|
Leipziger Straße
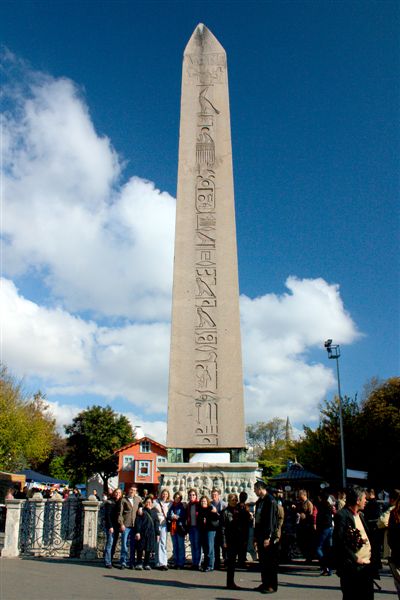
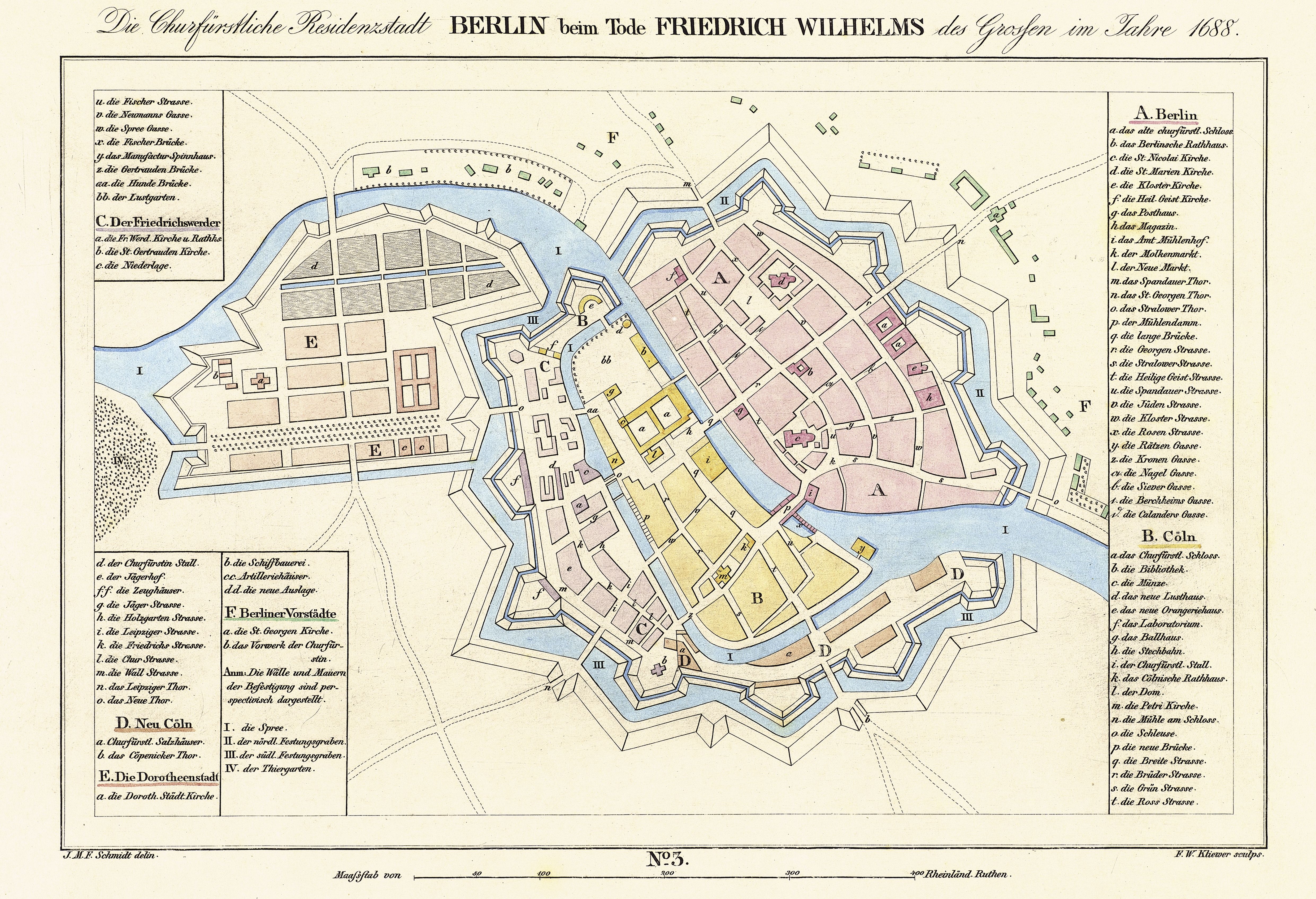
Leipziger Straße, or Leipziger Strasse (see ß), is a major thoroughfare in the central Mitte district of Berlin, capital of Germany. It runs from Leipziger Platz, an octagonal square adjacent to Potsdamer Platz in the west, to Spittelmarkt in the east. Part of the Bundesstraße 1 highway, it is today one of the city's main east–west road links. History Leipziger Straße has existed along this line since about the Baroque Friedrichstadt extension, laid out in 1688 at the behest of Elector Frederick III of Brandenburg. It was named after Leipzig Gate near Spittelmarkt, part of the Berlin Fortress which was finally slighted in 1738. In 1734 the road was extended up to the new Potsdam Gate, present-day Potsdamer Platz, one of the western entrances in what was then the Berlin Customs Wall. Near the eastern end, Leipziger Straße traversed , named after Prussian general lieutenant Alexander von Dönhoff (1683–1742), where an obelisk marked the zero point of the mileage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bundesstraße 1 Number
''Bundesstraße'' (, ), abbreviated ''B'', is the denotation for Germany, German and Austrian national highways. Germany Germany's ''Bundesstraßen'' network has a total length of about 40,000 km. German ''Bundesstraßen'' are labelled with rectangular yellow signs with black numerals, as opposed to the white-on-blue markers of the ''Autobahn'' controlled-access highways. ''Bundesstraßen'', like autobahns (''Autobahnen''), are maintained by the Federal agency (Germany), federal agency of the Federal Ministry of Transport, Building and Urban Development, Transport Ministry. In the German highway system they rank below autobahns, but above the ''Landesstraßen'' and ''Kreisstraßen'' maintained by the States of Germany, federal states and the Districts of Germany, districts respectively. The numbering was implemented by law in 1932 and has overall been retained up to today, except for those roads located in the former eastern territories of Germany. One distinguishing ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Friedrichstraße
Friedrichstraße, or Friedrichstrasse (see ß; ) (lit. ''Frederick Street''), is a major culture and shopping street in central Berlin, forming the core of the Friedrichstadt neighborhood and giving the name to Berlin Friedrichstraße station. It runs from the northern part of the old Mitte district (north of which it is called Chausseestraße) to the Hallesches Tor in the district of Kreuzberg. This downtown area is known for its expensive real estate market and the campus of the Hertie School of Governance. Due to its north-southerly direction, it forms important junctions with the east-western axes, most notably with Leipziger Straße and Unter den Linden. The U6 U-Bahn line runs underneath. During the Cold War it was bisected by the Berlin Wall and was the location of Checkpoint Charlie. Overview As central Berlin's traditional shopping street, Friedrichstraße is three blocks east of the parallel Wilhelmstraße, the historic heart of the old government quarte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Preußischer Landtag
The Landtag of Prussia () was the representative assembly of the Kingdom of Prussia implemented in 1849, a bicameral legislature consisting of the upper House of Lords (''Herrenhaus'') and the lower House of Representatives (''Abgeordnetenhaus''). After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918–19 the ''Landtag'' diet continued as the parliament of the Free State of Prussia between 1921 and 1934, when it was abolished by the Nazi regime. History Kingdom of Prussia In the course of the 1848 Revolution, King Frederick William IV of Prussia and his Minister President Gottfried Ludolf Camphausen had agreed to call for the general election of a national assembly in all Prussian provinces. The Prussian National Assembly however was dismissed by royal decree of 5 December 1848 and the King imposed the 1848 Constitution of Prussia. It contained a catalog of fundamental rights that included freedom of religion, speech and the press, and provided for a bicameral parliament consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karl August Von Hardenberg
Karl August Fürst von Hardenberg (31 May 1750, in Essenrode- Lehre – 26 November 1822, in Genoa) was a Prussian statesman and Chief Minister of Prussia. While during his late career he acquiesced to reactionary policies, earlier in his career he implemented a variety of Liberal reforms. To him and Baron vom Stein, Prussia was indebted for improvements in its army system, the abolition of serfdom and feudal burdens, the throwing open of the civil service to all classes, and the complete reform of the educational system. Family Hardenberg was the eldest son of Christian Ludwig von Hardenberg (1700-1781), a Hanoverian colonel, later to become field marshal and commander-in-chief of the Hanoverian Army under Elector George III from 1776 until his death. His mother was Anna Sophia Ehrengart von Bülow. He was born, one of eight children, at Essenrode Manor near Hanover in the Electorate of Hanover, his maternal grandfather's estate. The ancestral home of the ''knights of Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of Berlin, and lies embedded in a hilly morainic landscape dotted with many lakes, around 20 of which are located within Potsdam's city limits. It lies some southwest of Berlin's city centre. The name of the city and of many of its boroughs are of Slavic languages, Slavic origin. Potsdam was a residence of the Prussian kings and the German Emperor until 1918. Its planning embodied ideas of the Age of Enlightenment: through a careful balance of architecture and landscape, Potsdam was intended as "a picturesque, pastoral dream" which would remind its residents of their relationship with nature and reason. The city, which is over 1,000 years old, is widely known for its palaces, its lakes, and its overall historical and cultural significance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Obelisk
An obelisk (; , diminutive of (') ' spit, nail, pointed pillar') is a tall, slender, tapered monument with four sides and a pyramidal or pyramidion top. Originally constructed by Ancient Egyptians and called ''tekhenu'', the Greeks used the Greek term to describe them, and this word passed into Latin and ultimately English. Though William Thomas used the term correctly in his ''Historie of Italie'' of 1549, by the late sixteenth century (after reduced contact with Italy following the excommunication of Queen Elizabeth), Shakespeare failed to distinguish between pyramids and obelisks in his plays and sonnets. Ancient obelisks are monolithic and consist of a single stone; most modern obelisks are made of several stones. Ancient obelisks Egyptian Obelisks were prominent in the architecture of the ancient Egyptians, and played a vital role in their religion placing them in pairs at the entrance of the temples. The word "obelisk" as used in English today is of Greek rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexander Von Dönhoff
Alexander Graf von Dönhoff (9 February 1683 – 9 October 1742) was a Prussian lieutenant-general and confidant of King Friedrich Wilhelm I. He was born in Königsberg, the son of Friedrich von Dönhoff and Eleonore Katharina née von Schwerin, daughter of Otto von Schwerin, the President of the Elector of Brandenburg's Privy Council. In November 1699 he became enlisted in Brandenburg services. Then he went to Hesse-Kassel, where he was captain and in 1701 participated in the War of Spanish Succession against France. He was promoted to major in 1704, to 9nd lieutenant colonel in February 1705, and engaged in combat in northern Italy in 1706 and 1707. On 27 December 1709 he became a colonel, and led a separate regiment in 1720 and became major general on 13 July 1722, in the Prussian service. In the trial against the Prussian Crown Prince Frederick and Hans Hermann von Katte 1730, he was a member of the war court. In the years 1734 and 1735 he led the campaign on the Rhine, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a significant role in the unification of Germany in 1871 and was a major constituent of the German Empire until its German Revolution of 1918–1919, dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the Prussia (region), region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The list of monarchs of Prussia, kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. The polity of Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick the Great, Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Berlin Customs Wall
The Berlin Customs Wall (German: "Berliner Zoll- und Akzisemauer", literally ''Berlin customs and excise wall'' the German term had been originally "Akzisemauer" / excise wall but with the fading knowledge of the term "excise" most references incorporate "Zoll" / Customs to flag the function) was a ring wall around the historic city of Berlin, between 1737 and 1860; the wall itself had no defence function but was used to facilitate the levying of taxes on the import and export of goods (tariffs), which was the primary income of many cities at the time. History The wall was erected after the old Berlin Fortress was demolished in 1734; the walls of the latter had already started to crumble and its military function was questionable. Frederick William I of Prussia ordered the construction of stockades around the city which were completed in 1737 – the new ring fence incorporated the existing northern "palisade line" built in 1705. The location of this oldest stockade is recal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Potsdam Gate
The Potsdam Gate () was one of the western gates of the Berlin Customs Wall, south of the still-standing Brandenburg Gate. It was originally constructed in 1734, and then rebuilt in 1824 as a neoclassic imposing gateway. It was one of the few gates that were left when the Customs Wall was demolished (1867–1870) but it suffered severe damage during the bombing of Berlin in World War II (1943–1945). Its remains were demolished in 1961, when the Berlin Wall was erected. See also *Potsdamer Platz Potsdamer Platz (, ''Potsdam Square'') is a public square and traffic intersection in the center of Berlin, Germany, lying about south of the Brandenburg Gate and the Reichstag building, Reichstag (Bundestag, German Parliament Building), and ... References Buildings and structures in Mitte Buildings and structures completed in 1734 Gates in Berlin Monuments and memorials in Berlin Neoclassical architecture in Berlin Demolished buildings and structures in Germany {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Berlin Fortress
The Berlin Fortress (German "Festung Berlin") was the fortification of the historic city of Berlin. Construction started in 1650. The ramparts, walls, moats and glacis of the 17th-century bastion fort ran around the historic city limits. The demolition of its ramparts began in 1740. History Berlin was an important market place on the main east-west route (today Bundesstraße 1). However, it had no real fortifications, unlike Spandau in the west (Spandau Citadel) and Köpenick in the east ( Köpenick Palace). Although Berlin was not the site of any battles during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) it suffered heavily from the Swedish occupation; by the end of the war in 1631, a third of the buildings had been demolished and half the population had fled or died. Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg ordered the engineer architect Johann Gregor Memhardt to make plans for a fortification for the town. These began in 1650 following the contemporary fortification model of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Frederick I Of Prussia
Frederick I (; 11 July 1657 – 25 February 1713), of the Hohenzollern dynasty, was (as Frederick III) List of margraves and electors of Brandenburg, Elector of Brandenburg (1688–1713) and Duke of Prussia in personal union (Brandenburg–Prussia). The latter function he upgraded to royalty, becoming the first King in Prussia (1701–1713). From 1707 he was in personal union the sovereign prince of the Principality of Neuchâtel. Biography Family Born in Königsberg, Frederick was the third son of Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg by his father's first marriage to Louise Henriette of Orange-Nassau, eldest daughter of Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange and Amalia of Solms-Braunfels. His maternal cousin was King William III of England. Upon the death of his father on 29 April 1688, Frederick became Elector Frederick III of Electorate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg and Duchy of Prussia, Duke of Prussia. Right after ascending the throne Frederick founded a new city southerly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |