|
Life Expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where ''e''x denotes the average life remaining at age ''x''). This can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth Cohort (statistics), cohort (in this case, all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. Human remains from the early Bronze Age indicate an LEB of 24. In 2019, world LEB was 73.3. A combination of high infant mortality and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longevity
Longevity may refer to especially long-lived members of a population, whereas ''life expectancy'' is defined Statistics, statistically as the average number of years remaining at a given age. For example, a population's life expectancy at birth is the same as the average age at death for all people born in the same year (in the case of Cohort (statistics), cohorts). Longevity studies may involve putative methods to extend life. Longevity has been a topic not only for the scientific community but also for writers of Hyperborei, travel, science fiction, and utopian novels. The legendary fountain of youth appeared in the work of the Ancient Greek historian Herodotus. There are difficulties in authenticating the longest human maximum life span, life span, owing to inaccurate or incomplete birth statistics. Fiction, legend, and folklore have proposed or claimed life spans in the past or future vastly longer than those verified by modern standards, and longevity narratives and unverif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
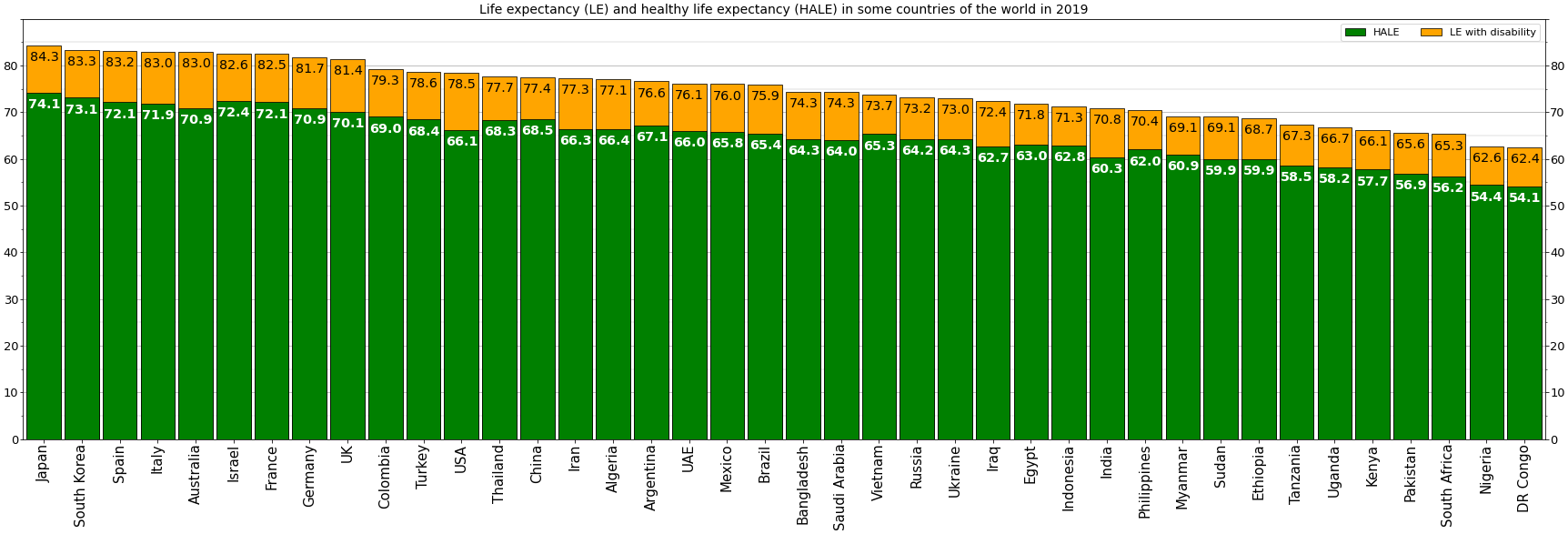
Healthy Life Expectancy Bar Chart -world
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, pain (including mental pain), or injury. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise and adequate sleep, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive Stress (biology), stress. Some factors affecting health are due to Agency (sociology), individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, while others are due to Social structure, structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still, other factors are beyond both individual and group choices, such as genetic disorders. History The meaning of health has evolved over time. In k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance (ecology), abundance, biomass (ecology), biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; ecological succession, successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopedia, online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest-running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, in three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size; the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810), it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent contributors, and the 9th (1875–1889) and Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 11th editions (1911) are landmark encyclopaedias for scholarship and literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Daily
''ScienceDaily'' is an American website launched in 1995 that aggregates press releases and publishes lightly edited press releases (a practice called churnalism) about science, similar to Phys.org and EurekAlert!. History The site was founded by married couple Dan and Michele Hogan in 1995; Dan Hogan formerly worked in the public affairs department of Jackson Laboratory writing press releases. The site makes money from selling advertisements. the site said that it had grown "from a two-person operation to a full-fledged news business with worldwide contributors". At the time, it was run out of the Hogans' home, had no reporters, and only reprinted press releases. In 2012, Quantcast ranked it at 614 with 2.6 million U.S. visitors. Sections As of August 2023, ''ScienceDaily'' mainly has five sections, Health, Tech, Enviro, Society, and Quirky, the last of which includes the top news. References External links * Alexa - ScienceDaily��{{Webarchive, url=https://web.a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Life Span
Maximum life span (or, for humans, maximum reported age at death) is a measure of the maximum amount of time one or more members of a population have been observed to survive between birth and death. The term can also denote an estimate of the maximum amount of time that a member of a given species could survive between birth and death, provided circumstances that are optimal to that member's longevity. Most living species have an upper limit on the number of times somatic cells not expressing telomerase can divide. This is called the Hayflick limit, although this number of cell divisions does not strictly control lifespan. Definition In animal studies, maximum span is often taken to be the mean life span of the most long-lived 10% of a given cohort. By another definition, however, maximum life span corresponds to the age at which the oldest known member of a species or experimental group has died. Calculation of the maximum life span in the latter sense depends upon the init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeanne Calment
Jeanne Louise Calment (; 21 February 1875 – 4 August 1997) was a French supercentenarian. With a documented lifespan of 122 years and 164 days, she was the oldest people, oldest person in history whose age has been verified. Her longevity attracted media attention and medical studies of her health and lifestyle. Calment is the only person in history who has been verified to have reached the age of 120. According to census records, Calment outlived both her daughter and her grandson. In January 1988, she was widely reported to be the oldest living person in the world. In 1995, at age 120, she was declared to be the oldest person in history with a verified date of birth. Early life Calment was born on 21 February 1875 in Arles, Bouches-du-Rhône, Provence. Some of her close family members also had above-average lifespans. Her older brother, François (1865–1962), lived to the age of 97; her father, Nicolas (1837–1931), who was a shipbuilding, shipbuilder, lived to be 93 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldest People
The following are tables of the oldest people in the world in ordinal ranks. To avoid including false or unconfirmed claims of old age, names here are restricted to those people whose ages have been validated by an international body dealing in longevity research, such as the Gerontology Research Group, LongeviQuest, or ''Guinness World Records'', and others who have otherwise been reliably sourced. The longest documented and verified human lifespan is that of Jeanne Calment of France (1875–1997), a woman who lived to the age of 122 years and 164 days. As women live longer than men on average, women predominate in combined records. The longest lifespan for a man is that of Jiroemon Kimura of Japan (1897–2013), who lived to the age of 116 years and 54 days. The oldest living person in the world whose age has been validated is Ethel Caterham of the United Kingdom, who has lived . She was born on 21 August 1909. The oldest living verified man is João Marinho Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riverhead Books
Riverhead Books is an imprint of Penguin Group (USA) founded in 1994 by Susan Petersen Kennedy. Writers published by Riverhead include Ali Sethi, Marlon James, Junot Díaz, George Saunders, Khaled Hosseini, Nick Hornby, Anne Lamott, Carlo Rovelli, Randall Munroe, Patricia Lockwood, Sarah Vowell, the Dalai Lama, Chang-rae Lee, Meg Wolitzer, Dinaw Mengestu, Daniel Alarcón, Daniel H. Pink, Steven Johnson, Jon Ronson, Ellen Burstyn, Elizabeth Gilbert, James McBride, Jing Tsu, C Pam Zhang, Garrard Conley and Nicholas Binge. Authors published by Riverhead won the Dayton Literary Peace Prize [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodewijck Huygens
Lodewijck Huygens (13 March 1631 – 1 July 1699) was a Dutch diplomat. Life Huyghens was the third son of the diplomat Constantijn Huygens and Suzanna van Baerle. His two older brothers were Constantijn Huygens, Jr. and the scientist Christiaan Huygens. He was admitted to the Orange College of Breda in 1649, but in 1651 got into trouble for fighting a duel. Soon after this he was sent on a diplomatic mission to England. Starting in 1669, Huygens and his brother Christiaan did some of the earliest work on life expectancy based on death statistics in London published by John Graunt. In 1672 the newly appointed Stadtholder William III of Orange, later King William III of England and Ireland and William II of Scotland, appointed Huygens as sheriff of Gorinchem. His actions as sheriff eventually resulted in considerable strife between local factions, whereby Huygens was faced with a formidable opponent, Jacob van der Ulft. Accusations of corruption against Huygens eventually resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution. In physics, Huygens made seminal contributions to optics and mechanics, while as an astronomer he studied the rings of Saturn and discovered its largest moon, Titan (moon), Titan. As an engineer and inventor, he improved the design of telescopes and invented the pendulum clock, the most accurate timekeeper for almost 300 years. A talented mathematician and physicist, his works contain the first idealization of a physical problem by a set of Mathematical model, mathematical parameters, and the first mathematical and mechanistic explanation of an unobservable physical phenomenon.Dijksterhuis, F.J. (2008) Stevin, Huygens and the Dutch republic. ''Nieuw archief voor wiskunde'', ''5'', pp. 100–10/ref> Huygens first identified the correct la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Graunt
John Graunt (24 April 1620 – 18 April 1674) has been regarded as the founder of demography. Graunt was one of the first demographers, and perhaps the first epidemiologist, though by profession he was a haberdasher. He was bankrupted later in life by losses suffered during Great Fire of London and the discrimination he faced following his conversion to Catholicism. Biography Born in London, John Graunt was the eldest of the seven or eight children of Henry and Mary Graunt. Graunt's father was a draper who had moved to London from Hampshire. In February 1641, Graunt married Mary Scott, with whom he had one son (Henry) and three daughters. He became a freeman of the Drapers' Company at age 21. Graunt worked in his father's shop until his father died in 1662, and Graunt became influential in the City. He was able to secure the post of professor of music for his friend William Petty in 1650. He served in various ward offices in Cornhill ward, becoming a common councilman about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |