|
Leonidas
Leonidas I (; , ''Leōnídas''; born ; died 11 August 480 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. He was the son of king Anaxandridas II and the 17th king of the Agiad dynasty, a Spartan royal house which claimed descent from the mythical demigod Heracles. Leonidas I ascended to the throne in , succeeding his half-brother king Cleomenes I. He ruled jointly along with king Leotychidas until his death in 480 BC, when he was succeeded by his son, Pleistarchus. At the Second Greco-Persian War, Leonidas led the allied Greek forces in a last stand at the Battle of Thermopylae (480 BC), attempting to defend the pass from the invading Persian army, and was killed early during the third and last day of the battle. Leonidas entered myth as a hero and the leader of the 300 Spartans who died in battle at Thermopylae. While the Greeks lost this battle, they were able to expel the Persian invaders in the following year. Life According to Herodotus, Leonidas' mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Polis, Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Graeco-Persian Wars. The engagement at Thermopylae occurred simultaneously with the naval Battle of Artemisium: between July and September during 480 BC. The second Persians, Persian invasion under Xerxes I was a delayed response to the failure of the first Persian invasion of Greece, first Persian invasion, which had been initiated by Darius the Great, Darius I and ended in 490 BC by an Classical Athens, Athenian-led Ancient Greece, Greek victory at the Battle of Marathon. By 480 BC, a decade after the Persian defeat at Marathon, Greece, Marathon, Xerxes had amassed a massive land and naval force, and subsequently set out to conquer all of Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
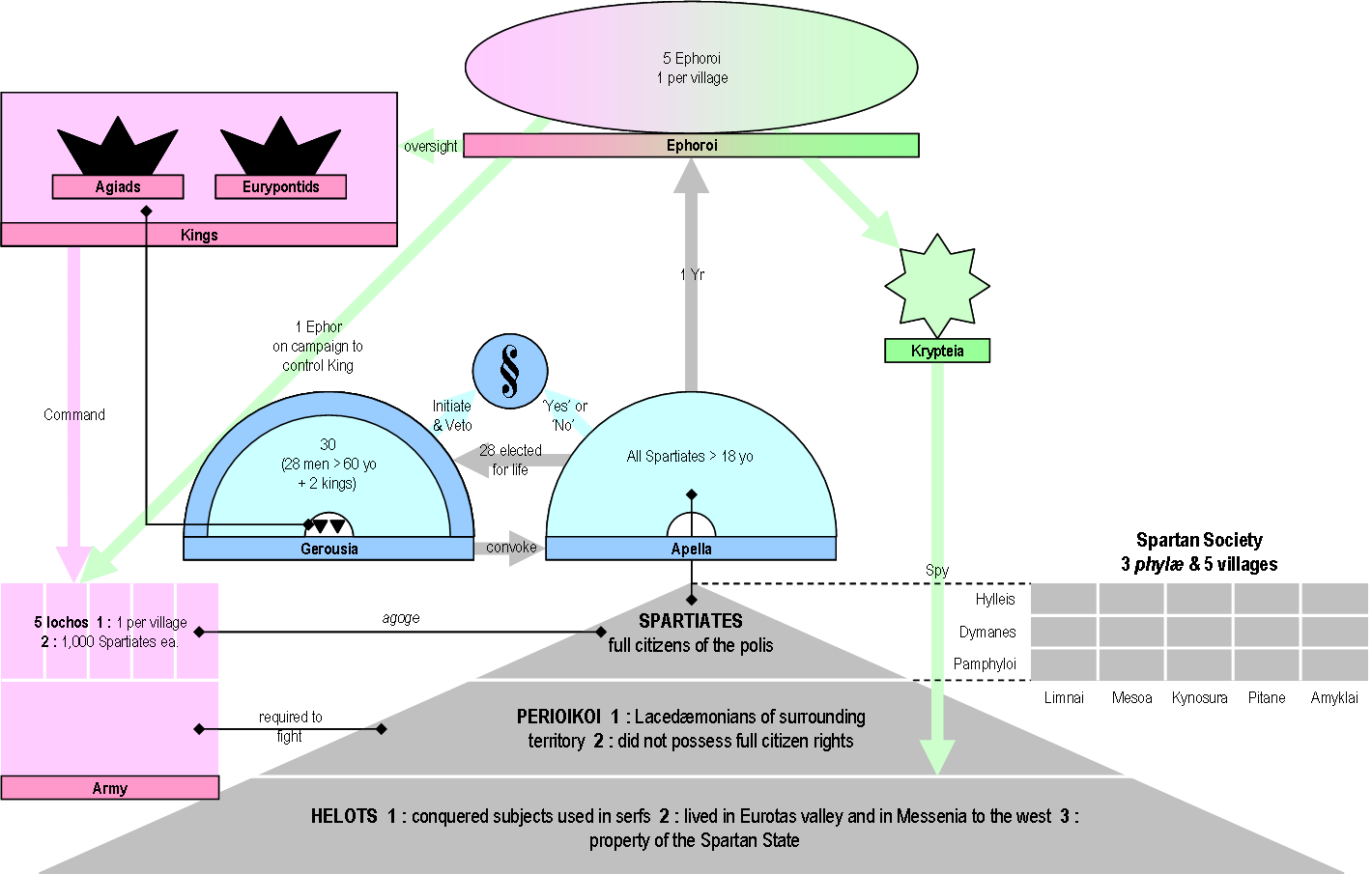
Agiad
The Agiad dynasty (, ''Agiádai'') was one of the two royal families of the ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. They ruled jointly along with the Eurypontid dynasty, possibly from the 8th century BC onwards, being the senior of the two houses. The hypothetical founder of the dynasty was Agis I, possibly the first king of Sparta at the end of the 10th century BC, who subsequently gave his name to the dynasty. The two lines, who maintained an enduring rivalry, were, according to tradition, respectively descended from the twins Eurysthenes and Procles, both descendants of Heracles. The most famous member of the Agiad dynasty was Leonidas I, known for his heroic death at the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. The last Agiad king was Agesipolis III, deposed by the Eurypontid Lycurgus in 215 BC. History In order to explain the peculiarity of the Spartan two kings, the Spartans elaborated a legend saying that Aristodemos—the first king of Sparta—had twins, Eurysthenes and Prokle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agiad Dynasty
The Agiad dynasty (, ''Agiádai'') was one of the two royal families of the ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. They ruled jointly along with the Eurypontid dynasty, possibly from the 8th century BC onwards, being the senior of the two houses. The hypothetical founder of the dynasty was Agis I, possibly the first king of Sparta at the end of the 10th century BC, who subsequently gave his name to the dynasty. The two lines, who maintained an enduring rivalry, were, according to tradition, respectively descended from the twins Eurysthenes and Procles, both descendants of Heracles. The most famous member of the Agiad dynasty was Leonidas I, known for his heroic death at the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. The last Agiad king was Agesipolis III, deposed by the Eurypontid Lycurgus in 215 BC. History In order to explain the peculiarity of the Spartan two kings, the Spartans elaborated a legend saying that Aristodemos—the first king of Sparta—had twins, Eurysthenes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgo, Queen Of Sparta
Gorgo (; ; fl. 480 BC) was a Spartan woman and wife to King Leonidas I (r. 489–480 BC). She was the daughter and the only known child of Cleomenes I, Leonidas' half-brother and King of Sparta (r. 520–490 BC). Gorgo was also the mother of King Pleistarchus, her only son with King Leonidas I. She is notably one of the few female historical figures actually named by Herodotus, and is depicted in sources as intelligent and wise. Her birth date is uncertain, but based on Herodotus' dating, it is most likely to have been between 518 and 508 BC. Early life and education According to Herodotus, Gorgo was the only child of King Cleomenes I of Sparta. The earliest anecdote of her life that he provides in '' The Histories'' comes when Aristagoras, seeking allies after the Ionian revolt, came to Sparta to try to convince Cleomenes to invade the Persian Empire. He cited the "disgrace" suffered by the Ionians in Anatolia and wove further tales of the wealth and resources to be reaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleomenes I
Cleomenes I (; Greek Κλεομένης; died c. 490 BC) was Agiad King of Sparta from c. 524 to c. 490 BC. One of the most important Spartan kings, Cleomenes was instrumental in organising the Greek resistance against the Persian Empire of Darius, as well as shaping the geopolitical balance of Classical Greece. Herodotus' account Most of the life of Cleomenes is known through the '' Histories'' of Herodotus, an Athenian historian of the second half of the 5th century. He is one the most important characters of books 5 and 6, covering the decades before the Persian Wars. Herodotus' account however contains many mistakes, especially on the chronology of several major events, and is also very biased against Cleomenes. It seems that Herodotus got his information on Cleomenes from his opponents: the descendants of his half-brothers Leonidas and Cleombrotus, as well as those of Demaratus, the other Spartan king who was deposed by Cleomenes in 491.Cartledge, ''Sparta and Lakonia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Persian Invasion Of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece (492–490 BC) at the Battle of Marathon, which ended Darius I's attempts to subjugate Greece. After Darius's death, his son Xerxes spent several years planning for the second invasion, mustering an enormous army and navy. The Athenians and Spartans led the Greek resistance. About a tenth of the Greek city-states joined the 'Allied' effort; most remained neutral or submitted to Xerxes. The invasion began in spring 480 BC, when the Persian army crossed the Hellespont and marched through Thrace and Macedon to Thessaly. The Persian advance was blocked at the pass of Thermopylae by a small Allied force under King Leonidas I of Sparta; simultaneously, the Persian fleet was blocked by an Allied fleet at the straits of Artemisium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistarchus
Pleistarchus ( ; died 458 BC) was the List of kings of Sparta, Agiad King of Sparta from 480 to 458 BC. Biography Pleistarchus was born as a prince, likely the only son of King Leonidas I and Gorgo, Queen of Sparta, Queen Gorgo. His grandparents were Kings Anaxandridas II and Cleomenes I. He was born from an avunculate marriage – his parents were uncle and Nephew and niece, niece. His uncle Cleombrotus (regent), Cleombrotus was his tutor. Pleistarchus' father King Leonidas perished in 480 BC at the Battle of Thermopylae. For the early part of Pleistarchus's reign, his uncle Cleombrotus acted as regent; after Cleombrotus's death in 479 BC, Pleistarchus's cousin Pausanias the Regent, Pausanias was regent. It is unknown whether Pleistarchus was married. He died without an heir, and was succeeded by Pleistoanax, son of Pausanias. He had no known surviving relatives after his death, marking the end of his bloodline. Notes [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta, Laconia
Sparta (, ) is a city and municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. It lies at the site of ancient Sparta within the Evrotas Valley. The municipality was merged with six nearby municipalities in 2011, for a total population (as of 2021) of 32,786, of whom 17,773 lived in the city. History Beginning in the 13th century, the political and cultural center of Laconia shifted to Mystras, some 4 km to the west. The settlement at ancient Sparta, named Lacedaemonia, continued to exist, although greatly depopulated, until modern times as a town of a few thousand people who lived among the ruins, in the shadow of Mystras. The Palaiologos family (the last Byzantine Greek imperial dynasty) also lived in Mystras. The Despotate of the Morea was captured by the Ottomans under Mehmed II in 1460. In 1834, after the Greek War of Independence, King Otto of Greece decreed the town should be expanded into a city. Modern-day Sparta, the capital of the prefecture of Lakonia, lies on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephor
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs. The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves. The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions. Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. p. 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, . Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras or Cyre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleombrotus (regent)
Cleombrotus (, ''Kleómbrotos''), regent of Sparta between 480 and 479 BC. He was a member of the Agiad dynasty, the son of Anaxandridas II and the brother of Cleomenes I, Dorieus and of Leonidas I. When the latter died, he became the tutor of his nephew Pleistarchus, son of Leonidas, and leader of the Greek infantry at the beginning of the second phase of the Greco-Persian Wars. Cleombrotus was in command of the Spartan and Peloponnesian troops who built the wall across the Isthmus of Corinth that was intended to keep the Persian army out of the Peloponnese. He died soon after returning to Sparta from the Isthmus. He was the father of Pausanias and the Spartan general Nicomedes.Thucydides I,107. Notes References *Herodotus ''The Greek–Persian War'' (Osiris, Budapest, 2000), . Government of Sparta 5th-century BC Spartans Spartans of the Greco-Persian Wars Ancient Greek regents Agiad dynasty 479 deaths {{Greece-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon Of Sparta
Leon () was the 14th Agiad dynasty King of Sparta, ruling from 590 BC to 560 BC. Name ''Leon'' means "lion". The grandson of Leon had a similar name: Leonidas. Biography Leon is mentioned in the seventh book of '' The Histories'' by Herodotus. He is said to have, like his father, fought to a draw with the Tegeans. Grandfather to Leonidis (famous king) Family Leon was the son of king Eurycratides and grandson of Anaxander. He was succeeded on the throne A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign (or viceroy A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory ... by his son Anaxandridas II, who managed to defeat Tegea. Family tree ...
|