|
Lexell's Comet
D/1770 L1, popularly known as Lexell's Comet after its orbit computer Anders Johan Lexell, was a comet discovered by astronomer Charles Messier in June 1770.Other comets named after their orbit computer, rather than discoverer, are 27P/Crommelin, 2P/Encke and 1P/Halley – Halley's Comet. It is notable for having passed closer to Earth than any other comet in recorded history, approaching to a distance of only ,Kronk, G. Cometography: D/1770 L1 (Lexell)', accessed November 20, 2008.Kronk, G. ', accessed November 20, 20, 2008. It was thought that C/1491 B1 may have approached even closer on February 20, 1491, but its orbit was retracted in 2002 due to a misunderstanding of the records. SeApproximate Orbits of Ancient and Medieval Comets: 3. Remarks and Discussion/ref> or six times the distance from the Earth to the Moon. The comet has not been seen since 1770 and is considered a lost comet. Lexell's Comet's 1770 passing still holds the record of closest observed approach of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects'', referred to with the letter M and their number between 1 and 110. Messier's purpose for list of Messier objects, the catalogue was to help astronomical observers distinguish between permanent and transient astronomical event, transient visually diffuse astronomical object, objects in the sky. Biography Messier was born in Badonviller in the Lorraine region of Kingdom of France, France, in 1730, the tenth of twelve children of Françoise B. Grandblaise and Nicolas Messier, a Court usher. Six of his brothers and sisters died while young, and his father died in 1741. Charles' interest in astronomy was stimulated by the appearance of the Great Comet of 1744, great six-tailed comet in 1744 and by an annular solar eclipse visible from his hometown on 25 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet is the only known List of periodic comets, short-period comet that is consistently visible to the naked eye from Earth, appearing every 72–80 years, though with the majority of recorded apparitions (25 of 30) occurring after 75–77 years. It last appeared in the inner parts of the Solar System in 1986 and will next appear in mid-2061. Officially designated 1P/Halley, it is also commonly called Comet Halley, or sometimes simply Halley. Halley's periodic returns to the inner Solar System have been observed and recorded by astronomers around the world since at least 240 BC, but it was not until 1705 that the English astronomer Edmond Halley understood that these appearances were re-appearances of the same comet. As a result of this discovery, the comet is named after Halley. During its 1986 visit to the inner Solar System, Halley's Comet became the first comet to be observed in detail by a spacecraft, ''Giotto (spacecraft), Giotto'', providing the first obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the sightline, line of sight to the observer. Unless stated otherwise, the word ''magnitude'' in astronomy usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale likely dates to before the ancient Ancient Greek astronomy#Astronomy in the Greco-Roman and Late Antique eras, Roman astronomer Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy, whose Star catalogue, star catalog popularized the system by listing stars from First-magnitude star, 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined to closely match this historical system by Norman Robert Pogson, Norman Pogson in 1856. The scale is reverse logarithmic scale, logarithmic: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth's circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (abbreviated as arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a minute of arc, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal (base 60) subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma (cometary)
The coma is the nebulous envelope around the nucleus of a comet, formed when the comet passes near the Sun in its highly elliptical orbit. As the comet warms, parts of it sublimate; this gives a comet a diffuse appearance when viewed through telescopes and distinguishes it from stars. The word ''coma'' comes from the Greek (), which means "hair" and is the origin of the word ''comet'' itself. The coma is generally made of ice and comet dust. Water composes up to 90% of the volatiles that outflow from the nucleus when the comet is within from the Sun. The H2O parent molecule is destroyed primarily through photodissociation and to a much smaller extent photoionization. The solar wind plays a minor role in the destruction of water compared to photochemistry. Larger dust particles are left along the comet's orbital path while smaller particles are pushed away from the Sun into the comet's tail by light pressure. On 11 August 2014, astronomers released studies, using the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
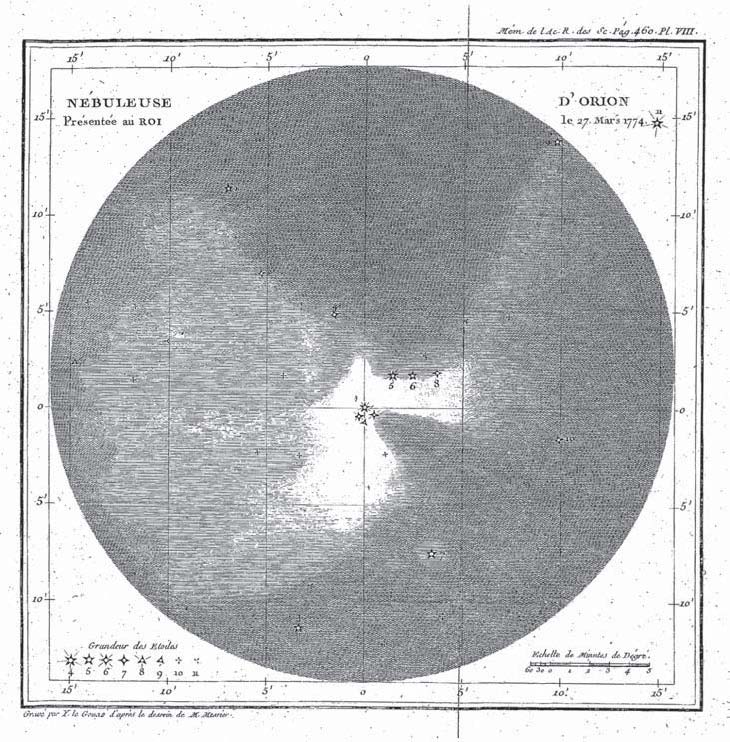
Nebulae
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space surrounding them, most nebulae are far less dense th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
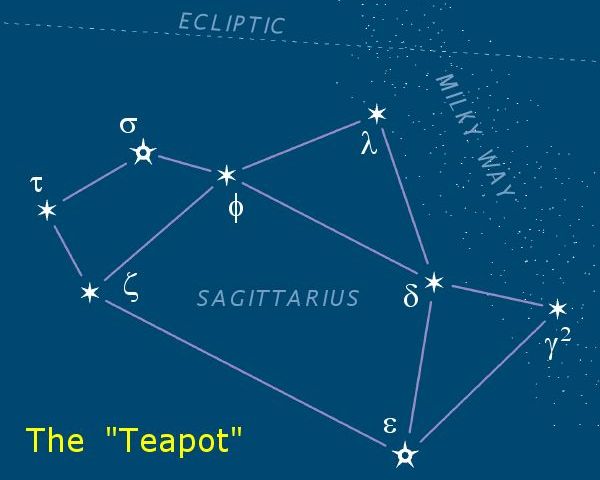
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its old astronomical symbol is (♐︎). Its name is Latin for "archery, archer". Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of Sagittarius (see Sagittarius A). Visualizations As seen from the northern hemisphere, the constellation's brighter stars form an easily recognizable asterism (astronomy), asterism known as "the Teapot". The stars Delta Sagittarii, δ Sgr (Kaus Media), Epsilon Sagittarii, ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), Zeta Sagittarii, ζ Sgr (Ascella), and Phi Sagittarii, φ Sgr form the body of the pot; Lambda Sagittarii, λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the point of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P/1999 J6 (SOHO)
P/1999 J6 (SOHO) is a small comet, notable for being among those that made a close approach to the Earth. It was first observed by the space-based Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) on 10 May 1995. It is next expected to come to perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) in June 2026 at . The most notable Earth approach was on June 12, 1999 when it passed between to from Earth. The uncertainty is a result of the large number of observations at roughly the same time as there were around 50 observations on April 19, 2010. The discovery was made on March 20, 2000, during a review of previously captured images. It next came to perihelion in November 2004, when it was known as "C/2004 V9", and then on April 19, 2010 when it was known as "C/2010 H3". On August 15, 2015 it should have been 0.56 AU from Earth. See also * 55P/Tempel–Tuttle * 109P/Swift–Tuttle * 460P/PANSTARRS * D/1770 L1 (Lexell) D/1770 L1, popularly known as Lexell's Comet after its orbit compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Comet
A lost comet is one which was not detected during its most recent perihelion passage. This generally happens when data is insufficient to reliably calculate the comet's location or if the solar elongation is unfavorable near perihelion passage. The ''D/'' designation is used for a periodic comet that no longer exists or is deemed to have disappeared. Lost comets can be compared to lost asteroids ( lost minor planets), although calculation of comet orbits differs because of nongravitational forces, such as emission of jets of gas from the nucleus. Some astronomers have specialized in this area, such as Brian G. Marsden, who successfully predicted the 1992 return of the once-lost periodic comet Swift–Tuttle. Overview Loss There are a number of reasons why a comet might be missed by astronomers during subsequent apparitions. Firstly, cometary orbits may be perturbed by interaction with the giant planets, such as Jupiter. This, along with nongravitational forces, can resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
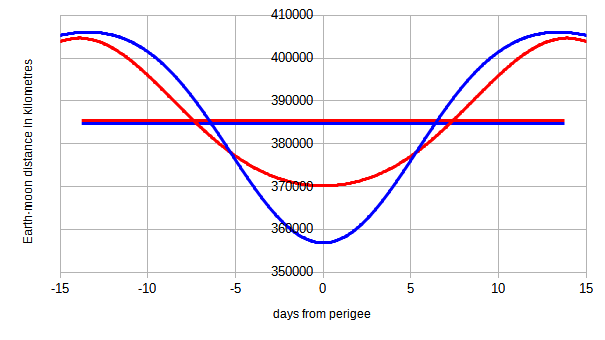
Lunar Distance (astronomy)
The instantaneous Earth–Moon distance, or distance to the Moon, is the distance from the center of Earth to the center of the Moon. In contrast, the Lunar distance (LD or \Delta_), or Earth–Moon characteristic distance, is a unit of measure in astronomy. More technically, it is the semi-major axis of the geocentric orbit of the Moon, lunar orbit. The average lunar distance is approximately , or 1.3 light-seconds. It is roughly 30 times Earth radius, Earth's diameter and a non-stop plane flight traveling that distance would take more than two weeks. Around 389 lunar distances make up an astronomical unit (roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun). Lunar distance is commonly used to express the distance to near-Earth object encounters. Lunar semi-major axis is an important astronomical datum. It has implications for testing gravitational theories such as general relativity and for refining other astronomical values, such as the Earth mass, mass, Earth radius, radius, and Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |