|
Law Of Constancy Of Interfacial Angles
The law of constancy of interfacial angles (; ) is an Empirical research, empirical law in the fields of crystallography and mineralogy concerning the shape, or morphology, of crystals. The law states that the angles between adjacent corresponding faces of crystals of a particular substance are always constant despite the different shapes, sizes, and mode of growth of crystals. The law is also named the ''first law of crystallography'' or ''Nicolas Steno, Steno's law''. Definition The International Union of Crystallography (IUCr) gives the following definition: "The law of the constancy of interfacial angles (or 'first law of crystallography') states that the angles between the crystal faces of a given species are constant, whatever the lateral extension of these faces and the origin of the crystal, and are characteristic of that species." The law is valid at constant temperature and pressure. This law is important in identifying different mineral species as small changes in at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Just Haüy
René Just Haüy () FRS MWS FRSE (28 February 1743 – 1 June 1822) was a French priest and mineralogist, commonly styled the Abbé Haüy after he was made an honorary canon of Notre-Dame de Paris, Notre Dame. Due to his innovative work on crystal structure and his four-volume ''Traité de Minéralogie'' (1801), he is often referred to as the "Father of Modern Crystallography". During the French Revolution he also helped to establish the metric system. Biography Early life René-Just Haüy was born at Saint-Just-en-Chaussée on February 28, 1743, in the Provinces of France, province of Picardy (later the ''département in France, département'' of Oise). His parents were Just Haüy, a poor linen-weaver, and his wife Magdeleine Candelot. Haüy's interest in the services and music of the local church brought him to the attention of the Prior (ecclesiastical), prior of a nearby abbey of Premonstratensians, Premonstrants. Through him, Haüy was introduced to a colleague in Paris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Rational Indices
The law of rational indices is an Empirical research, empirical law in the field of crystallography concerning crystal structure. The law states that "when referred to three intersecting axes all faces occurring on a crystal can be described by numerical indices which are integers, and that these integers are usually small numbers." The law is also named the ''law of rational intercepts'' or the ''second law of crystallography''. Definition The International Union of Crystallography (IUCr) gives the following definition: "The law of rational indices states that the intercepts, ''OP'', ''OQ'', ''OR'', of the natural faces of a crystal form with the unit-cell axes a, b, c are inversely proportional to prime integers, , , . They are called the Miller index, Miller indices of the face. They are usually small because the corresponding lattice planes are among the densest and have therefore a high interplanar spacing and low indices." History The law of constancy of interfacial ang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for lattice planes in crystal (Bravais) lattices. In particular, a family of lattice planes of a given (direct) Bravais lattice is determined by three integers ''h'', ''k'', and ''ℓ'', the ''Miller indices''. They are written (''hkℓ''), and denote the family of (parallel) lattice planes (of the given Bravais lattice) orthogonal to \mathbf_ = h\mathbf_1 + k\mathbf_2 + \ell\mathbf_3 , where \mathbf_i are the basis or primitive translation vectors of the reciprocal lattice for the given Bravais lattice. (Note that the plane is not always orthogonal to the linear combination of direct or original lattice vectors h\mathbf_1 + k\mathbf_2 + \ell\mathbf_3 because the direct lattice vectors need not be mutually orthogonal.) This is based on the fact that a reciprocal lattice vector \mathbf (the vector indicating a reciprocal lattice point from the reciprocal lattice origin) is the wavevector of a plane wave in the Fouri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleavage (crystal)
Cleavage, in mineralogy and materials science, is the tendency of crystalline materials to split along definite crystallographic structural planes. These planes of relative weakness are a result of the regular locations of atoms and ions in the crystal, which create smooth repeating surfaces that are visible both in the microscope and to the naked eye. If bonds in certain directions are weaker than others, the crystal will tend to split along the weakly bonded planes. These flat breaks are termed "cleavage".Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, '' Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., Wiley, The classic example of cleavage is mica, which cleaves in a single direction along the basal pinacoid, making the layers seem like pages in a book. In fact, mineralogists often refer to "books of mica". Diamond and graphite provide examples of cleavage. Each is composed solely of a single element, carbon. In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four others in a tetrahedral patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit very different physical or mechanical properties when measured along different axes, e.g. absorbance, refractive index, conductivity, and tensile strength. An example of anisotropy is light coming through a polarizer. Another is wood, which is easier to split along its grain than across it because of the directional non-uniformity of the grain (the grain is the same in one direction, not all directions). Fields of interest Computer graphics In the field of computer graphics, an anisotropic surface changes in appearance as it rotates about its geometric normal, as is the case with velvet. Anisotropic filtering (AF) is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures on surfaces that are far away and viewed at a shallow angle. Older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Growth
Crystal growth is a major stage of a crystallization, crystallization process, and consists of the addition of new atoms, ions, or polymer strings into the characteristic arrangement of the crystalline lattice. The growth typically follows an initial stage of either homogeneous or heterogeneous (surface catalyzed) nucleation, unless a "seed" crystal, purposely added to start the growth, was already present. The action of crystal growth yields a crystalline solid whose atoms or molecules are close packed, with fixed positions in space relative to each other. The crystalline states of matter, state of matter is characterized by a distinct structural rigidity and very high resistance to Plastic deformation in solids, deformation (i.e. changes of shape and/or volume). Most crystalline solids have high values both of Young's modulus and of the shear modulus of elasticity (physics), elasticity. This contrasts with most liquids or fluids, which have a low shear modulus, and typically exh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bravais Lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by : \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n_3 \mathbf_3, where the ''ni'' are any integers, and a''i'' are ''primitive translation vectors'', or ''primitive vectors'', which lie in different directions (not necessarily mutually perpendicular) and span the lattice. The choice of primitive vectors for a given Bravais lattice is not unique. A fundamental aspect of any Bravais lattice is that, for any choice of direction, the lattice appears exactly the same from each of the discrete lattice points when looking in that chosen direction. The Bravais lattice concept is used to formally define a ''crystalline arrangement'' and its (finite) frontiers. A crystal is made up of one or more atoms, called the ''basis'' or ''motif'', at each lattice point. The ''basis'' may consist of atoms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
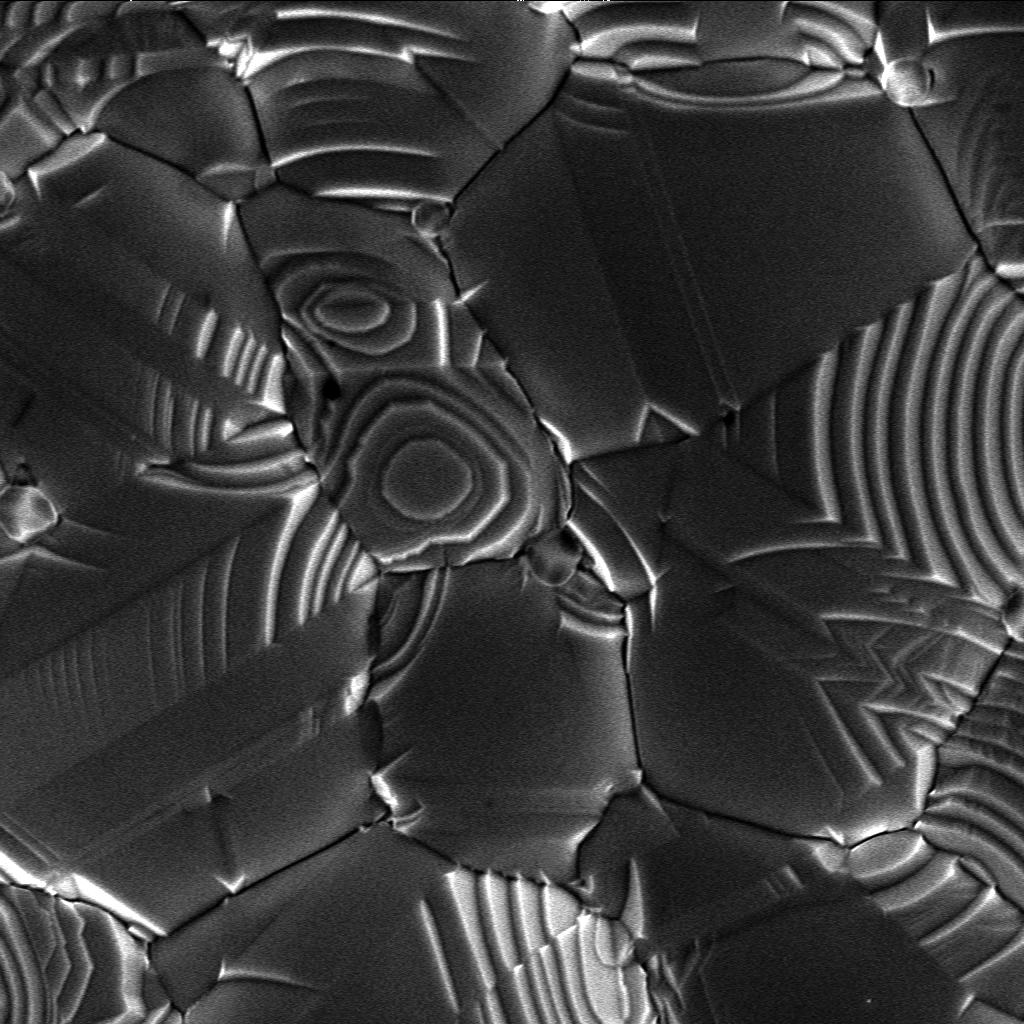
Cristal Densite Surface
Cristal may refer to: * Cristal Global, chemical company * Cristal (wine), a brand of champagne * Cristal (aguardiente), brands of aguardiente * ''Cristal'' (1985), a Venezuelan telenovela * ''Cristal'' (2006), a Brazilian telenovela * Cristal, Rio Grande do Sul, a city in Brazil * MS ''Cristal'', a cruise ship * Clube Atlético Cristal, a Brazilian football club * Cristal, a prize awarded at the Annecy International Animation Film Festival * Cristal, the iliac crest in supracristal plane * Bic Cristal, a brand of disposable ballpoint pens * Cristal, a typeface by French foundry Deberny & Peignot * ''Cristal'' (album), an album by Brazilian singer Simone Bittencourt de Oliveira * Cerveza Cristal, a Chilean brand of pilsner beer People with the surname * Linda Cristal (1931–2020), Argentine actress See also * Crystal (other) * Sporting Cristal Club Sporting Cristal S.A., shortened to Sporting Cristal, is a Peruvian sports club located in the city of Lima, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite ( ), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what is now called pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usually found associated with other sulfides or oxides in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecahedron
In geometry, a dodecahedron (; ) or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid. There are also three Kepler–Poinsot polyhedron, regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry, order 120. Some dodecahedra have the same combinatorial structure as the regular dodecahedron (in terms of the graph formed by its vertices and edges), but their pentagonal faces are not regular: The #Pyritohedron, pyritohedron, a common crystal form in pyrite, has pyritohedral symmetry, while the #Tetartoid, tetartoid has tetrahedral symmetry. The rhombic dodecahedron can be seen as a limiting case of the pyritohedron, and it has octahedral symmetry. The elongated dodecahedron and trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron variations, along with the rhombic dodecahedra, are space-filling polyhedra, space-filling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |