|
Leleges
The Leleges (; ) were an aboriginal people of the Aegean Sea, Aegean region, before the Greek people, Greeks arrived. They were distinct from another pre-Hellenic people of the region, the Pelasgians. The exact areas to which they were native are uncertain, since they were apparently pre-literate and the only references to them are in ancient Greek sources. These references are casual and (it is alleged) sometimes fictitious. Likewise, little is known about the language of the ''Leleges''. Many Greek authors link the Leleges to the Carians of south-west Anatolia. Homer names the Leleges among the Trojan Battle Order, Trojan allies alongside the Carians, Pelasgians, Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonians and Paphlagonia, Gaucones. Etymology It is thought that the name ''Leleges'' is an exonym, in a long-extinct language, rather than an endonym (or autonym). That is, during the Bronze Age the word ''lulahi'' apparently meaning "strangers" was used in the Luwian language and in other Anatolian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carians
The Carians (; , ''Kares'', plural of , ''Kar'') were the ancient inhabitants of Caria in southwest Anatolia, who spoke the Carian language. Historical accounts Karkisa It is not clear when the Carians enter into history. The definition is dependent on corresponding Caria and the Carians to the "Karkiya" or "Karkisa" mentioned in the Hittites, Hittite records. Bronze Age Karkisa are first mentioned as having aided the Assuwa League against the Hittite King Tudhaliya I. Later in 1323 BC, King Arnuwandas II was able to write to Karkiya for them to provide asylum for the deposed Manapa-Tarhunta of "the land of the Seha River", one of the principalities within the Luwians, Luwian Arzawa complex in western Anatolia. This they did, allowing Manapa-Tarhunta to take back his kingdom. In 1274 BC, Karkisa are also mentioned among those who fought on the History of the Hittites, Hittite Empire side against the Egyptians in the Battle of Kadesh. Taken as a whole, Hittite records seem to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelasgian
The name Pelasgians (, ) was used by Classical Greece, Classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the Greeks#Origins, emergence of the Greeks. In general, "Pelasgian" has come to mean more broadly all the Indigenous peoples, indigenous inhabitants of the Aegean Sea region and their cultures, and British historian Peter Green comments on it as . In the Classic period, enclaves under that name survived in several locations of mainland Greece, Crete, and other regions of the Aegean. Populations identified as "Pelasgian" spoke a language or languages that at the time Greeks identified as "barbarian#etymology, barbarian", though some ancient writers nonetheless described the Pelasgians as Greeks. A tradition also survived that large parts of Greece had once been Pelasgian before being Hellenization, Hellenized. These parts fell largely, though far from exclusively, within the territory which by the 5th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gargara
Gargara () was an ancient Greek city on the southern coast of the Troad region of Anatolia. It was initially located beneath Mount Gargaron, one of the three peaks of Mount Ida, today known as Koca Kaya (). At some point in the 4th century BCE the settlement moved approximately 5.8 km south of Koca Kaya to a site on the small coastal plain near the modern villages of Arıklı and Nusratlı (), at which point the previous site came to be known as Old Gargara (). Both sites are located in the Ayvacık district of Çanakkale Province in Turkey. Mount Gargaron Mount Gargaron has been identified with the mountain today called Koca Kaya ( Turkish ''Great Rock''), a western spur of Mount Ida with a maximum elevation of 780 m. The poet Epicharmus (''fl.'' 540 - 450 BCE) refers to the mountain as "snowcapped" (ἀγάννιφα), and the ''Etymologicum Magnum'' (ca. 1150 CE) knew a tradition according to which the inhabitants of Old Gargara moved to their new site to escape the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
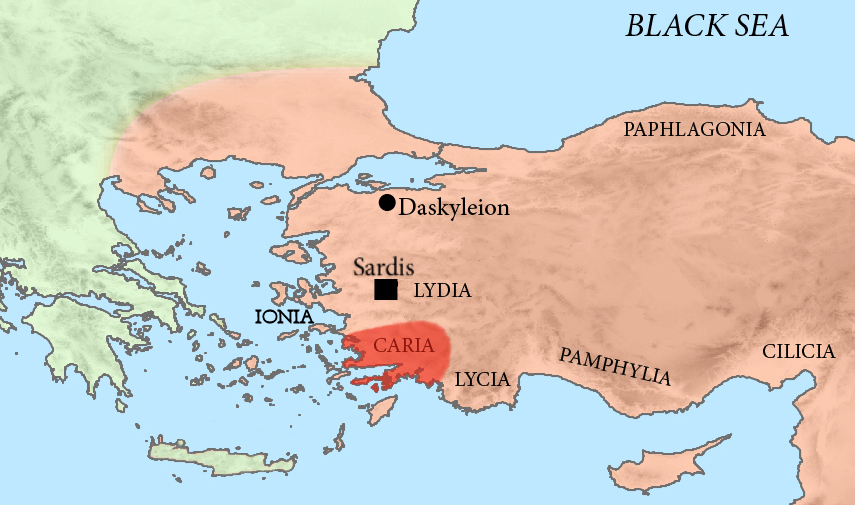
Caria
Caria (; from Greek language, Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; ) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Carians were described by Herodotus as being Anatolian mainlanders and they called themselves Caria because of the name of their king.''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. He reports the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian language, Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian language, Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and geomorphic features, such as bays and headlands, reveal an ethnic layering consistent with the known colonization. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedasus
Pedasus (Ancient Greek: Πήδασος) has been identified with several personal and place names in Greek history and mythology. Persons In Homer's ''Iliad'', Pedasus was the name of a Trojan warrior, and the son of the naiad Abarbarea and human Bucolion. His twin brother was Aesepus; both were slain by Euryalus, the son of Mecisteus, during the Trojan War. In Homer's ''Iliad'', Pedasus was also the name of a swift horse taken as booty by Achilles when he killed Eetion. This horse was killed by a spear during a duel between Patroclus and Sarpedon. Places Pedasus (Caria): In Caria, according to Herodotus, the Battle of Pedasus (Summer of 496 BCE) was a night ambush where the Carians annihilated a Persian army. This engagement occurred during the Ionian Revolt (499-494 BCE). Pedasus (Messenia): In Peloponnese, Methone has been identified with the vine-covered Pedasus, one of the seven cities offered by Agamemnon to Achilles to quell his rage and to persuade him t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( ; ; ) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his '' Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology, which is providing evidence of the sites and cultural details he mentions although knowledge of their existence may have become lost or relegated to myth or legend. Biography Nothing is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is probable that he was born into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From until his death around 180, Pausanias travelled throughout the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing his '' Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( ; ) is a regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a prefecture (''nomos'') covering the same territory. The capital and largest city of Messenia is Kalamata. Geography Physical Messenia borders on Elis to the north, Arcadia to the northeast, and Laconia to the southeast. The Ionian Sea lies to the west, and the Gulf of Messinia to the south. The most important mountain ranges are the Taygetus in the east, the Kyparissia mountains in the northwest and the Lykodimo in the southwest. The main rivers are the Neda in the north and the Pamisos in central Messenia. Off the south coast of the southwesternmost point of Messenia lie the Messinian Oinousses islands. The largest of these are Sapientza, Schiza and Venetiko. The small island Sphacteria closes off the bay of Pylos. All these islands are virtua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troad
The Troad ( or ; , ''Troáda'') or Troas (; , ''Trōiás'' or , ''Trōïás'') is a historical region in northwestern Anatolia. It corresponds with the Biga Peninsula ( Turkish: ''Biga Yarımadası'') in the Çanakkale Province of modern Turkey. Bounded by the Dardanelles to the northwest, by the Aegean Sea to the west and separated from the rest of Anatolia by the massif that forms Mount Ida, the Troad is drained by two main rivers, the Scamander ( Karamenderes) and the Simoeis, which join at the area containing the ruins of Troy. History The Troad is first mentioned by that name in Hittite records as ''Taruiša''. This identification was first put forth by Emil Forrer, but largely disputed by most Hittite experts until 1983 when Houwink ten Cate showed that two fragments were from the same original cuneiform tablet and in his discussion of the restored letter showed that ''Taruiša'' and ''Wiluša'' (Troy) were correctly placed in northwestern Anatolia. Greek settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyzicus
Cyzicus ( ; ; ) was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula (the classical Arctonnesus), a tombolo which is said to have originally been an island in the Sea of Marmara only to be connected to the mainland in historic times either by artificial means or an earthquake. The site of Cyzicus, located on the Erdek and Bandırma roads, is protected by Turkey's Turkish Ministry of Culture, Ministry of Culture. History Ancient The city was said to have been founded by Pelasgians from Thessaly, according to tradition at the coming of the Argonauts; later it received many colonies from Miletus, allegedly in 756 BC, but its importance began near the end of the Peloponnesian War when the conflict centered on the sea routes connecting Greece to the Black Sea. At this time, the cities of Athens and Miletus diminished in importance while Cyzicus began to prosper. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achilles
In Greek mythology, Achilles ( ) or Achilleus () was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. The central character in Homer's ''Iliad'', he was the son of the Nereids, Nereid Thetis and Peleus, king of Phthia and famous Argonauts, Argonaut. Achilles was raised in Phthia along with his childhood companion Patroclus and received his education by the centaur Chiron. In the ''Iliad'', he is presented as the commander of the mythical tribe of the Myrmidons. Achilles' most notable feat during the Trojan War was the slaying of the Trojan prince Hector outside the gates of Troy. Although the death of Achilles is not presented in the ''Iliad'', other sources concur that he was killed near the end of the Trojan War by Paris (mythology), Paris, who shot him with an arrow. Later legends (beginning with Statius' unfinished epic ''Achilleid'', written in the first century CE) state that Achilles was invulnerable in all of his body except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalogue Of Ships
The Catalogue of Ships (, ''neōn katálogos'') is an epic catalogue in Book 2 of Homer's ''Iliad'' (2.494–759), which lists the contingents of the Achaean army that sailed to Troy. The catalogue gives the names of the leaders of each contingent, lists the settlements in the kingdom represented by the contingent, sometimes with a descriptive epithet that fills out a half-verse or articulates the flow of names and parentage and place, and gives the number of ships required to transport the men to Troy, offering further differentiations of weightiness. A similar, though shorter, Catalogue of the Trojans and their allies follows (2.816–877). A similar catalogue appears in the Pseudo-Apollodoran ''Bibliotheca''. Historical background In the debate since antiquity over the Catalogue of Ships, the core questions have concerned the extent of historical credibility of the account, whether it was composed by Homer himself, to what extent it reflects a pre-Homeric document or memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Dowden
Ken Dowden (born 1950) is Professor Emeritus of Classics at the University of Birmingham, England. Dowden is from Newcastle upon Tyne and studied at Worcester College, Oxford University The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the second-oldest continuously operating u .... He came to Birmingham in 1988, acting as Head of the School of Humanities from 2000 to 2003, as Director of the Institute of Archaeology and Antiquity from 2005 to 2012, and as Head of the School of Philosophy, Theology and Religion from 2012 to 2016. Bibliography *1989, ''Death and the Maiden: Girls' Initiation Rites in Greek Mythology'', London and New York: Routledge. *1992, ''Religion and the Romans'', London: Bristol Classical Press. *1992, ''The Uses of Greek Mythology'', London and New York: Routledge. *2000, ''European Paganism: the reali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |