|
Labour Government, 1974–1979
The Labour Party governed the United Kingdom from 1974 to 1979. During this period, Harold Wilson and James Callaghan were successively appointed as Prime Minister by Queen Elizabeth II. The end of the Callaghan ministry was presaged by the Winter of Discontent, a period of serious industrial discontent. This was followed by the election of Conservative leader Margaret Thatcher in 1979. The government consisted of three ministries: the third and fourth Wilson ministry, and then the Callaghan ministry. __TOC__ History Formation Following the February 1974 general election, no party had a majority of seats. The incumbent Conservative Party won the popular vote, but Labour took a plurality of seats. Edward Heath, the Conservative Prime Minister, attempted to negotiate a coalition agreement with the Liberal Party, but resigned as prime minister after failing to do so. The Labour Party, led by Harold Wilson, then established a minority government, which took office on 4 Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Wilson
James Harold Wilson, Baron Wilson of Rievaulx (11 March 1916 – 23 May 1995) was a British statesman and Labour Party (UK), Labour Party politician who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, from 1964 to 1970 and again from 1974 to 1976. He was Leader of the Labour Party (UK), Leader of the Labour Party from 1963 to 1976, Leader of the Opposition (United Kingdom), Leader of the Opposition twice from 1963 to 1964 and again from 1970 to 1974, and a Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) from 1945 United Kingdom general election, 1945 to 1983 United Kingdom general election, 1983. Wilson is the only Labour leader to have formed administrations following four general elections. Born in Huddersfield, Yorkshire, to a politically active lower middle-class family, Wilson studied a combined degree of philosophy, politics and economics at Jesus College, Oxford. He was later an Economic History lecturer at New College, Oxford, and a research fello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
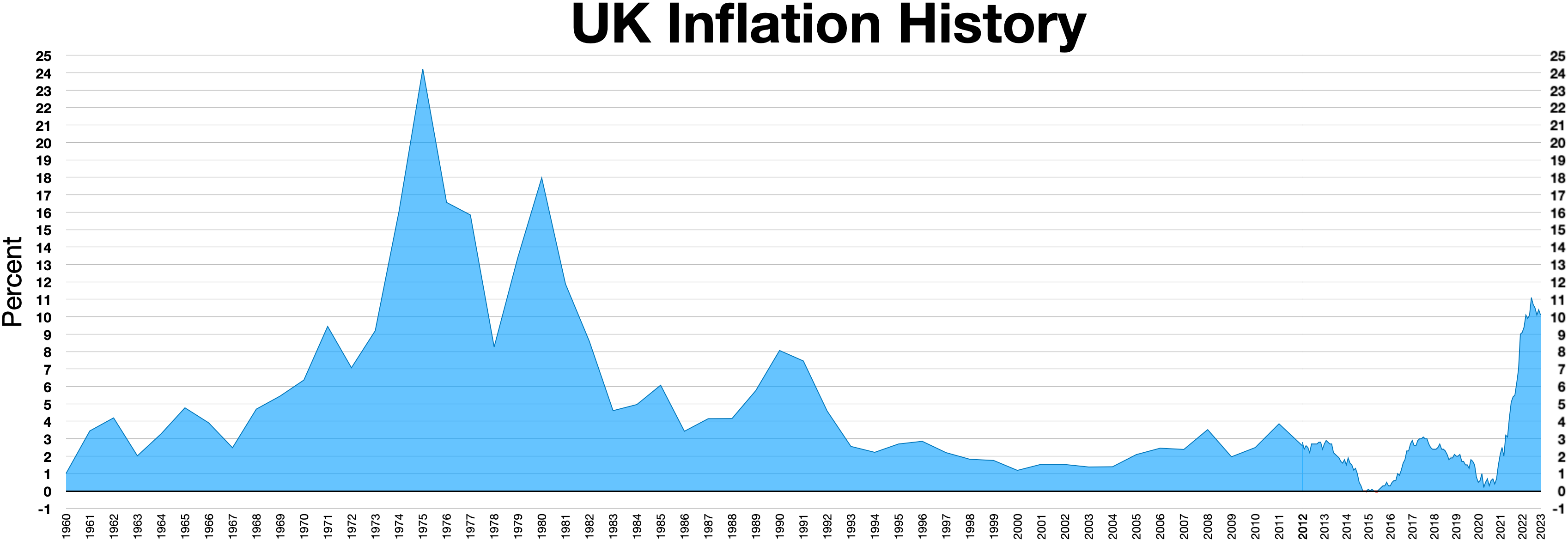
1976 Sterling Crisis
The 1976 sterling crisis was a currency crisis in the United Kingdom. Inflation (at close to 25% in 1975, causing high bond yields and borrowing costs), a balance-of-payments deficit, a public-spending deficit, and the 1973 oil crisis were contributors. The origins of the crisis have been attributed to the 1972 Conservative "spend for growth" budget initiating the inflation cycle. James Callaghan's Labour government had to borrow $3.9 billion from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), with the intention of maintaining the value of sterling. At the time this was the largest loan ever to have been requested from the IMF. History Initiation of the inflationary cycle is traced to Anthony Barber's 1972 budget which was designed to return the Conservatives to power in an election expected in 1974 or 1975. This budget led to a brief period of growth known as "The Barber Boom," followed by a wage-price spiral, high inflation and currency depreciation, culminating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-Contributory Invalidity Pension
Severe Disablement Allowance (SDA) was a United Kingdom state benefit intended for those below the state pension age who cannot work because of illness or disability. It was replaced by Incapacity Benefit in April 2001, which itself was replaced by Employment and Support Allowance. However, although it is no longer possible to make a claim for SDA, individuals who are already receiving the benefit have continued to do so. The benefit is administered by Jobcentre Plus (an executive agency of the Department for Work and Pensions). Eligibility An individual could have been eligible for Severe Disablement Allowance if: *they were assessed as being at least 80 per cent disabled and: **they were incapable of work because of illness or disability for at least 28 weeks in a row **they were between 16 and 64 years old It was also possible for claimants of Severe Disablement Allowance to receive a 'top-up' of Income Support Income Support is an income-related benefit in the United K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invalid Care Allowance
Carer's Allowance is a non-contributory benefit in the United Kingdom payable to people who care for a disabled person for at least 35 hours a week. It was first established as Invalid Care Allowance in 1976, and married women were not eligible. This policy was held to be unlawful sexual discrimination by the European Court in 1986 in the case of Jackie Drake. See Carers rights movement In May 2020 around 1.1 million people in England were entitled to Carer’s Allowance, of which 780,000 people were being paid it, according to the National Audit Office. Main conditions The claimant must be caring for a person who gets Disability Living Allowance (middle or higher rate for personal care), Attendance Allowance or Constant Attendance Allowance, Personal Independence Payment daily living component or Armed Forces Independence Payment and must care for them for at least 35 hours during the week. Residence conditions The claimant must have been present in Great Britain for 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Housing Rents And Subsidies Act 1975
Housing refers to a property containing one or more shelter as a living space. Housing spaces are inhabited either by individuals or a collective group of people. Housing is also referred to as a human need and human right, playing a critical role in shaping the quality of life for individuals, families, and communities. As a result, the quality and type of housing an individual or collective inhabits plays a large role in housing organization and housing policy. Overview Housing is a physical structure indented for dwelling, lodging or shelter that homes people and provides them with a place to reside. Housing includes a wide range of sub-genres from apartments and houses to temporary shelters and emergency accommodations. Access to safe, affordable, and stable housing is essential for a person to achieve optimal health, safety, and overall well-being. Housing affects economic, social, and cultural opportunities as it is directly linked to education, employment, healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rehabilitation Of Offenders Act 1974
The Rehabilitation of Offenders Act 1974 (c. 53) of the UK Parliament enables some criminal convictions to be ignored after a rehabilitation period. Its purpose is that people do not have a lifelong blot on their records because of a relatively minor offence in their past. The rehabilitation period is automatically determined by the sentence. After this period, if there has been no further conviction the conviction is "spent" and, with certain exceptions, need not be disclosed by the ex-offender in any context such as when applying for a job, obtaining insurance, or in civil proceedings. A conviction for the purposes of the ROA includes a conviction issued outside Great Britain (see s1(4) of the 1974 Act) and therefore foreign convictions are eligible to receive the protection of the ROA. Under the Legal Aid, Sentencing and Punishment of Offenders Act 2012 (section 139), the act as it applies in England and Wales was updated to provide new rehabilitation periods – with mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Commission
The Price Commission was set up in the UK under the Counter-Inflation Act 1973, alongside the Pay Board, in an attempt to control inflation. The Conservative government of Edward Heath, elected at the 1970 general election, had previously abolished the Prices and Incomes Board in November 1970, shortly after taking power, relying on competition to keep prices down. At the same time, the Industrial Relations Act 1971 was intended to rein in the trades unions. The Conservatives' economic policy was not successful, and the government took a U-turn. A 90-day freeze of pay and prices (as well as rents and dividends) was introduced on 6 November 1972 under the Counter-Inflation (Temporary Provisions) Act 1972. This was replaced by a Price and Pay Code, which strictly limited increases, supervised by a new Price Commission and a Pay Board. The Conservatives were unable to keep power after the inconclusive February 1974 UK general election, and the Pay Board was abolished in Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manpower Services Commission
The Manpower Services Commission (MSC) was a non-departmental public body of the Department of Employment in the United Kingdom created by Edward Heath's Conservative Government on 1 January 1974 under the terms of the Employment and Training Act 1973. The MSC had a remit to co-ordinate employment and training services in the UK through a ten-member commission drawn from industry, trade unions, local authorities and education interests. This was an example of the contemporary corporatist influence on British economic policy. MSC agencies The MSC originally had two executive agencies, the Employment Services Agency and the Training Services Agency. A third agency the Special Programmes Division was established, the body was led by Geoffrey Holland of the Policy and Planning Division under the overall management of Sir John Cassells. The Policy and Planning Division was initially based in Selkirk House, High Holborn, London and later moved to the Moorfoot Building in S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Jones (trade Unionist)
James Larkin Jones (29 March 1913 – 21 April 2009), known as Jack Jones, was a British trade union leader and General Secretary of the Transport and General Workers' Union. Early life Jones was born in Garston, Liverpool, Lancashire. He was named after the Liverpool-born Irish trade unionist James Larkin. He left school at 14 and worked as an engineering apprentice. After the Wall Street crash, Jones lost his job, eventually finding employment with a firm of signmakers and painters. He then joined his father as a Liverpool docker. Jack Jones was converted to socialism by reading '' The Ragged Trousered Philanthropists'' by Robert Tressell, and he later explained how the book "was passed from hand to hand among people in the Labour movement and had a remarkable effect on our thinking". He became a member of the Transport and General Workers Union, and was elected shop steward, then a delegate on the National Docks Group Committee. Spanish Civil War Strongly opposed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acas
The Advisory, Conciliation and Arbitration Service (Acas) is a non-departmental public body of the Her Majesty's Government, Government of the United Kingdom. Its purpose is to improve organisations and working life through the promotion and facilitation of strong industrial relations practice. Acas provides employment law and employment relations advice for employers and employees through its website and helpline. It also offers dispute resolution services such as arbitration or mediation, although the service is perhaps best known for its collective conciliation function – that is resolving disputes between groups of employees or workers, often represented by a trade union, and their employers. Acas is an independent and impartial organisation that does not side with a particular party, but rather will help the parties to reach suitable resolutions in a dispute. Today, the employment world has mostly moved away from large-scale industrial disputes that characterised the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |