|
Likelihood Ratios In Diagnostic Testing
In evidence-based medicine, likelihood ratios are used for assessing the value of performing a diagnostic test. They combine sensitivity and specificity into a single metric that indicates how much a test result shifts the probability that a condition (such as a disease) is present. The first description of the use of likelihood ratios for decision rules was made at a symposium on information theory in 1954. In medicine, likelihood ratios were introduced between 1975 and 1980.. There is a multiclass version of these likelihood ratios. Calculation Two versions of the likelihood ratio exist, one for positive and one for negative test results. Respectively, they are known as the (LR+, likelihood ratio positive, likelihood ratio for positive results) and (LR–, likelihood ratio negative, likelihood ratio for negative results). The positive likelihood ratio is calculated as : \text+ = \frac which is equivalent to : \text+ = \frac or "the probability of a person who has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evidence-based Medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research." The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of the patient, and the best available scientific information to guide decision-making about clinical management. The term was originally used to describe an approach to teaching the practice of medicine and improving decisions by individual physicians about individual patients. The EBM Pyramid is a tool that helps in visualizing the hierarchy of evidence in medicine, from least authoritative, like expert opinions, to most authoritative, like systematic reviews. Adoption of evidence-based medicine is necessary in a human Rights-based approach to development, rights-based approach to public health and a precondition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity (tests)
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Statistics
Medical statistics (also health statistics) deals with applications of statistics to medicine and the health sciences, including epidemiology, public health, forensic medicine, and clinical research. Medical statistics has been a recognized branch of statistics in the United Kingdom for more than 40 years, but the term has not come into general use in North America, where the wider term 'biostatistics' is more commonly used.Dodge, Y. (2003) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', OUP. However, "biostatistics" more commonly connotes all applications of statistics to biology. Medical statistics is a subdiscipline of statistics. It is the science of summarizing, collecting, presenting and interpreting data in medical practice, and using them to estimate the magnitude of associations and test hypotheses. It has a central role in medical investigations. It not only provides a way of organizing information on a wider and more formal basis than relying on the exchange of anecdot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Predictive Value
The positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV respectively) are the proportions of positive and negative results in statistics and diagnostic tests that are true positive and true negative results, respectively. The PPV and NPV describe the performance of a diagnostic test or other statistical measure. A high result can be interpreted as indicating the accuracy of such a statistic. The PPV and NPV are not intrinsic to the test (as true positive rate and true negative rate are); they depend also on the prevalence. Both PPV and NPV can be derived using Bayes' theorem. Although sometimes used synonymously, a ''positive predictive value'' generally refers to what is established by control groups, while a post-test probability refers to a probability for an individual. Still, if the individual's pre-test probability of the target condition is the same as the prevalence in the control group used to establish the positive predictive value, the two are numerically equal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre- And Post-test Probabilities
Pre-test probability and post-test probability (alternatively spelled pretest and posttest probability) are the probabilities of the presence of a condition (such as a disease) before and after a diagnostic test, respectively. ''Post-test probability'', in turn, can be ''positive'' or ''negative'', depending on whether the test falls out as a positive test, positive test or a negative test, respectively. In some cases, it is used for the probability of developing the condition of interest in the future. Test, in this sense, can refer to any medical test (but usually in the sense of diagnostic tests), and in a broad sense also including questions and even assumptions (such as assuming that the target individual is a female or male). The ability to make a difference between pre- and post-test probabilities of various conditions is a major factor in the Medical test#Indications, indication of medical tests. Pre-test probability The pre-test probability of an individual can be chosen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flank (anatomy)
The flank or latus is the side of the body between the rib cage and the iliac bone of the hip (below the rib cage and above the ilium). It is sometimes called the lumbar In tetrapod anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum. Naming and location The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lowe ... region. References Abdomen {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
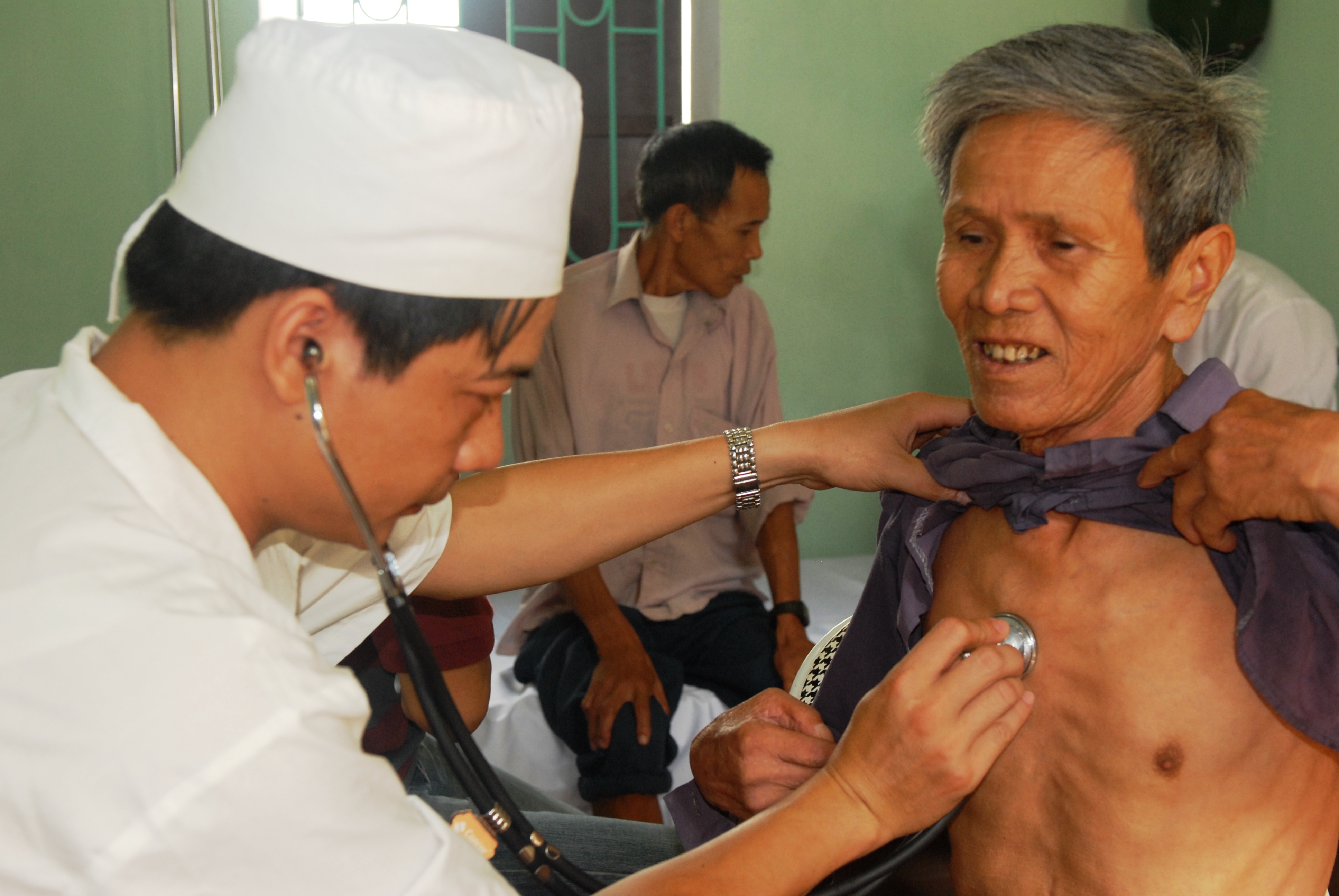
Physical Exam
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, a physical therapist, ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascites
Ascites (; , meaning "bag" or "sac") is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In the developed world, the most common cause is liver cirrhosis. Other causes include cancer, heart failure, tuberculosis, pancreatitis, and blockage of the hepatic vein. In cirrhosis, the underlying mechanism involves high blood pressure in the portal system and dysfunction of blood vessels. Diagnosis is typically based on an examination together with ultrasound or a CT scan. Testing the fluid can help in determining the underlying cause. Treatment often involves a low-salt diet, medication such as diuretics, and draining the fluid. A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Distension
Abdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. People with this condition often describe it as "feeling bloated". Affected people often experience a sensation of fullness, abdominal pressure, and sometimes nausea, pain, or cramping. In the most extreme cases, upward pressure on the diaphragm and lungs can also cause shortness of breath. Through a variety of causes (see below), bloating is most commonly due to a build up of gas in the stomach, small intestine, or colon. The pressure sensation is often relieved, or at least lessened, by belching or flatulence. Medications that settle gas in the stomach and intestines are also commonly used to treat the discomfort and lessen the abdominal distension. Causes One of the causes of abnormal bloating is excessive eating and air swallowing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specificity (tests)
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomized Controlled Trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures, diets or other medical treatments. Participants who enroll in RCTs differ from one another in known and unknown ways that can influence study outcomes, and yet cannot be directly controlled. By randomly allocating participants among compared treatments, an RCT enables ''statistical control'' over these influences. Provided it is designed well, conducted properly, and enrolls enough participants, an RCT may achieve sufficient control over these confounding factors to deliver a useful comparison of the treatments studied. Definition and examples An RCT in clinical research typically compares a proposed new treatment against an existing standard of care; these are then termed the 'expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |