|
Kőszegi Family
The Kőszegi () was a noble family in the Kingdom of Hungary and the Kingdom of Croatia in the 13th and 14th centuries. The ancestor of the family, Henry the Great, descended from the ''gens'' ("clan") Héder. Henry's paternal great-grandfather was the clan's co-founder Wolfer. Notable members * Henry I the Great (fl. 1237–1274), Palatine of Hungary ** Nicholas I (fl. 1266–1299), Palatine of Hungary *** Nicholas II (fl. 1314–1332), Master of the horse, ancestor of the ''Rohonci family'' *** John, ancestor of the ''Béri family'' ** Ivan (fl. 1266–1308), Palatine of Hungary *** Gregory (fl. 1287–1297), Master of the stewards for the Prince **** Nicholas III (fl. 1308–1313), Master of the treasury **** Andrew (fl. 1311–1324), ''ispán'' of Vas County; last member who bore the Kőszegi nameEngel: ''Genealógia'' (Genus Héder 4., Kőszegi branch) *** a daughter, married Dominic Csák (?) *** John the "Wolf" (fl. 1325–1382), ancestor of the ''Bernst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAPPEN GUENSER
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas III Kőszegi
Nicholas (III) Kőszegi (; died early 1314) was a Hungarian lord in the early 14th century, who served as Master of the treasury in 1307 and from 1311 to 1314. Family Nicholas was born around 1285 into the powerful and wealthy Kőszegi family, as one of the two sons of Gregory. His younger brother was Andrew.Engel: ''Genealógia'' (Genus Héder 4. Kőszegi nd Rohoncibranch) His father was killed by a lightning strike in 1297, leaving the child Nicholas as the heir of his grandfather Ivan, who had established a province in Western Transdanubia independently of the royal power. Nicholas had no descendants. Career Nicholas first appeared in contemporary records in February 1307, when he was referred to as Master of the treasury in the court of Otto of Bavaria, one of the pretenders to the Hungarian throne, whose aspirations was supported by Ivan Kőszegi. Nicholas lost the dignity still in that year, as Otto was captured and imprisoned by Ladislaus Kán in the following months. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ban Of Slavonia
Ban of Slavonia (; ; ) sometimes also Ban of "Whole Slavonia" (; ; ), was the title of the governor of a territory part of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary and Croatia in union with Hungary, Kingdom of Croatia. From 1102, the title Ban (title), Ban of Croatia was appointed by the king of Hungary, kings of Hungary, and there was at first a single ban for all of the Kingdom of Croatia and Dalmatia, but later the Slavonian domain got a separate ban. It included parts of present-day Central Croatia, western Slavonia and parts of northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. From 1225, the title started being held by a separate dignitary from the title of the Ban of Croatia, Ban of Croatia and Dalmatia, and existed until 1476, when it was joined with the latter title. In the 13th century, 13th and 14th century, 14th centuries, the more extensive title of Duke of Slavonia (meaning all lands of the Kingdom of Croatia and Dalmatia and Slavonian domain) was granted, mainly to relatives of King of Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Kőszegi
Henry (II) Kőszegi (, , ; died between March and May 1310) was a Hungarian influential lord at the turn of the 13th and 14th centuries. He was a member of the powerful Kőszegi family. He extended his influence over Slavonia, Upper Slavonia since the 1280s, becoming one of the so-called "Oligarch (Kingdom of Hungary), oligarchs", who ruled their dominion ''de facto'' independently of the monarch. After the extinction of the Árpád dynasty, House of Árpád, he participated in the dynastic struggles. He drew Transdanubia, Southern Transdanubia under his suzerainty by then. He served as Ban of Slavonia three times (1290–1291, 1293, 1301–1310) and Master of the treasury (1302–1305). After his death, Charles I of Hungary defeated his sons and eliminated their province in 1316. Through his two sons, Henry Kőszegi was the progenitor of the Tamási family, Tamási and Herceg family, Herceg de Szekcső noble families. Family Henry II was born into the powerful and wealthy Kősze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Veszprém
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role or office of the bishop is called episcopacy or the episcopate. Organisationally, several Christian denominations utilise ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority within their dioceses. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Kőszegi
Peter Kőszegi (; killed May 1289) was a Hungarian prelate in the 13th century, who served as Bishop of Veszprém from 1275 until his death. He was also unrecognized Archbishop-elect of Esztergom between 1277 and 1278. As a member of the powerful Kőszegi family, he subordinated his diocese to his family's political interests in order to extend their influence over Western Hungary. Background Peter was born in the second half of the 1240s into the influential and wealthy Kőszegi family, as one of the four sons of the powerful lord Henry I Kőszegi.Engel: ''Genealógia'' (Genus Héder 4. Kőszegi nd Rohoncibranch) His three brothers – Nicholas I, Ivan and the much younger Henry II – were elevated into high dignities during the age of the late Árpáds. When the minor Ladislaus IV of Hungary ascended the Hungarian throne in 1272, the kingdom fell into anarchy and many groupings of barons fought against each other for supreme power. Peter's father Henry was one of the key fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Győr
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role or office of the bishop is called episcopacy or the episcopate. Organisationally, several Christian denominations utilise ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority within their dioceses. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illegitimate Child
Legitimacy, in traditional Western common law, is the status of a child born to parents who are legally married to each other, and of a child conceived before the parents obtain a legal divorce. Conversely, ''illegitimacy'', also known as ''bastardy'', has been the status of a child born outside marriage, such a child being known as a bastard, a love child, a natural child, or illegitimate. In Scots law, the terms natural son and natural daughter carry the same implications. The importance of legitimacy has decreased substantially in Western countries since the sexual revolution of the 1960s and 1970s and the declining influence of Christian churches in family and social life. A 2009 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicated that in 2007 a substantial proportion of births in Western countries occurred outside marriage. Law England's Statute of Merton (1235) stated, regarding illegitimacy: "He is a bastard that is born before the marriage of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Kőszegi (bishop)
Nicholas Kőszegi (; 1282 – April/July 1336) was a Hungarian prelate in the 14th century, who served as Bishop of Győr from 1308 until his death. He was an illegitimate son of the powerful lord Ivan Kőszegi. His ambivalent relationship with the rebellious Kőszegi family overshadowed most of his governance as bishop. His ecclesiastical career rose to its peak due to the pressure and influence of his kinship, but later he pledged alliance to Charles I of Hungary, despite the king's distrust. Early life Nicholas was an illegitimate descendant of the Kőszegi family, according to a letter of Pope Clement V. His parentage is uncertain; initially, 19th-century historian Antal Pór considered he was the son of Ivan Kőszegi, then modified his standpoint and claimed his father was Gregory, Ivan's son. Genealogist Pál Engel placed his name on the family tree as the son of Ivan's brother, another powerful oligarch Henry Kőszegi, but without explanation and reference.Engel: ''Genea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iban Von Bernstein
Iban ''Graf'' von Bernstein (born John Kőszegi, also known as John the Wolf; ; 1300s – after 1382) was a Hungarian-born Austrian nobleman in the 14th century. He was a member of the powerful Kőszegi family, of which he became head in 1324. He launched plundering raids against both the Kingdom of Hungary and the Duchy of Austria. After his defeat and downfall in Hungary in 1327, he settled down in Styria and pledged allegiance to the House of Habsburg. Gradually integrating into the Austrian nobility, he became forefather of the Bernstein (or Pernstein) family. Origins John the Wolf was born into the illustrious Kőszegi family as the son of the powerful oligarch Ivan Kőszegi. He was born in the 1300s, not long before the death of his elderly father (April 1308), as he first appeared in contemporary records only in 1325, and Ivan's province in Western Transdanubia was inherited by John's nephews Nicholas III, then Andrew, who were definitely older than their uncle. In Septemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominic Csák
Dominic from the kindred Csák (; died after 1300) was a Hungarian lord in the 13th century. Initially, he was a confidant of '' rex iunior'' Stephen, but later joined the partisans of the elderly Béla IV of Hungary. During the era of feudal anarchy, he served as a courtier of Queen Dowager Elizabeth the Cuman. Family Dominic was born into the Dobóc (or Orbova) branch of the ''gens'' (clan) Csák as the son of Peter (I). Formerly, 19th-century genealogist Iván Nagy considered that Dominic belonged to the clan's Újlak branch.Engel: ''Genealógia'' (Genus Csák 2., Dobóc rbovabranch) He had three brothers, Michael, who served as ''ispán'' of Veszprém County in 1272, Simon and possibly Beers. Dominic had three sons from his marriage with an unidentified noblewoman: Nicholas, Stephen (I) and Peter (II). All of them were first mentioned by contemporary records in 1280. Dominic's branch became extinct by the middle of the 14th century. Some historians – including Renáta Skor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
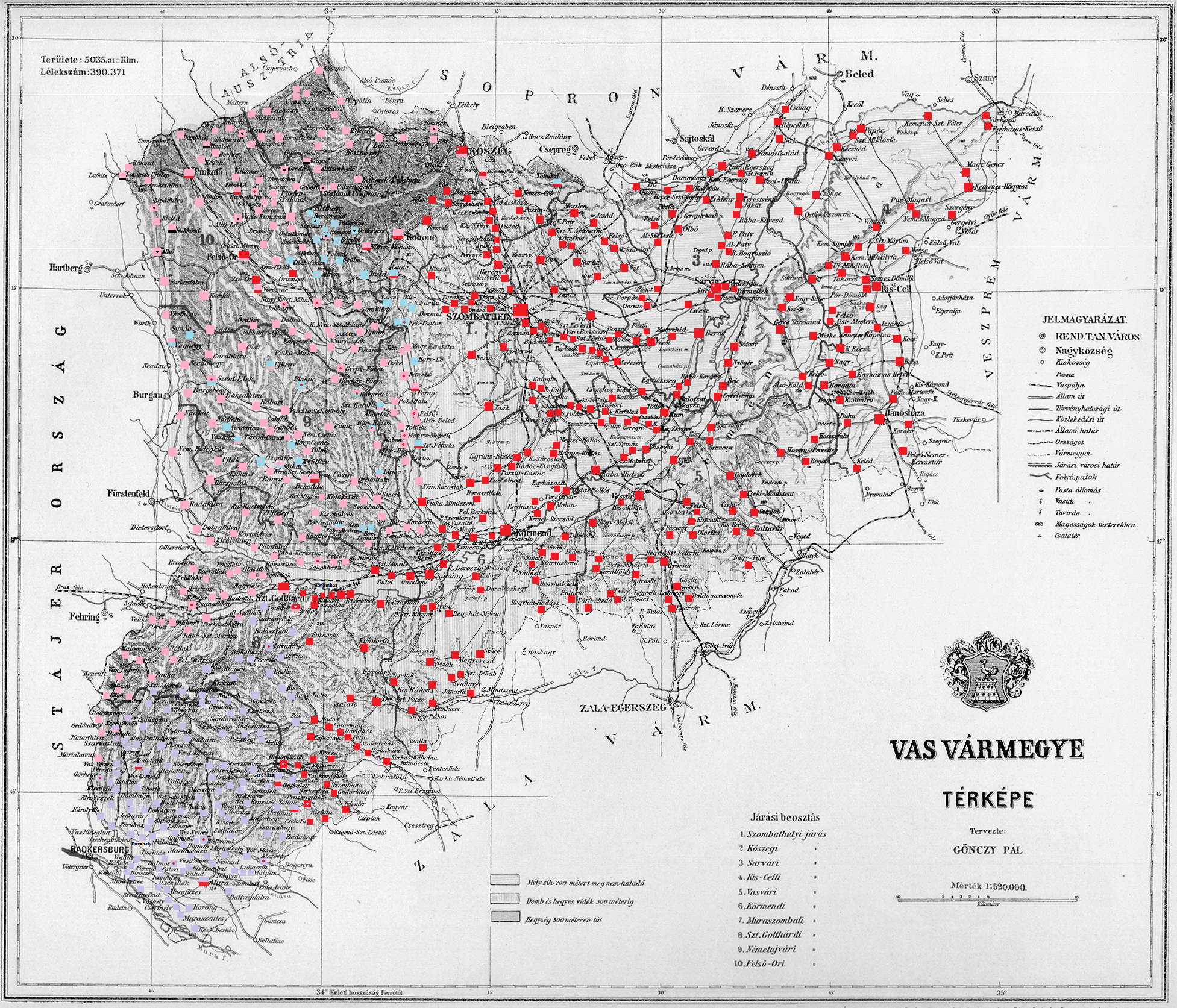
Vas County (former)
Vas (, , or ) was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between Hungary, Austria and Slovenia. Geography Vas County shared borders with the Austrian lands Lower Austria and Styria (duchy), Styria and the Hungarian counties Sopron County, Sopron, Veszprém County (former), Veszprém and Zala County (former), Zala. It stretched between the river Mur River, Mura in the south, the foothills of the Alps in the west and the river Marcal in the east. The Rába River flowed through the county. Its area was 5474 km² around 1910. History Vas County arose as one of the first ''comitatuses'' of the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon, the western part of the county became part of First Austrian Republic, Austria, and a small part in the southwest became part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (from 1929 as Yugoslavia). The remainder stayed in Hungary. The fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |