|
Levant Sparrowhawk
The Levant sparrowhawk (''Tachyspiza brevipes'') is a small bird of prey. It measures in length with a wingspan of . The female is larger than the male, but the difference is not as marked as with Eurasian sparrowhawk. The adult male is blue-grey above, with dark wingtips, and barred reddish below. It breeds in forests from Greece and the Balkans east to southern Russia. It is migratory, wintering from Egypt across to southwestern Iran. It will migrate in large flocks, unlike the more widespread Eurasian sparrowhawk. Taxonomy The Levant sparrowhawk was formally described in 1850 by the Russian naturalist Nikolai Severtzov under the binomial name ''Astur brevipes''. The species was formerly placed in the large and diverse genus '' Accipiter''. In 2024 a comprehensive molecular phylogenetic study of the Accipitridae confirmed earlier work that had shown that the genus was polyphyletic. To resolve the non-monophyly, ''Accipiter'' was divided into six genera. The genus '' Tachysp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Alekseevich Severtzov
Nikolai Alekseyevich Severtsov (; 5 November 1827 – 7 February 1885) was a Russian Exploration, explorer and natural history, naturalist. He was among the early promoters of Darwinian ideas in Russia. Life and work Severtsov was born in Khvoshchevatovo, Zemlyansky district, Voronezh, where his father Aleksey Petrovich was a retired guard officer who had served in the Patriotic War of 1812, losing an arm in the Battle of Borodino. He had become interested in natural history after reading Buffon's work as a child and going out on hunts. and studied at the Moscow University where he was influenced by Karl Rouillier who considered what Haeckel called as ecology as "general zoology". His master's dissertation was on the seasonal life of animals in Voronezh province. At the age of eighteen he came into contact with Grigory Karelin and took an interest in central Asia. In 1855 he applied for an associate professor position but failed to be appointed. In 1857, he joined a mission t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Jakob Kaup
Johann Jakob von Kaup (10 April 1803 – 4 July 1873) was a German naturalist. A proponent of natural philosophy, he believed in an innate mathematical order in nature and he attempted biological classifications based on the Quinarian system. Kaup is also known for having coined popular prehistoric taxa like ''Pterosauria'', ''Machairodus'', ''Deinotherium'', ''Dorcatherium'', and ''Chalicotherium''. Biography He was born at Darmstadt. After studying at Göttingen and Heidelberg he spent two years at Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie, Leiden, where his attention was specially devoted to the amphibians and fishes. He then returned to Darmstadt as an assistant in the grand ducal museum, of which in 1840 he became inspector. In 1829 he published ''Skizze zur Entwickelungsgeschichte der europäischen Thierwelt'', in which he regarded the animal world as developed from lower to higher forms, from the amphibians through the birds to the beasts of prey; but subsequently he repudiated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
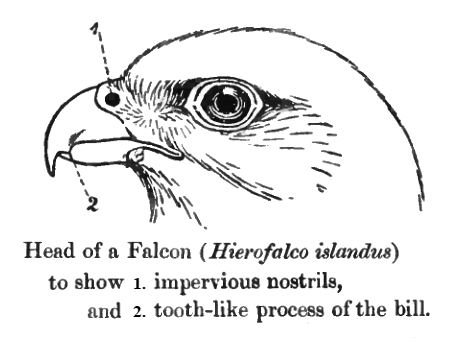
Falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Some small species of falcons with long, narrow wings are called hobbies, and some that hover while hunting are called kestrels. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broadwing. This makes flying easier while still learning the aerial skills required to be effective hunters like the adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which also includes two other subfamilies comprising caracaras and a few other species of "falcons". All these birds kill prey with their beaks, using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Of Prey
Birds of prey or predatory birds, also known as (although not the same as) raptors, are hypercarnivorous bird species that actively predation, hunt and feed on other vertebrates (mainly mammals, reptiles and smaller birds). In addition to speed and strength, these predators have bird vision, keen eyesight for detecting prey from a distance or during flight, strong feet with sharp talon (anatomy), talons for grasping or killing prey, and powerful, curved beaks for tearing off flesh. Although predatory birds primarily hunt live prey, many species (such as fish eagles, vultures and condors) also scavenge and eat carrion. Although the term "bird of prey" could theoretically be taken to include all birds that actively hunt and eat other animals, ornithologists typically use the narrower definition followed in this page, excluding many piscivorous predators such as storks, Crane (bird), cranes, herons, gulls, skuas, penguins, and kingfishers, as well as many primarily insectivorous bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accipiter Brevipes, Nestos River, Topiros, Greece 3
''Accipiter'' () is a genus of birds of prey in the family Accipitridae. Some species are called sparrowhawks, but there are many sparrowhawks in other genera such as '' Tachyspiza''. These birds are slender with short, broad, rounded wings and a long tail which helps them maneuver in flight. They have long legs and long, sharp talons used to kill their prey, and a sharp, hooked bill used in feeding. Females tend to be larger than males. They often ambush their prey, mainly small birds and mammals, capturing them after a short chase. The typical flight pattern is a series of flaps followed by a short glide. They are commonly found in wooded or shrubby areas. The genus ''Accipiter'' was introduced by the French zoologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson in 1760. The type species is the Eurasian sparrowhawk (''Accipiter nisus''). The name is Latin for "hawk", from ''accipere'', "to grasp". Procoracoid foramen The procoracoid foramen (or coracoid foramen, coracoid fenestra) is a hole th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific name, infraspecific ranks, such as variety (botany), variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes, bacterial nomenclature and virus clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid (biology)
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different varieties, subspecies, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Generally, it means that each cell has genetic material from two different organisms, whereas an individual where some cells are derived from a different organism is called a chimera. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents such as in blending inheritance (a now discredited theory in modern genetics by particulate inheritance), but can show hybrid vigor, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosomes. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species are. Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridization, which include genetic and morph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Group
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each other, further blurring any distinctions. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two (or more) species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use. Two or more taxa that were once considered conspecific (of the same species) may later be subdivided into infraspecific taxa (taxa within a species, such as plant variety (botany), varieties), which may be a complex ranking but it is not a species complex. In most cases, a specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicobar Sparrowhawk
The Nicobar sparrowhawk (''Tachyspiza butleri'') is a species of bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It is endemic to the Nicobar Islands of India. There are two subspecies, the nominate race which is found on Car Nicobar in the north of the archipelago, and ''T. b. obsoleta'', from Katchal and Camorta in the central part of the Nicobars. A museum specimen originally attributed to this species from the island of Great Nicobar was later found to be a misidentified Besra. This species was formerly placed in the genus '' Accipiter''. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease .... References External links BirdLife Species Factsheet. Nicobar sparrowhawk Birds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Sparrowhawk
The Chinese sparrowhawk (''Tachyspiza soloensis'') is a bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. This species was formerly placed in the genus '' Accipiter''. Taxonomy The Chinese sparrowhawk was formally described in 1821 by the American naturalist Thomas Horsfield under the binomial name ''Falco soloensis''. Horsfield designated the type locality as the Solo River, on the Indonesian island of Java. This species was formerly placed in the large and diverse genus '' Accipiter''. In 2024 a comprehensive molecular phylogenetic study of the Accipitridae confirmed earlier work that had shown that the genus was polyphyletic. To resolve the non-monophyly, ''Accipiter'' was divided into six genera. The genus '' Tachyspiza'' was resurrected to accommodate the Chinese sparrowhawk and 26 other species that had previously been placed in ''Accipiter''. The resurrected genus had been introduced in 1844 by the German naturalist Johann Jakob Kaup. The species is monotypic: no subspecies are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within lineages. Charles Darwin was the first to describe the role of natural selection in speciation in his 1859 book ''On the Origin of Species''. He also identified sexual selection as a likely mechanism, but found it problematic. There are four geographic modes of speciation in nature, based on the extent to which speciating populations are isolated from one another: allopatric speciation, allopatric, peripatric speciation, peripatric, parapatric speciation, parapatric, and sympatric speciation, sympatric. Whether genetic drift is a minor or major contributor to speciation is the subject of much ongoing discussion. Rapid sympatric speciation can take place through polyploidy, such as by doubling of chromosome number; the result is progeny wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contiguous
Contiguity or contiguous may refer to: *Contiguous data storage, in computer science *Contiguity (probability theory) *Contiguity (psychology) *Contiguous distribution of species, in biogeography *Geographic contiguity Geographic contiguity is the characteristic in geography of political or geographical land divisions, as a group, not being interrupted by other land or water. Such divisions are referred to as being ''contiguous.'' In the United States, for exam ... of territorial land * Contiguous zone in territorial waters See also * * {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |