|
List Of Intel Pentium M Microprocessors
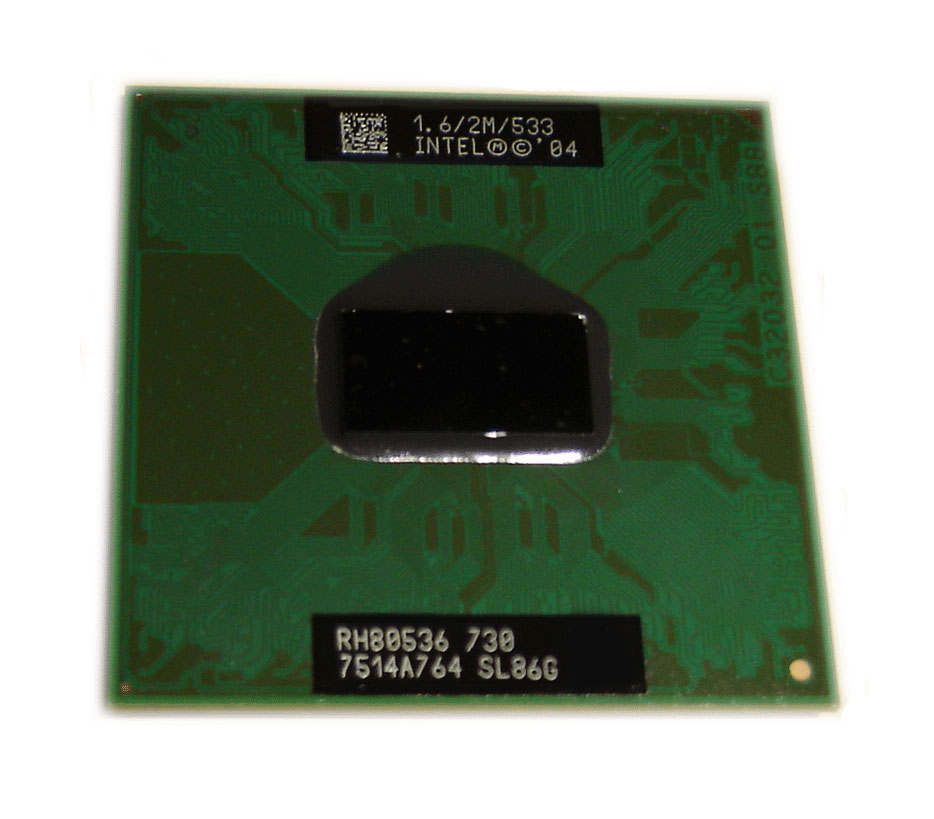
This is a list of Intel Pentium M processors. They are all single-core 32-bit CPUs codenamed ''Banias'' and ''Dothan'', and targeted at the consumer market of mobile computers. Mobile processors Pentium M "Banias" (130 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST)'' * Die size: 83 mm2 "Dothan" (90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST)'' * '' PAE, XD bit (an NX bit implementation)'': supported by C0 stepping * Die size: 87 mm2 * Steppings: B0, B1, C0 *C1 stepping Pentium M's are fabbed on a 65 nm process with an actual C0 stepping See also * List of Intel Pentium processors * List of Intel Pentium 4 processors § Mobile processors * Pentium M (microarchitecture) References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Intel Pentium M Microprocessors *Pentium M Intel Pentium M The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Address Extension
In computing, Physical Address Extension (PAE), sometimes referred to as Page Address Extension, is a memory management feature for the x86 architecture. PAE was first introduced by Intel in the Pentium Pro, and later by AMD in the Athlon processor. It defines a page table hierarchy of three levels (instead of two), with table entries of 64 bits each instead of 32, allowing these CPUs to directly access a physical address space larger than 4 gigabytes (232 bytes). The page table structure used by x86-64 CPUs when operating in long mode further extends the page table hierarchy to four or more levels, extending the virtual address space, and uses additional physical address bits at all levels of the page table, extending the physical address space. It also uses the topmost bit of the 64-bit page table entry as a no-execute or "NX" bit, indicating that code cannot be executed from the associated page. The NX feature is also available in protected mode when these CPUs are run ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium M (microarchitecture)
The P6 microarchitecture is the sixth-generation Intel x86 microarchitecture, implemented by the Pentium Pro microprocessor that was introduced in November 1995. It is frequently referred to as i686. It was planned to be succeeded by the NetBurst microarchitecture used by the Pentium 4 in 2000, but was revived for the Pentium M line of microprocessors. The successor to the Pentium M variant of the P6 microarchitecture is the Core microarchitecture which in turn is also derived from P6. P6 was used within Intel's mainstream offerings from the Pentium Pro to Pentium III, and was widely known for low power consumption, excellent integer performance, and relatively high instructions per cycle (IPC). The P6 core was the sixth generation Intel microprocessor in the x86 line. The first implementation of the P6 core was the Pentium Pro CPU in 1995, the immediate successor to the original Pentium design (P5). P6 processors dynamically translate IA-32 instructions into sequences of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Pentium 4 Processors
The Pentium 4 was a seventh-generation CPU from Intel targeted at the consumer and enterprise markets. It is based on the NetBurst microarchitecture. Desktop processors Pentium 4 Willamette (180 nm) * Intel Family 15 Model 1 * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2'' * Transistors: 42 million * Die size: 217 mm2 * Steppings: B2, C1, D0, E0 Northwood (130 nm) * Intel Family 15 Model 2 * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2'' * Model SL68R has box version only, supplied with unattached fan heatsink. * Transistors: 55 million * Die size: 146 mm2 (B0 pre-shrink) and 131 mm2 (B0 Shrink, C1, D1) * Steppings: B0, C1, D1, M0 Prescott (90 nm) * Intel Family 15 ''Model 3'' (C0, D0), Intel Family 15 ''Model 4'' (E0, G1) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3'' * ''Intel 64'': supported by 5x6, 511 and 519K * ''XD bit (an NX bit implementation)'': supported by 5x5J, 5x6, 511, 519J and 519K * Transistors: 125 million * Die size: 112 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Pentium Processors
The Intel Pentium brand was a line of mainstream x86-architecture microprocessors from Intel. Processors branded Pentium Processor with MMX Technology (and referred to as P5 (microarchitecture)#MMX, Pentium MMX for brevity) are also listed here. It was replaced by the Intel Processor brand in 2023. Desktop processors P5 based Pentiums "P5" (800 nm) * Based on P5 (microarchitecture), P5 * Stepping level, Steppings: B1, C1, D1 (Note: D1 stepping processors do not have FDIV bug) "P54C" (600 nm) * Based on P5 (microarchitecture), P5 microarchitecture * Steppings: B1, B3, B5, C2, E0 (Note: D1 stepping processors do not have FDIV bug) "P54CQS" (350 nm) * Based on P5 (microarchitecture), P5 microarchitecture "P54CS" (350 nm) * Based on P5 (microarchitecture), P5 microarchitecture "P55C" (350 nm) * Based on P5 (microarchitecture), P5 microarchitecture P6 based Pentiums Desktop processors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stepping (version Numbers)
Stepping may refer to: * Walking Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined as an " inverted pendulum" gait in which the body vaults o ..., one of the main gaits of locomotion among legged animals Computing * Stepping level, an aspect of microprocessor version designation * Stepping (debugging), a method of debugging Dance * Chicago stepping, a type of dance originating in Chicago * Step dance, generic term for dance styles where the footwork is the most important part of the dance * Stepping (African-American), a percussive dance in which the participant's entire body is used as an instrument * ''Steppin''', album by the Pointer Sisters See also * Step (other) * Stepping stone (other) * Mast Stepping {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NX Bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certain areas of the virtual address space as non-executable, preventing the processor from running any code stored there. This technique, known as executable space protection or Write XOR Execute, protects computers from malicious software that attempts to insert harmful code into another program’s data storage area and execute it, such as in a buffer overflow attack. The term "NX bit" was introduced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) as a marketing term. Intel markets this feature as the XD bit (execute disable), while the MIPS architecture refers to it as the XI bit (execute inhibit). In the ARM architecture, introduced in ARMv6, it is known as XN (execute never). The term NX bit is often used broadly to describe similar executable space p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dothan (microprocessor)
The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors (with the modified Intel P6 microarchitecture) introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Carmel notebook platform under the then new Centrino brand. The ''Pentium M'' processors had a maximum thermal design power (TDP) of 5–27 W depending on the model, and were intended for use in laptops (thus the "M" suffix standing for ''mobile''). They evolved from the core of the last Pentium III–branded CPU by adding the front-side bus (FSB) interface of Pentium 4, an improved instruction decoding and issuing front end, improved branch prediction, SSE2 support, and a much larger cache. The Pentium M replaced the laptop version of the Pentium 4 (the ''Pentium 4-Mobile'', or ''P4-M''), which suffered from power consumption and heat problems. The first Pentium M–branded CPU, code-named Banias, was followed by Dothan. The Pentium M line was removed from the official price lists in July 2009, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium M
The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors (with the modified Intel P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture) introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Centrino#Carmel platform (2003), Carmel notebook platform under the then new Centrino brand. The ''Pentium M'' processors had a maximum thermal design power (TDP) of 5–27 W depending on the model, and were intended for use in laptops (thus the "M" suffix standing for ''mobile''). They evolved from the core of the last Pentium III–branded CPU by adding the front-side bus (FSB) interface of Pentium 4, an improved instruction decoding and issuing front end, improved branch predictor, branch prediction, SSE2 support, and a much larger cache. The Pentium M replaced the laptop version of the Pentium 4 (the ''Pentium 4-Mobile'', or ''P4-M''), which suffered from power consumption and heat problems. The first Pentium M–branded CPU, code-named Banias, was followed by Dothan. The Pent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 479
Socket 479 (mPGA479M) is a CPU socket used by some Intel microprocessors. It is primarily known as the socket used by Pentium M and Celeron M mobile processors normally found in laptops, however the socket has also been used with Tualatin (microprocessor), Tualatin-M Mobile Celeron and Pentium III processors years before it. The official naming by Intel is μFCPGA and μPGA479M. Technical specifications Socket 479 has 479 pin holes. Pentium M processors in PGA package have 479 pins that plug into this zero insertion force socket. Only 478 pins are electrically connected (B2 is reserved and "depopulated on the Micro-FCPGA package"). Although mechanically similar, Socket 478 has one pin fewer, making it impossible to use a Pentium M processor in a Socket 478 board. For this reason, some manufacturers like Asus have made drop-in boards (e.g. CT-479) which allow the use of Socket 479 processors in Socket 478 boards. Conversely, it is impossible to use any Socket 478 desktop Celeron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
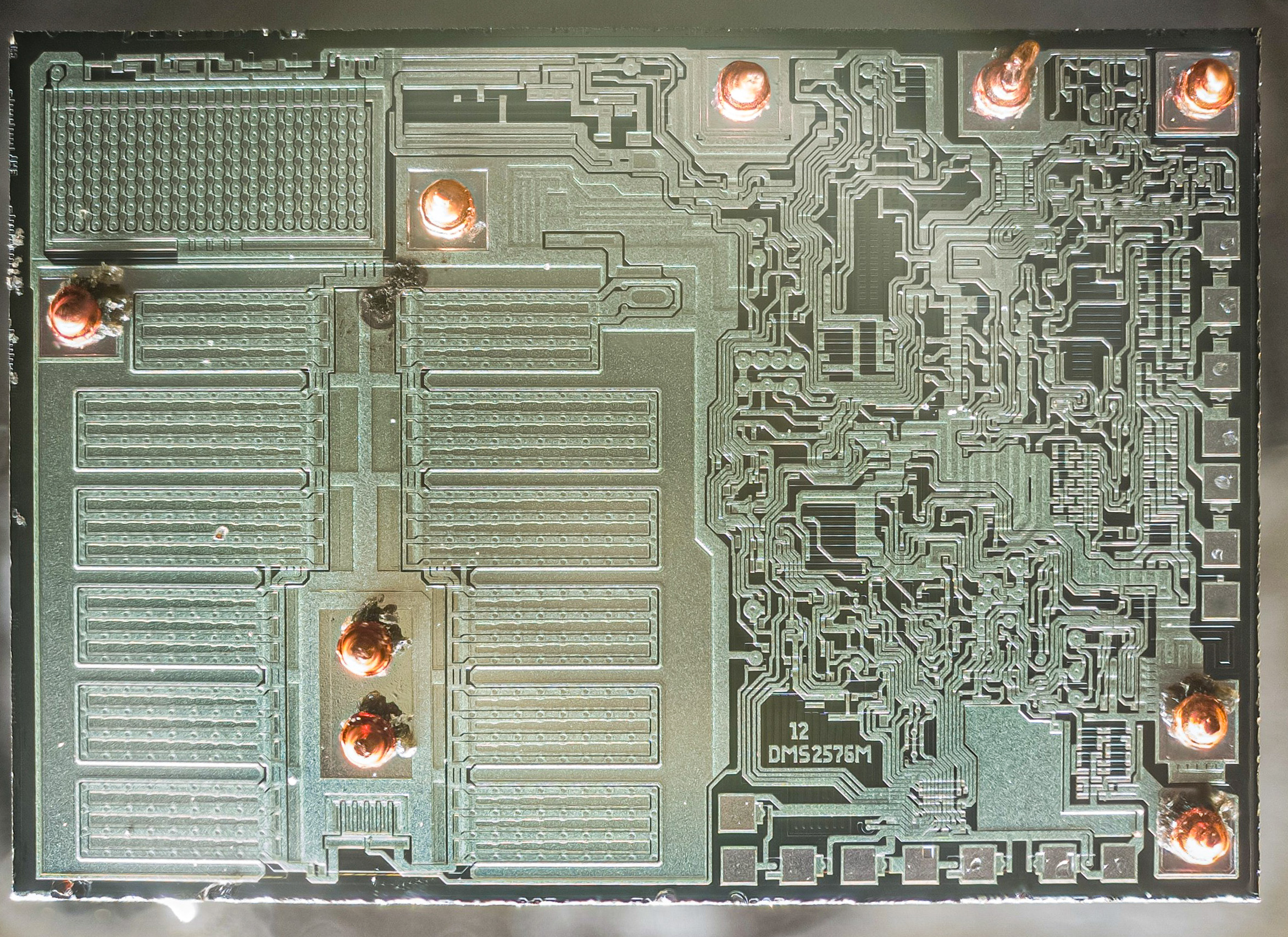
Die (integrated Circuit)
A die, in the context of integrated circuits, is a small block of semiconducting material on which a given functional circuit is Semiconductor fabrication, fabricated. Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer (electronics), wafer of electronic-grade Monocrystalline silicon, silicon (EGS) or other semiconductor (such as Gallium arsenide, GaAs) through processes such as photolithography. The wafer is cut (wafer dicing, diced) into many pieces, each containing one copy of the circuit. Each of these pieces is called a die. There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies,'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a printed circuit board, most dies are integrated circuit packaging, packaged in List of electronic component packaging types, various forms. Manufacturing process Most dies are composed of silicon and used for integrated circuits. The process begins with the production of Single crystal, monocrystalline sili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |