|
Liquid-crystal Polymer
Liquid crystal polymers (LCPs) are polymers with the property of liquid crystal, usually containing aromatic rings as mesogens. Despite uncrosslinked LCPs, polymeric materials like liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs) and liquid crystal networks (LCNs) can exhibit liquid crystallinity as well. They are both crosslinked LCPs but have different cross link density. They are widely used in the digital display market. In addition, LCPs have unique properties like thermal actuation, anisotropic swelling, and soft elasticity. Therefore, they can be good actuators and sensors. One of the most famous and classical applications for LCPs is Kevlar, a strong but light fiber with wide applications, notably bulletproof vests. Background Liquid crystallinity in polymers may occur either by dissolving a polymer in a solvent (lyotropic liquid-crystal polymers) or by heating a polymer above its glass or melting transition point (thermotropic liquid-crystal polymers). Liquid-crystal polymers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Gravity
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest (at ); for gases, the reference is air at room temperature (). The term "relative density" (abbreviated r.d. or RD) is preferred in SI, whereas the term "specific gravity" is gradually being abandoned. If a substance's relative density is less than 1 then it is less dense than the reference; if greater than 1 then it is denser than the reference. If the relative density is exactly 1 then the densities are equal; that is, equal volumes of the two substances have the same mass. If the reference material is water, then a substance with a relative density (or specific gravity) less than 1 will float in water. For example, an ice cube, with a relative density of about 0.91, will float. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermotropic
A liquid crystal phase is thermotropic if its order parameter is determined by temperature. At high temperatures, liquid crystals become an isotropic liquid and at low temperatures, they tend to glassify. In a thermotropic crystal, those phase transition In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic Sta ...s occur only at temperature extremes; the phase is insensitive to concentration. Most thermotropic liquid crystals are composed of rod-like molecules, and admit nematic, smectic, or cholesterolic phases. See also * Thermochromism * Thermotropic liquid crystals References * External links What are Liquid Crystals? Liquid crystals {{chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
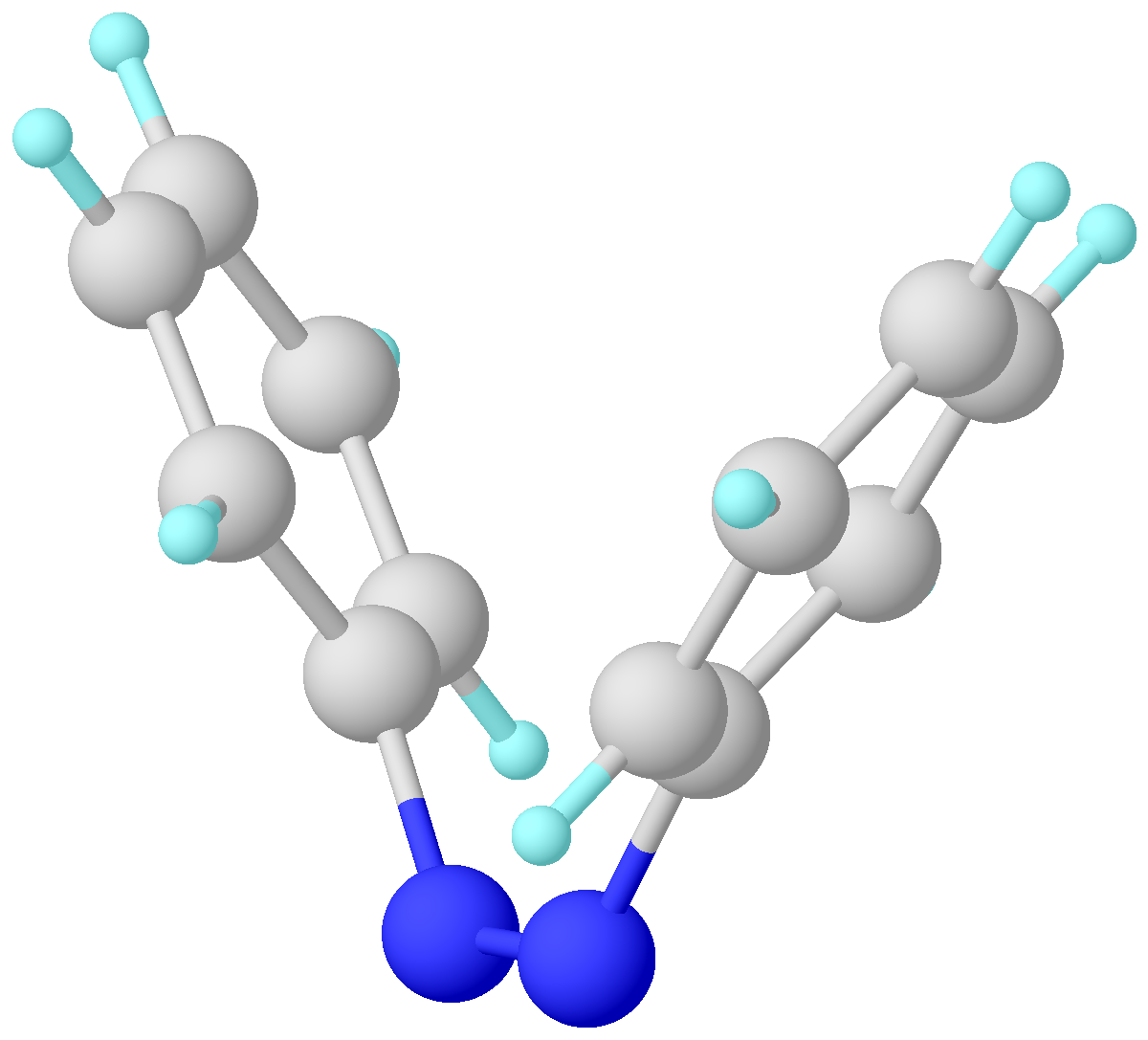
Azobenzene
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a azo compound, N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar Chemical compound, compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Different classes of azo dyes exist, most notably the ones substituted with heteroaryl rings. Structure and synthesis Azobenzene was first described by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1834. Yellowish-red crystalline flakes of azobenzene were obtained in 1856. Its original preparation is similar to the modern one. According to the 1856 method, nitrobenzene is reduced by iron filings in the presence of acetic acid. In the modern synthesis, zinc is the reductant in the presence of a base. Industrial electrosynthesis using nitrobenzene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit very different physical or mechanical properties when measured along different axes, e.g. absorbance, refractive index, conductivity, and tensile strength. An example of anisotropy is light coming through a polarizer. Another is wood, which is easier to split along its grain than across it because of the directional non-uniformity of the grain (the grain is the same in one direction, not all directions). Fields of interest Computer graphics In the field of computer graphics, an anisotropic surface changes in appearance as it rotates about its geometric normal, as is the case with velvet. Anisotropic filtering (AF) is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures on surfaces that are far away and viewed at a shallow angle. Older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomers
A monomer ( ; ''wikt:mono-, mono-'', "one" + ''wikt:-mer, -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can chemical reaction, react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Chemistry classifies monomers by type, and two broad classes based on the type of polymer they form. By type: * natural vs synthetic, e.g. glycine vs caprolactam, respectively * polar vs nonpolar, e.g. vinyl acetate vs ethylene, respectively * cyclic vs linear, e.g. ethylene oxide vs ethylene glycol, respectively By type of polymer they form: * those that participate in condensation polymerization * those that participate in addition polymerization Differing stoichiometry causes each class to create its respective form of polymer. : The polymerization of one kind of monomer gives a polymer#Monomers and repeat units, homopolymer. Many polymers are copolymers, meaning that they are derived from two diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Transition
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and Reversible reaction, reversible transition in amorphous solid, amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within Crystallinity, semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rubbery state as the temperature is increased. International Organization for Standardization, ISO 11357-2: Plastics – Differential scanning calorimetry – Part 2: Determination of glass transition temperature (1999). An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. The reverse transition, achieved by supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state, is called vitrification. The glass-transition temperature ''T''g of a material characterizes the range of temperatures over which this glass transition occurs (as an experimental definition, typically marked as 100 s of relaxation time). It is always lower than the melting point, melting temperature, ''T''m, of the cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micelle
A micelle () or micella () ( or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension (also known as associated colloidal system). A typical micelle in water forms an aggregate, with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the micelle centre. This phase is caused by the packing behavior of single-tail lipids in a bilayer. The difficulty in filling the volume of the interior of a bilayer, while accommodating the area per head group forced on the molecule by the hydration of the lipid head group, leads to the formation of the micelle. This type of micelle is known as a normal-phase micelle (or oil-in-water micelle). Inverse micelles have the head groups at the centre with the tails extending out (or water-in-oil micelle). Micelles are approximately spherical in shape. Other shapes, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer Solution
Polymer solutions are solutions containing dissolved polymers. These may be (e.g. in ), or solid solutions (e.g. a substance which has been plasticized). The introduction into the polymer of small amounts of a solvent (plasticizer) reduces the temperature of glass transition, the yield temperature, and the viscosity of a melt. An understanding of the thermodynamics of a polymer solution is critical to prediction of its behavior in manufacturing processes — for example, its shrinkage or expansion in injection molding processes, or whether pigments and solvents will mix evenly with a polymer in the manufacture of paints and coatings. A recent theory on the viscosity of polymer solutions gives a physical explanation for various well-known empirical relations and numerical values including the Huggins constant, but reveals also novel simple concentration and molar mass dependence. Applications Polymer solutions are used in producing fibers, films, glues, lacquers, paints, and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyotropic
Lyotropic liquid crystals result when amphiphiles, which are both hydrophobic and hydrophilic, dissolve into a solution that behaves both like a liquid and a solid crystal. This liquid crystalline mesophase includes everyday mixtures like soap and water. The term ' comes . Historically, the term was used to describe the common behavior of materials composed of amphiphilic molecules upon the addition of a solvent. Such molecules comprise a hydrophilic (literally 'water-loving') head- group (which may be ionic or non-ionic) attached to a hydrophobic ('water-hating') group. The micro-phase segregation of two incompatible components on a nanometer scale results in different type of solvent-induced extended anisotropic arrangement, depending on the volume balances between the hydrophilic part and hydrophobic part. In turn, they generate the long-range order of the phases, with the solvent molecules filling the space around the compounds to provide fluidity to the system. In con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCP Structure
LCP may refer to: Science, medicine and technology *Large Combustion Plant, see Large Combustion Plant Directive *Le Chatelier's principle, equilibrium law in chemistry *Left Circular polarization, in radio communications * Legg–Calvé–Perthes syndrome, hip disorder *Licensed Clinical Psychologist, see Clinical psychology * Ligand close packing theory, in chemistry * Light compensation point, in biology *Linear complementarity problem, in mathematical optimisation *Link Control Protocol, in computer networking *Liquid Crystal Polymer, a kind of polymer *Liverpool Care Pathway for the Dying Patient, care guidance for dying hospital patients * Living cationic polymerization, a process in chemistry * Locking Compression Plate, an implant aiding the healing of a bone fracture * Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid * Longest Common Prefix array, in computer science Organisations * Latvijas Centrālās Padomes, Latvian Central Council *Lebanese Communist Party *Liberal and Country Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesteric Liquid Crystal
Cholesteric liquid crystals (ChLCs), also known as chiral nematic liquid crystals, are a Supramolecular chemistry, supramolecular assembly and a subclass of liquid crystal characterized by their chirality. Contrary to achiral liquid crystals, the common orientational direction of ChLCs (known as the director) is arranged in a helix whose axis of rotation is perpendicular to the director in each layer. ChLCs can be Thermotropic crystal, thermotropic and Lyotropic liquid crystal, lyotropic. ChLCs are formed from a variety of Anisotropy, anisotropic molecules, including chiral small molecules and Polymer, polymers. ChLCs can be also formed by introducing a chiral dopant at low concentrations into achiral liquid crystalline phases. Examples of ChLCs range from Scarabaeidae, scarab beetle shells to liquid crystal displays. Many natural molecules and polymers spontaneously form the cholesteric phase. ChLCs have been used to manufacture products ranging from Smart material, smart Paint, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |