|
Laws Of Hywel Dda
''Cyfraith Hywel'' (; ''Laws of Hywel''), also known as ''Welsh law'' (), was the system of law practised in medieval Wales before its conquest of Wales by Edward I, final conquest by England. Subsequently, the Welsh law's criminal codes were superseded by the Statute of Rhuddlan in AD 1284 and its civil codes by Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII's series of Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542, Laws in Wales Acts between 1535 and 1542. Welsh law was a form of Celtic law with many similarities to the Early Irish law, Brehon law of Ireland and particularly the customs and terminology of the Britons of Kingdom of Strathclyde, Strathclyde. It was passed down orally by jurists and bards and, according to tradition, only first codified during the reign of Hywel Dda in the mid-10th century. The earliest surviving manuscripts, however, are in Latin, date from the early 13th century, and show marked regional differences.Wade-Evans, Arthur. ''s:Page:Welsh Medieval Law.djvu/13, Welsh Medieval L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jurist
A jurist is a person with expert knowledge of law; someone who analyzes and comments on law. This person is usually a specialist legal scholar, mostly (but not always) with a formal education in law (a law degree) and often a Lawyer, legal practitioner. In the United Kingdom the term "jurist" is mostly used for legal academics, while in the United States the term may also be applied to a judge. With reference to Roman law, a "jurist" (in English) is a jurisconsult (''iurisconsultus''). The English term ''jurist'' is to be distinguished from similar terms in other European languages, where it may be synonymous with legal professional, meaning anyone with a professional law degree that qualifies for admission to the legal profession, including such positions as judge or attorney. In Germany, Scandinavia and a number of other countries ''jurist'' denotes someone with a professional law degree, and it may be a protected title, for example Legal education in Norway, in Norway. Thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Early Irish Law
Early Irish law, also called Brehon law (from the old Irish word breithim meaning judge), comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norman invasion of 1169, but underwent a resurgence from the 13th until the 17th century, over the majority of the island, and survived into Early Modern Ireland in parallel with English law. Early Irish law was often mixed with Christian influence and juristic innovation. These secular laws existed in parallel, and occasionally in conflict, with canon law throughout the early Christian period. The laws were a civil rather than a criminal code, concerned with the payment of compensation for harm done and the regulation of property, inheritance and contracts; the concept of state-administered punishment for crime was foreign to Ireland's early jurists. They show Ireland in the early medieval period to have been a hierarchical society, taking great care to define social sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Powys
The Kingdom of Powys (; ) was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain. It very roughly covered the northern two-thirds of the modern county of Powys and part of today's English West Midlands (see map). More precisely, and based on the Romano-British tribal lands of the Ordovices in the west and the Cornovii in the east, its boundaries originally extended from the Cambrian Mountains in the west to include the modern West Midlands region of England in the east. The fertile river valleys of the Severn and Tern are found there, and this region is referred to in later Welsh literature as "the Paradise of Powys" (an epithet retained in Welsh for the modern UK county). Name The name Powys is thought to derive from Latin ''pagus'' 'the countryside' and ''pagenses'' 'dwellers in the countryside', also the origins of French "pays" and English "peasant". During the Roman Empire, this regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
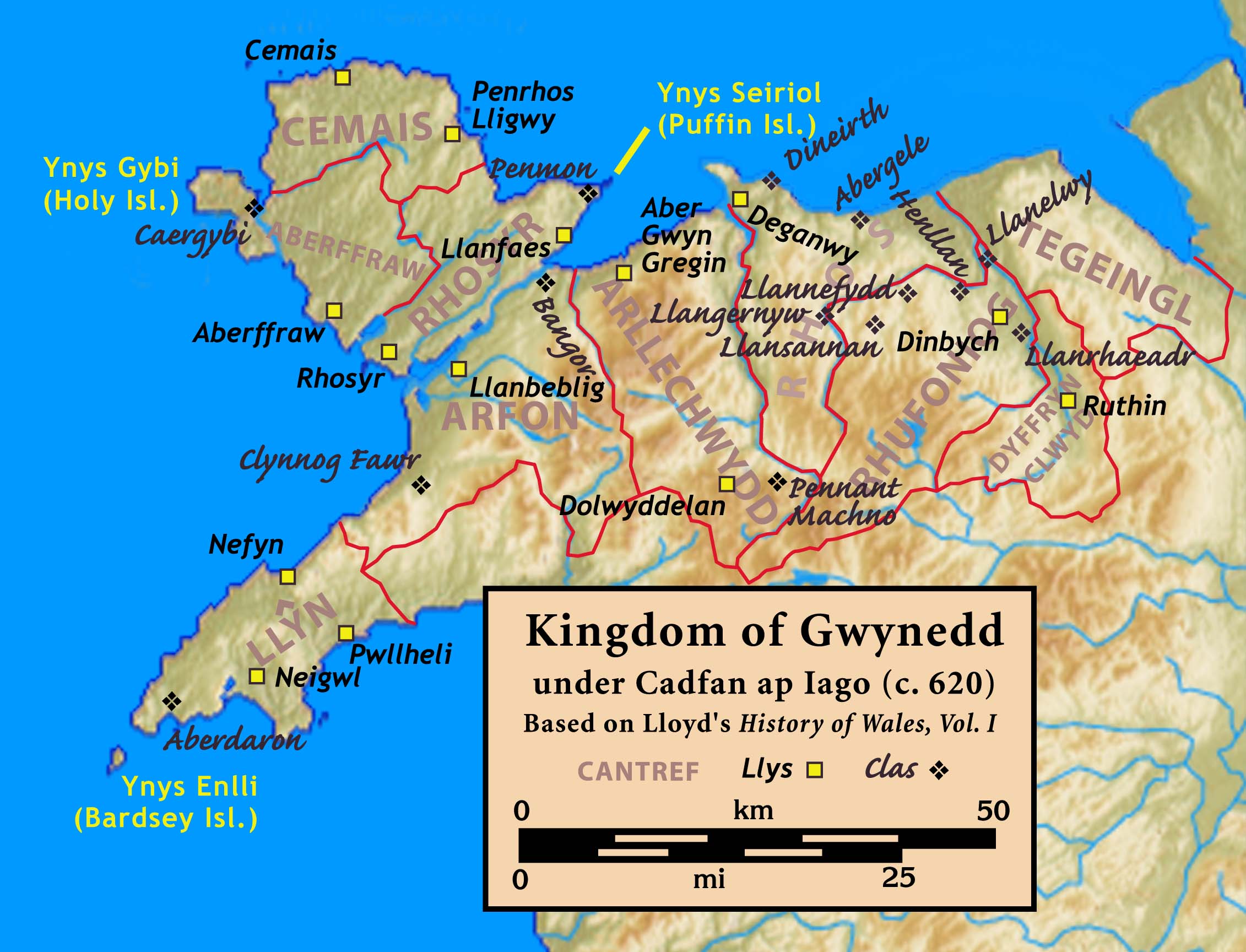
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the list of rulers of Gwynedd, rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain, Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Medieval Wales
Wales in the Middle Ages covers the history of the country that is now called Wales, from the departure of the Romans in the early fifth century to the annexation of Wales into the Kingdom of England in the early sixteenth century. This period of about 1,000 years saw the development of regional Welsh kingdoms, Celtic conflict with the Anglo-Saxons, reducing Celtic territories, and conflict between the Welsh and the Anglo-Normans from the 11th century. Early Middle Ages: 411–1066 When the Roman garrison of Britain was withdrawn in 410, the various British states were left self-governing. Evidence for a continuing Roman influence after the departure of the Roman legions is provided by an inscribed stone from Gwynedd dated between the late 5th and mid-6th centuries commemorating a certain Cantiorix who was described as a citizen (''cives'') of Gwynedd and a cousin of Maglos the magistrate (''magistratus''). There was considerable Irish colonisation in Dyfed, where there are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Christ, temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark and Gospel of Luke, Luke, before beginning his Ministry of Jesus, public ministry. Lent is usually observed in the Catholic Church, Catholic, Lutheranism, Lutheran, Moravian Church, Moravian, Anglican Communion, Anglican, United and uniting churches, United Protestant and Eastern Orthodoxy, Orthodox Christian traditions, among others. A number of Anabaptism, Anabaptist, Baptists, Baptist, Methodism, Methodist, Calvinism, Reformed (including certain Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continental Reformed, Presbyterianism, Presbyterian and Congregational church, Congregationalist churches), and Nondenominational Christianity, nondenominational Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Capital Punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence (law), sentence ordering that an offender be punished in such a manner is called a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Etymologically, the term ''capital'' (, derived via the Latin ' from ', "head") refers to execution by Decapitation, beheading, but executions are carried out by List of methods of capital punishment, many methods, including hanging, Execution by shooting, shooting, lethal injection, stoning, Electric chair, electrocution, and Gas chamber, gassing. Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Compurgation
Compurgation, also called trial by oath, wager of law, and oath-helping, was a defence used primarily in medieval law. A defendant could establish his innocence or nonliability by taking an oath and by getting a required number of persons, typically twelve, to swear they believed the defendant's oath. The wager of law was essentially a character reference, initially by kin and later by neighbours (from the same region as the defendant), often 11 or 12 men, and it was a way to give credibility to the oath of a defendant at a time when a person's oath had more credibility than a written record. It can be compared to a legal wager, which is the provision of surety at the beginning of legal action to minimize frivolous litigation. Compurgation was found in early Germanic law, in early French law (''très ancienne coutume de Bretagne''), in Welsh law, and in the English ecclesiastical courts until the seventeenth century. In common law it was substantially abolished as a defence in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Canon Law
Canon law (from , , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical jurisdiction, ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. Canon law includes the internal ecclesiastical law, or operational policy, governing the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and the Eastern Catholic Churches), the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox churches, and the individual national churches within the Anglican Communion. The way that such church law is legislative power, legislated, interpreted and at times court, adjudicated varies widely among these four bodies of churches. In all three traditions, a canon (canon law), canon was originally a rule adopted by a church council; these canons formed the foundation of canon law. Etymology Greek language, Greek / , Arabic language, Arabic / , Hebrew language, Hebrew / , 'straigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Christian Views On Divorce
Christian views on divorce find their basis both in biblical sources and in texts authored by the Church Fathers of the early Christian Church, who were unanimous in condemning the practice. Background According to the synoptic Gospels, Jesus emphasized the permanence of marriage (see Mark 10 at verses 1 to 12, Matthew 19; Luke 16:18) but also its integrity. In the King James Version of the Gospel of Mark, verses 11 and 12, Jesus says "Whosoever shall put away his wife, and marry another, committeth adultery against her. And if a woman shall put away her husband, and be married to another, she commits adultery." The Gospel of Luke adds that those who marry divorced persons also commit adultery, as recorded in Luke 16:18. 1 Corinthians 6:9–10 states that adulterers "shall not inherit the kingdom of God". The only lawful ground for divorce available to the innocent spouse is fornication, or adultery, on the part of the guilty mate, as recorded in Matthew 19:9. Nevertheless, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |