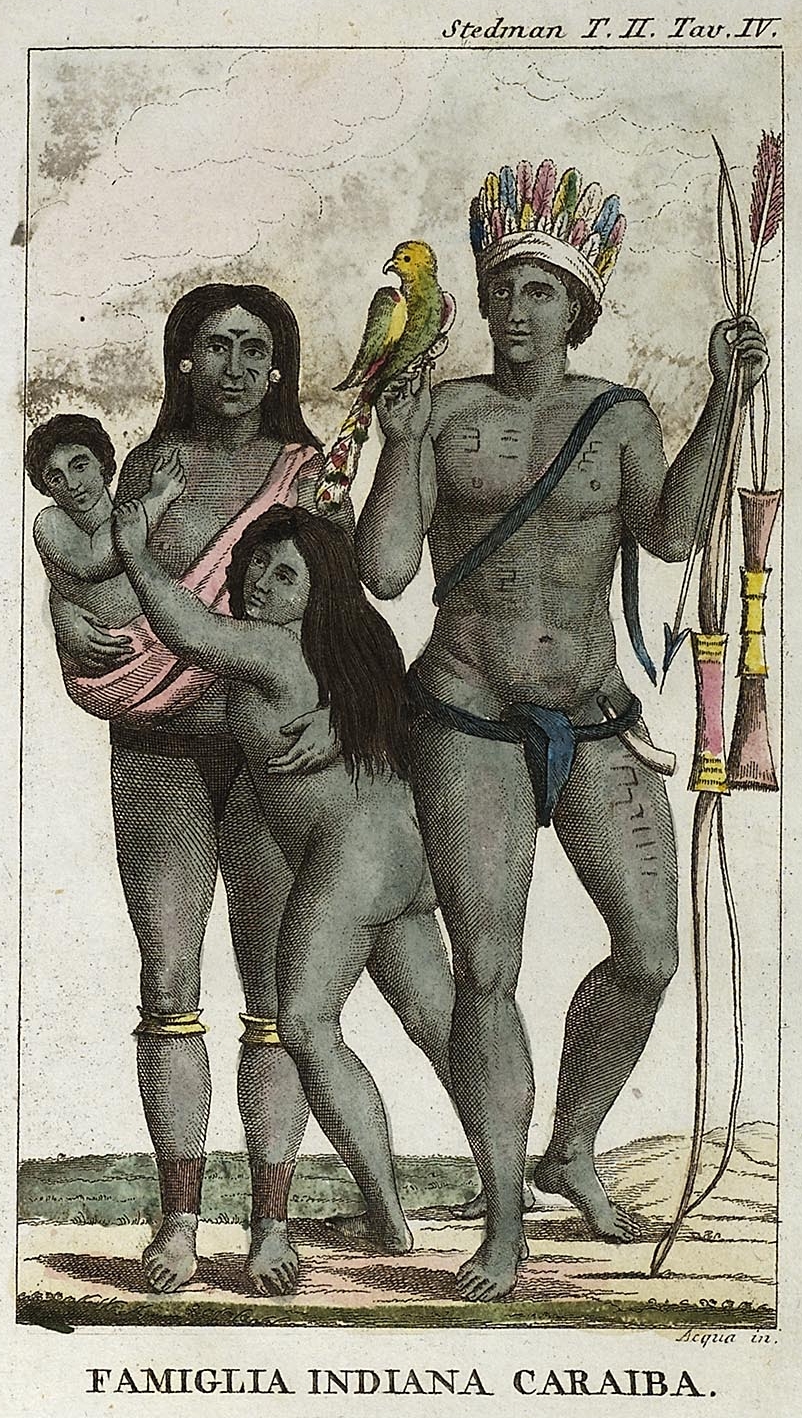|
Lesser Antillean Macaw
The Lesser Antillean macaw or Guadeloupe macaw (''Ara guadeloupensis'') is a hypothetical extinct species of macaw that is thought to have been endemic to the Lesser Antillean island region of Guadeloupe. In spite of the absence of conserved specimens, many details about the Lesser Antillean macaw are known from several contemporary accounts, and the bird is the subject of some illustrations. Austin Hobart Clark described the species on the basis of these accounts in 1905. Due to the lack of physical remains, and the possibility that sightings were of macaws from the South American mainland, doubts have been raised about the existence of this species. A phalanx bone from the island of Marie-Galante confirmed the existence of a similar-sized macaw inhabiting the region prior to the arrival of humans and was correlated with the Lesser Antillean macaw in 2015. Later that year, historical sources distinguishing between the red macaws of Guadeloupe and the scarlet macaw (''A. macao'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Du Tertre
Jean-Baptiste Du Tertre (''Jacques Du Tertre''; 1610 in Calais – 1687 in Paris) was a French Dominican Order, blackfriar and botanist. In 1633 he joined the Dutch army where he worked in the headquarters in Maastricht. Subsequently, he joined the Dominican Order where he adapted his first name Jean-Baptiste. In 1640 he was sent as missionary to the Antilles from where he returned to France in 1658. He is the author of several works about the Antilles where he described the indigenous peoples, the animals, and the plant world, including ''Histoire générale des îles Saint-Christophe, de la Guadeloupe, de la Martinique et autres de l'Amérique'' (Paris, 1654), ''Histoire naturelle et morale des îles Antilles de l'Amérique avec un vocabulaire caraïbe'' (1658), ''La Vie de Sainte Austreberte'' (1659) and ''l'Histoire générale des Antilles habitées par les Français'' (four volumes, 1667–1671). Particularly in his last work Du Tertre created the myth of the "Bon Sauv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Caribs
The Kalinago, also called Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, Indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Kalina people, Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Kalinago language, Kalinago or Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean (the name of which is derived from "Carib", as the Kalinago were once called). They lived throughout north-eastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Macaw
The Dominican green-and-yellow macaw (''Ara atwoodi''), Atwood's macaw or Dominican macaw, is an extinct species of macaw that may have lived on the island of Dominica. It is known only through the writings of British colonial judge Thomas Atwood in his 1791 book, ''The History of the Island of Dominica'': Austin Hobart Clark initially included these macaws in '' Ara guadeloupensis'' in 1905, but upon being referred to Atwood's writings, he listed them as a distinct species in 1908. As no archeological Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology ... remains are known, it is widely considered a hypothetical extinct species. Atwood described a bird which was commonly captured for food and pets. The Dominican macaw probably became extinct in the late 18th or early 19th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Rothschild
Lionel Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild, Baron de Rothschild, (8 February 1868 – 27 August 1937) was a British banker, politician, zoologist, and soldier, who was a member of the Rothschild family. As a Zionist leader, he was presented with the Balfour Declaration, which pledged British support for a Jewish national home in Mandatory Palestine. Rothschild was the president of the Board of Deputies of British Jews from 1925 to 1926. Early life Walter Rothschild was born in London as the eldest son and heir of Emma Louise von Rothschild and Nathan Rothschild, 1st Baron Rothschild, an immensely wealthy financier of the international Rothschild financial dynasty and the first Jewish peer in England. The eldest of three children, Walter was deemed to have delicate health and was educated at home. As a young man, he travelled in Europe, attending the University of Bonn for a year before entering Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1889, leaving Cambridge after two years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Birds (book)
__NOTOC__ ''Extinct Birds'' (complete title: ''Extinct birds. An attempt to unite in one volume a short account of those Birds which have become extinct in historical times—that is, within the last six or seven hundred years. To which are added a few which still exist, but are on the verge of extinction.'') is a book by Walter Rothschild which covers globally extinct and rare birds, as well as hypothetical extinct species which include bird taxa whose existence is based only on written or oral reports or on paintings. The accounts of the extinct bird taxa are based on Rothschild's lecture ''On extinct and vanishing birds'' published in the Proceedings of the 4th International Ornithological Congress 1905 in London. Subsequent authors like Errol Fuller were influenced by Rothschild's reference work. Fuller published an eponymous book in 1987 with a foreword written by Miriam Rothschild and also used color plates from Rothschild's work. Limited number Only 300 copies were pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼnja. A part of the French West Indies (Antilles), Martinique is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region and a single territorial collectivity of France. It is a part of the European Union as an outermost region within the special territories of members of the European Economic Area, and an associate member of the Caribbean Community, CARICOM, the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS), the Association of Caribbean States (ACS), and the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) but is not part of the Schengen Area or the European Union Customs Union. The currency in use is the euro. It has been a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve since 2021 for its entire land and sea territory. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominica
Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. It is part of the Windward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. Dominica's closest neighbours are two Special member state territories and the European Union, constituent territories of the European Union, both overseas departments of France: Guadeloupe to the northwest and Martinique to the south-southeast. Dominica comprises a land area of , and the highest point is Morne Diablotins, at in elevation. The population was 71,293 at the 2011 census. The island was settled by the Arawak arriving from South America in the fifth century. The Kalinago displaced the Arawak by the 15th century. Christopher Columbus is said to have passed the island on Sunday, 3 November 1493. It was later colonised by Europeans, predominantly by the French from the 1690s to 1763. The French trafficked slaves from W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Macaw
The Cuban macaw or Cuban red macaw (''Ara tricolor'') is an extinct species of macaw native to the main island of Cuba and the nearby Isla de la Juventud. It became extinct in the late 19th century. Its relationship with other macaws in its genus was long uncertain, but it was thought to have been closely related to the scarlet macaw, which has some similarities in appearance. It may also have been closely related, or identical, to the hypothetical Jamaican red macaw. A 2018 DNA study found that it was the sister species of two red and two green species of extant macaws. At about long, the Cuban macaw was one of the smallest macaws. It had a red, orange, yellow, and white head, and a red, orange, green, brown, and blue body. Little is known of its behaviour, but it is reported to have nested in hollow trees, lived in pairs or families, and fed on seeds and fruits. The species' original distribution on Cuba is unknown, but it may have been restricted to the central and western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green-winged Macaw
The red-and-green macaw (''Ara chloropterus''), also known as the green-winged macaw, is a large, mostly-red macaw of the genus ''Ara''. It is popular in aviculture, and is the second most commonly kept macaw species after the Blue and Yellow. However, they are not as common in captivity as the Blue-and-yellow macaw, and are much more expensive; prices are often double that of the blue and gold. This is the largest of the genus ''Ara'', widespread in the forests and woodlands of northern and central South America. However, in common with other macaws, in recent years there has been a marked decline in its numbers due to habitat loss and illegal capture for the parrot trade. Description The green-winged macaw can be readily distinguished from the scarlet macaw. While the breast of both birds are bright red, the upper-wing covert feathers of the green-winged macaw is mostly green (as opposed to mostly yellow, or a strong mix of yellow and green in the scarlet macaw). In additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Name
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammar, Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the ''generic name (biology), generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Latham (ornithologist)
John Latham (27 June 1740 – 4 February 1837) was an English physician, natural history, naturalist and author. His main works were ''A General Synopsis of Birds'' (1781–1801) and ''A General History of Birds'' (1821–1828). He was able to examine specimens of Australian birds that reached England in the final twenty years of the 18th century, and was responsible for providing English names for many of them. He named some of Australia's most famous birds, including the emu, sulphur-crested cockatoo, wedge-tailed eagle, superb lyrebird, Australian magpie, magpie-lark, white-throated needletail and pheasant coucal. Latham has been called the "grandfather" of Australian ornithology. He was also the first to describe the hyacinth macaw from South America. Biography John Latham was born on 27 June 1740 at Eltham in northwest Kent. He was the eldest son of John Latham (died 1788), a surgeon, and his mother, who was a descendant of the Sothebys, in Yorkshire. He was educated at Merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Edwards (naturalist)
George Edwards (3 April 1694 – 23 July 1773) was an English natural history, naturalist and ornithology, ornithologist, known as the "father of British ornithology". Edwards was born at West Ham, then in the county of Essex. In his early years, he travelled extensively through mainland Europe, studying natural history, and gained a reputation for his coloured drawings of animals, especially birds. He was appointed as beadle to the Royal College of Physicians in 1733. Over a period of 21 years, Edwards published seven volumes containing descriptions and hand-coloured etchings of birds. In a few cases, he depicted other animals. None of the species were native to the British Isles. The first four volumes were published between 1743 and 1751 with the title ''A Natural History of Uncommon Birds''. The three subsequent volumes were published between 1758 and 1764 with the title ''Gleanings Of Natural History''. The volumes contain a total of 362 hand-coloured etchings of which 317 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |