|
Labour Law Of The People's Republic Of China
The Labour Law of the People's Republic of China () is the basic labour law of China, which has been enforced since 1995. It was promulgated by the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress of China on July 5, 1994, and came into effect on January 1, 1995. It is sometimes confused with the Labour Contract Law of the People's Republic of China because of their similar names and focuses, as well as imprecise media reports. As the Labour Contract Law is more recent, having gone into effect January 1, 2008, the Labour Law is also sometimes called the "old labour law", though this is incorrect as both are still in effect simultaneously. Contents of the law The law has 107 articles in 13 chapters. The titles of all the chapters are listed below. # General Provisions # Promotion of Employment # Labour Contracts and Collective Contracts # Working Hours, Rests, and Leaves # Wages # Labour Safety and Sanitation # Special Protection for Female Staff and Workers and Juvenile Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour Law
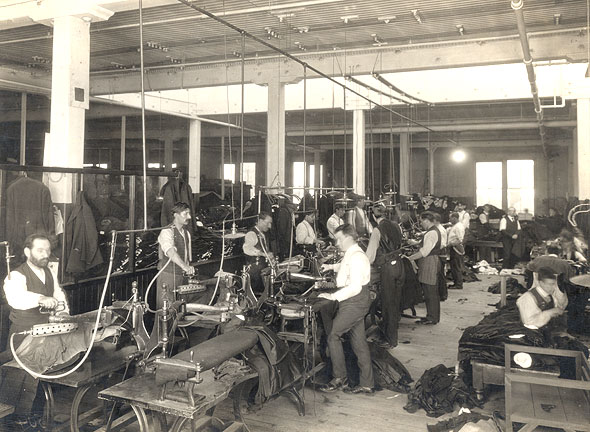
Labour laws (also spelled as labor laws), labour code or employment laws are those that mediate the relationship between workers, employing entities, trade unions, and the government. Collective labour law relates to the tripartite relationship between employee, employer, and union. Individual labour law concerns employees' rights at work also through the contract for work. are social norms (in some cases also technical standards) for the minimum socially acceptable conditions under which employees or contractors are allowed to work. Government agencies (such as the former US Employment Standards Administration) enforce labour law (legislature, regulatory, or judicial). History Following the unification of the List of cities of the ancient Near East, city-states in Assyria and Sumer by Sargon of Akkad into a Akkadian Empire, single empire ruled from his Akkad (city), home city circa 2334 BC, Ancient Mesopotamian units of measurement, common Mesopotamian standards for length, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Committee Of The National People's Congress
The Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (NPCSC) is the permanent body of the National People's Congress (NPC), the national legislature of the People's Republic of China. It exercises the powers of the NPC when it is not in session. The NPCSC is composed of a chairman, vice chairpersons, a secretary-general, and regular members, all of whom are elected by regular NPC sessions. The day-to-day operations of the Standing Committee are handled by the Council of Chairpersons, which is composed of the chairman, vice chairpersons, and the secretary-general. Although the parent NPC officially has superiority over the Standing Committee, and certain authorities are not delegated, the Standing Committee is generally viewed to have more ''de facto'' power, as the NPC convenes only once a year for two weeks, leaving its Standing Committee the only body that regularly drafts and approves decisions and laws. History In 1954, the 1st National People's Congress was held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour Contract Law Of The People's Republic Of China
The ''Labour Contract Law of the People's Republic of China'' () is the primary source of labour law in China and went into effect on January 1, 2008, following a series of staff- sacking scandals in many companies. The Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of the People's Republic of China is the responsible government department for administrating this law. The Law While the enforcement of the law and its efficacity is sometimes questioned, the labor contract law promised to enable workers to get their employment granted only on basis of a contract, provide guidelines for standing working hour regulations of maximum 40 hours per week, non-tolerance for delayed payment of wages, relaxations in terms of paid leave etc. Background The All-China Federation of Trade Unions (ACFTU) had the major role in advancing the Labor Contract Law. The ACFTU drafted the law and proposed it to the National People's Congress. The NPC conducted research trips to regions with labor-int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Insurance
Social insurance is a form of Social protection, social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of Welfare spending, social assistance, individuals' claims are partly dependent on their contributions, which can be considered insurance premiums to create a common fund out of which the individuals are then paid benefits in the future. Types of social insurance include: * Universal health care, Public health insurance * Social Security (United States), Social Security * Unemployment Insurance, Public Unemployment Insurance * Public auto insurance * Parental leave, Universal parental leave Features * The contributions of individuals is nominal and never goes beyond what they can afford * the Social welfare, benefits, eligibility requirements and other aspects of the program are defined by statute; * explicit provision is made to account for the incom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employment
Employment is a relationship between two party (law), parties Regulation, regulating the provision of paid Labour (human activity), labour services. Usually based on a employment contract, contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other entity, pays the other, the employee, in return for carrying out assigned work. Employees work in return for wage, wages, which can be paid on the basis of an hourly rate, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does, the prevailing conditions of the sector and the bargaining power between the parties. Employees in some sectors may receive gratuity, gratuities, bonus payments or employee stock option, stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits may include health insurance, housing, and disability insurance. Employment is typically governed by Labour law, employment laws, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Agreement
A collective agreement, collective labour agreement (CLA) or collective bargaining agreement (CBA) is a written contract negotiated through collective bargaining for employees by one or more trade unions with the management of a company (or with an employers' association) that regulates the terms and conditions of employees at work. This includes regulating the wages, benefits, and duties of the employees and the duties and responsibilities of the employer or employers and often includes rules for a dispute resolution process. Finland In Finland, collective labour agreements are universally valid. This means that a collective agreement in an economic sector becomes a universally applicable legal minimum for any individual's employment contract, whether or not they are a union member. For this condition to apply, half of the workforce in that sector needs to be union members, thus supporting the agreement. Workers are not forced to join a union in a specific workplace. Neverthele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Bargaining
Collective bargaining is a process of negotiation between employers and a group of employees aimed at agreements to regulate working salaries, working conditions, benefits, and other aspects of workers' compensation and labour rights, rights for workers. The interests of the employees are commonly presented by representatives of a trade union to which the employees belong. A collective agreement reached by these negotiations functions as a Labor and employment law, labour contract between an employer and one or more unions, and typically establishes terms regarding wage scales, working hours, training, health and safety, overtime, Grievance (labour), grievance mechanisms, and rights to participate in workplace or company affairs. Such agreements can also include 'productivity bargaining' in which workers agree to changes to working practices in return for higher pay or greater job security. The union may negotiate with a single employer (who is typically representing a company's s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleaner Production Promotion Law
Cleaner Production Promotion Law was approved by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress (NPC) of the People’s Republic of China in the 28th Session on June 29, 2002. The law was enacted to promote cleaner production, increase the efficiency of the utilization rate of resources, reduce and avoid the generation of pollutants, protect and improve environments, ensure the health of human beings and promote the sustainable development of the economy and society. Article 28 of the law stipulates that: "Enterprises shall monitor resource consumption Resource consumption is about the consumption of non-renewable, or less often, renewable resources. Specifically, it may refer to: * water consumption * energy consumption ** electric energy consumption ** world energy consumption * natural ... and generation of wastes during the course of production and provision of services, and conduct cleaner production audits with respect to production and service procedu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laws Of China
Chinese law is one of the oldest law, legal traditions in the world. The core of modern Chinese law is based on Germanic-style civil law (legal system), civil law, socialist law, and Traditional Chinese law, traditional Chinese approaches. For most of the history of China, its legal system has been based on the Confucianism, Confucian philosophy of social control through moral education, as well as the Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalist emphasis on legal code, codified law and punishment, criminal sanction. Following the Xinhai Revolution, the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China adopted a largely Western-style legal code in the Civil law (legal system), civil law tradition (specifically German law, German and Law of Switzerland, Swiss based). The establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949 brought with it a more USSR, Soviet-influenced system of socialist law#Chinese Socialist law, socialist law. However, earlier traditions from Chinese history h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Relations In China
As the economy of the People's Republic of China has developed, issues of labor relations have evolved. Prior to the Chinese economic reform, Chinese citizens were only allowed to work where they originated from. Since 1978, when China began labor force reforms, the overwhelming majority of the labor force were either working at State owned enterprises or as farm workers in the rural countryside. However, over time China began to reform and by the late 90's many had moved from the countryside into the cities in hopes of higher paying jobs and more opportunities. The only connection between the countryside and the city soon became that there was a huge floating population connecting them. Independent unions are illegal in China with only the All-China Federation of Trade Unions (ACFTU) permitted by the Chinese state and the Chinese Communist Party to operate. China has been the largest exporter of goods in the world since 2009. Not only that, in 2013 China became the largest tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Labour Law
Labour laws (also spelled as labor laws), labour code or employment laws are those that mediate the relationship between workers, employing entities, trade unions, and the government. Collective labour law relates to the tripartite relationship between employee, employer, and union. Individual labour law concerns employees' rights at work also through the contract for work. are social norms (in some cases also technical standards) for the minimum socially acceptable conditions under which employees or contractors are allowed to work. Government agencies (such as the former US Employment Standards Administration) enforce labour law (legislature, regulatory, or judicial). History Following the unification of the city-states in Assyria and Sumer by Sargon of Akkad into a single empire ruled from his home city circa 2334 BC, common Mesopotamian standards for length, area, volume, weight, and time used by artisan guilds in each city was promulgated by Naram-Sin of Akkad (c. 2254� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |