|
Lead(II) Thiocyanate
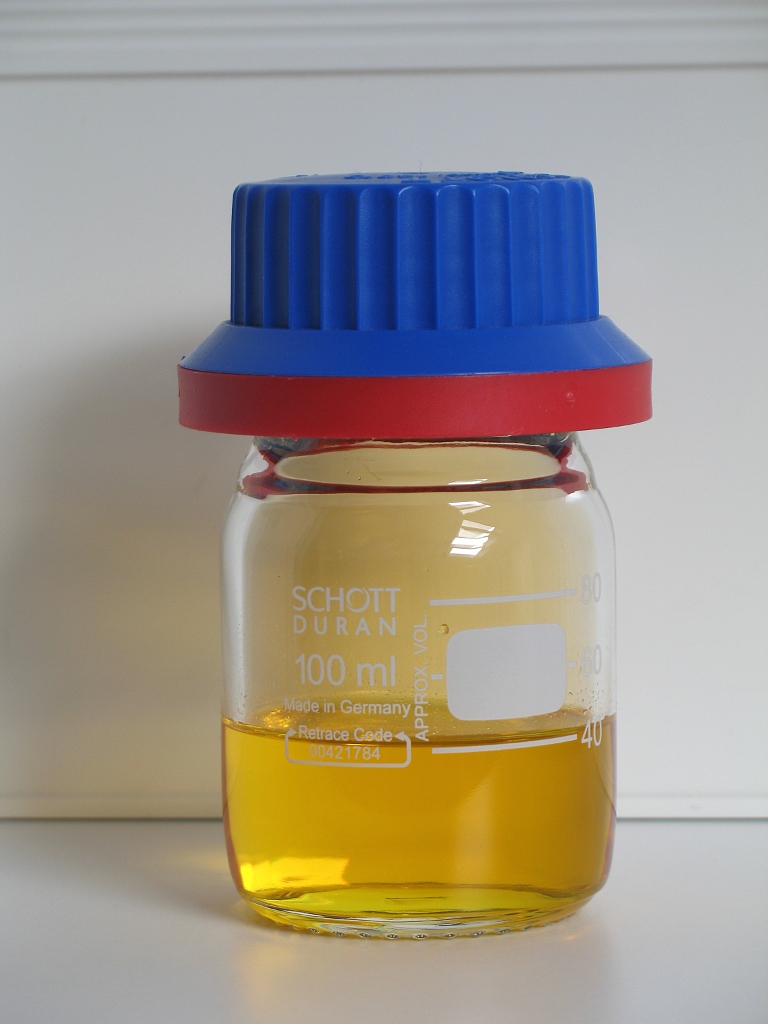
Lead(II) thiocyanate is a compound, more precisely a salt, with the formula Pb(SCN)2. It is a white crystalline solid, but will turn yellow upon exposure to light. It is slightly soluble in water and can be converted to a basic salt (Pb(CNS)2·Pb(OH)2 when boiled. Salt crystals may form upon cooling. Lead thiocyanate can cause lead poisoning if ingested and can adversely react with many substances. It has use in small explosives, matches, and dyeing. Lead(II) thiocyanate is reasonably soluble at room temperature, thus it may be difficult to identify in a solution with low concentration of lead(II) thiocyanate. Although it has not been confirmed by other sources than the author of this article, experiments show that even if there is no precipitation of lead(II) thiocyanate in the solution, crystals of the salt may form. Synthesis Lead(II) thiocyanate can be formed from the acidification of lead(II) nitrate, Pb(NO3)2, with nitric acid, HNO3, in the presence of thiocyanic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Polymer
Coordination may refer to: * Coordination (linguistics), a compound grammatical construction * Coordination complex, consisting of a central atom or ion and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions ** A chemical reaction to form a coordination complex * Coordination number or ligancy of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it * Language coordination, the tendency of people to mimic the language of others * Coordination (political culture), a Utopian form of political regime * Motor coordination In physiology, motor coordination is the orchestrated movement of multiple body parts as required to accomplish intended actions, like walking. This coordination is achieved by adjusting kinematic and kinetic parameters associated with each bo ..., in animal motion * '' Gleichschaltung'' the process of Nazification in Germany after 1933, often translated as "coordination" See also * Coordinate (other) * Coordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite Solar Cell
A perovskite solar cell (PSC) is a type of solar cell that includes a perovskite-structured compound, most commonly a hybrid organic–inorganic lead or tin halide-based material as the light-harvesting active layer. Perovskite materials, such as methylammonium lead halides and all-inorganic cesium lead halide, are cheap to produce and simple to manufacture. Solar-cell efficiencies of laboratory-scale devices using these materials have increased from 3.8% in 2009 to 25.7% in 2021 in single-junction architectures, and, in silicon-based tandem cells, to 29.8%, exceeding the maximum efficiency achieved in single-junction silicon solar cells. Perovskite solar cells have therefore been the fastest-advancing solar technology . With the potential of achieving even higher efficiencies and very low production costs, perovskite solar cells have become commercially attractive. Core problems and research subjects include their short- and long-term stability. Advantages The raw materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyeing
Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular chemical material. Dye molecules are fixed to the fiber by absorption, diffusion, or bonding with temperature and time being key controlling factors. The bond between the dye molecule and fiber may be strong or weak, depending on the dye used. Dyeing and printing are different applications; in printing, color is applied to a localized area with desired patterns. In dyeing, it is applied to the entire textile. The primary source of dye, historically, has been nature, with the dyes being extracted from plants or animals. Since the mid-19th century, however, humans have produced artificial dyes to achieve a broader range of colors and to render the dyes more stable for washing and general use. Different classes of dyes are used for different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Paint
Lead paint or lead-based paint is paint containing lead. As pigment, lead(II) chromate (, "chrome yellow"), lead(II,IV) oxide, (, "red lead"), and lead(II) carbonate (, "white lead") are the most common forms.. Lead is added to paint to accelerate drying oil, drying, increase durability, maintain a fresh appearance, and resist moisture that causes corrosion. It is one of the main health and environmental issues with paint, environmental hazards associated with paint. Lead paint has been generally phased out of use due to the toxic nature of lead. Alternatives such as water-based, lead-free traffic paint are readily available. In some countries, lead continues to be added to paint intended for domestic use, whereas countries such as the United States and the lead-based paint in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom have regulations prohibiting its use. However, lead paint may still be found in older properties painted prior to the introduction of such regulations. Although lead has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision. Skin reactions Human medicine Sensitivity of the skin to a light source can take various forms. People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn. Particular medications make the skin more sensitive to sunlight; these include most of the tetracycline antibiotics, heart drugs amiodarone, and sulfonamides. Some dietary supplements, such as St. John's Wort, include photosensitivity as a possible side effect. Particular conditions lead to increased light sensitivity. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus experience skin symptoms after sunlight exposure; some typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paresthesia
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or Chronic condition, chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly in the arms and legs. The most familiar kind of paresthesia is the sensation known as ''pins and needles'' after having a limb "fall asleep" (''obdormition''). A less common kind is formication, the sensation of insects crawling on the skin. Causes Transient Paresthesias of the hands, feet, legs, and arms are common transient symptoms. The briefest electric shock type of paresthesia can be caused by tweaking the ulnar nerve near the elbow; this phenomenon is colloquially known as bumping one's "funny bone". Similar brief shocks can be experienced when any other nerve is tweaked (e.g. a pinched neck nerve may cause a brief shock-like paresthesia toward the scalp). In the older a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Nitrate
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt (chemistry), salt is also known as Chile saltpeter (large deposits of which were historically mined in Chile) to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate. The mineral form is also known as nitratine, nitratite or soda niter. Sodium nitrate is a white deliquescent solid very soluble in water. It is a readily available source of the nitrate anion (NO3−), which is useful in several reactions carried out on industrial scales for the production of fertilizers, pyrotechnics, smoke bombs and other explosives, glass and pottery vitreous enamel, enamels, food preservatives (esp. meats), and rocket propellant, solid rocket propellant. It has been mined extensively for these purposes. History The first shipment of saltpeter to Europe arrived in England from Peru in 1820 or 1825, right after that country's independence from Spain, but did not find any buyers and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of metals refining and the burning of Sour gas, sulfur-Sour crude oil, bearing fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide is somewhat toxic to humans, although only when inhaled in relatively large quantities for a period of several minutes or more. It was known to medieval alchemy, alchemists as "volatile spirit of sulfur". Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v Point groups in three dimensions, symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance (chemistry), resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued Precursor (chemistry), precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals. Large-scale applications are for the production of potassium cyanide and adiponitrile, used in mining and plastics, respectively. It is more toxic than solid cyanide compounds due to its Volatility (chemistry), volatile nature. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water (molecule), water, represented as HCN(aqueous, aq), is called ''hydrocyanic acid''. The Salt (chemistry), salts of the cyanide anion are known as cyanides. Whether hydrogen cyanide is an organic compound or not is a topic of debate among chemists, and opinions vary from author to author. Traditionally, it is considered ino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Thiocyanate
Barium thiocyanate refers to salts of the formula . Both an anhydrous salt and a trihydrate are known. The anhydrous salt is hygroscopic. The trihydrate is soluble in most alcohols but insoluble in simple alkanes. Barium thiocyanate is used in dyeing textiles and in some photographic solutions. But because of its toxicity, it has limited uses. Preparation and structure Barium thiocyanate is prepared by mixing barium hydroxide and ammonium thiocyanate in water. :2 NH4SCN + Ba(OH)2 → Ba(SCN)2 + 2 NH3 + 2 H2O According to X-ray crystallography, the anhydrous salt is a coordination polymer. The Ba2+ ions are each bonded to eight thiocyanate anions, with four Ba-S and four Ba-N bonds. The motif is reminiscent of the fluorite structure The fluorite structure refers to a common motif for compounds with the formula MX2. The X ions occupy the eight tetrahedral interstitial sites whereas M ions occupy the regular sites of a face-centered cubic In crystallography, the cubic (or is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |