds of works can be broadly classified into fiction (containing invented content, often narratives) and non-fiction (containing content intended as factual truth). But a physical book may not contain a written work: for example, it may contain ''only'' drawings, engravings, photographs, sheet music, puzzles, or removable content like pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Netherworld
The tomb of Tutankhamun (reigned ), a pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt, is located in the Valley of the Kings. The tomb, also known by its tomb number KV62, consists of four chambers and an entrance staircase and corridor. It is smaller and less extensively decorated than other Egyptian royal tombs of its time, and it probably originated as a tomb for a non-royal individual that was adapted for Tutankhamun's use after his premature death. Like other pharaohs, Tutankhamun was buried with a wide variety of funerary objects and personal possessions, such as coffins, furniture, clothing and jewelry, though in the unusually limited space these goods had to be densely packed. Robbers entered the tomb twice in the years immediately following the burial, but Tutankhamun's mummy and most of the burial goods remained intact. The tomb's low position, dug into the floor of the valley, allowed its entrance to be hidden by debris deposited by flooding and tomb construction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Book Of Gates
The Book of Gates is an Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, ancient Egyptian funerary text dating from the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The ''Book of Gates'' is long and detailed, consisting of one hundred scenes. It narrates the passage of a newly deceased Soul (spirit), soul into the next world journeying with the sun god, Ra, through the Duat, underworld during the hours of the night towards his resurrection. The soul is required to pass through a series of 'gates' at each hour of the journey. Each gate is guarded by a different serpent deity that is associated with Gate deities of the underworld, a different goddess. It is important that the deceased knows the names of each guardian. Depictions of the judgment of the dead are shown in the last three hours. The text implies that some people will pass through unharmed, but others will suffer torment in a lake of fire. At the end of Ra's journey through the underworld, he emerges anew to take his place back in the sky. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spell Of The Twelve Caves
The Spell of the Twelve Caves (also called the Wandering of the Soul; ) is an ancient Egyptian funerary text from the New Kingdom. The earliest known copy is on a papyrus found in KV35 the tomb of Amenhotep II, and another copy was inscribed in the Osireion at Abydos under Merenptah. Although the text also appears in some copies of the Book of the Dead, where it is classified as Spell 168, the Egyptologist Alexandre Piankoff treated it as a distinct composition.Hornung (1999) pp. 54–55 The text describes the Duat, or underworld, as a realm divided into twelve caves, much like the twelve hours found in the Amduat and the Book of Gates The Book of Gates is an ancient Egyptian funerary text dating from the New Kingdom. The ''Book of Gates'' is long and detailed, consisting of one hundred scenes. It narrates the passage of a newly deceased soul into the next world journeying wi ..., two other funerary texts from the early New Kingdom. Each cave is described as containing seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amduat
The ''Amduat'' (, () is an important Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, ancient Egyptian funerary text of the New Kingdom of Egypt. Similar to previous funerary texts, such as the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom's Pyramid Texts, or the First Intermediate Period of Egypt, First Intermediate Period's Coffin Texts, the ''Amduat'' was found carved on the internal walls of a pharaoh's tomb. Unlike other funerary texts, however, it was reserved almost exclusively for Pharaoh, pharaohs until the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt, Twenty-first Dynasty, or very select nobility. The ''Amduat'' tells the story of Ra, the Egyptian sun god who makes a daily journey through the underworld, from the time when the sun sets in the west till it rises again in the east. This is associated with imagery of continual death and rebirth, as the sun 'dies' when it sets, and through the trials of rebirth in the underworld, it is once again 'reborn' at the beginning of a new day. It is said that the deceased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' is the name given to an Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom (around 1550 BC) to around 50 BC. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. In 1842, the Egyptologist Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as 'Book of the Dead'. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated , is translated as ''Spells of Coming Forth by Day''. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a tradition of funerary texts which includes the earlier Pyramid Texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffin Texts
The Coffin Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian funerary spells written on coffins beginning in the First Intermediate Period. They are partially derived from the earlier Pyramid Texts, reserved for royal use only, but contain substantial new material related to everyday desires, indicating a new target audience of common people. Coffin texts are dated back to 2100 BCE. Ordinary Egyptians who could afford a coffin had access to these funerary spells and the pharaoh no longer had exclusive rights to an afterlife. As the modern name of this collection of some 1,185 spells implies, they were mostly inscribed on Middle Kingdom coffins. They were also sometimes written on tomb walls, stelae, canopic chests, papyri and mummy masks. Due to the limited writing surfaces of some of these objects, the spells were often abbreviated, giving rise to long and short versions, some of which were later copied in the Book of the Dead. Content In contrast to the Pyramid Texts which focus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Funerary Texts
The literature that makes up the ancient Egyptian funerary texts is a collection of religious documents that were used in ancient Egypt, usually to help the spirit of the concerned person to be preserved in the afterlife. They evolved over time, beginning with the Pyramid Texts in the Old Kingdom through the Coffin Texts of the Middle Kingdom and into several books, most famously the Book of the Dead, in the New Kingdom and later times. Old Kingdom The funerary texts of the Old Kingdom were initially reserved for the king only. Towards the end of the period, the texts appeared in the tombs of royal wives. Middle Kingdom These are a collection of ancient Egyptian funerary spells written on coffins beginning in the First Intermediate Period. Nearly half of the spells in the Coffin Texts derive from those in the Pyramid Texts. New Kingdom *Book of the Dead * Amduat * Spell of the Twelve Caves * The Book of Gates * Book of the Netherworld *Book of Caverns * Book of the Earth * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |