|
Kraken
The kraken (, from , "the crookie") is a legendary sea monster of enormous size, per its etymology something akin to a cephalopod, said to appear in the Norwegian Sea off the coast of Norway. It is believed that the legend of the Kraken may have originated from sightings of giant squid, which may grow to in length. The kraken, as a subject of sailors' superstitions and mythos, was first described in the modern era in a travelogue by Francesco Negri in 1700. This description was followed in 1734 by an account from Dano-Norwegian missionary and explorer Hans Egede, who described the kraken in detail and equated it with the '' hafgufa'' of medieval lore. However, the first description of the creature is usually credited to the Danish bishop Pontoppidan (1753). Pontoppidan was the first to describe the kraken as an octopus (polypus) of tremendous size, and wrote that it had a reputation for pulling down ships. The French malacologist Denys-Montfort, of the 19th century, is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Monster
Sea monsters are beings from folklore believed to dwell in the sea and are often imagined to be of immense size. Marine monsters can take many forms, including sea dragons, sea serpents, or tentacled beasts. They can be slimy and scaly and are often pictured threatening ships or spouting jets of water. The definition of a "monster" is subjective; further, some sea monsters may have been based on scientifically accepted creatures, such as whales and types of giant squid, giant and colossal squid. Sightings and legends Sea monster accounts are found in virtually all cultures that have contact with the sea. For example, Avienius relates of Himilco the Navigator, Carthaginian explorer Himilco's voyage "...there monsters of the deep, and beasts swim amid the slow and sluggishly crawling ships." (lines 117–29 of ''Ora Maritima''). Humphrey Gilbert, Sir Humphrey Gilbert claimed to have encountered a lion-like monster with "glaring eyes" on his return voyage after formally claiming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailors' Superstitions
Sailors' superstitions are superstitions particular to sailors or mariners, and which traditionally have been common around the world. Some of these beliefs are popular superstitions, while others are better described as traditions, stories, folklore, trope (literature), tropes, myths, or legends. The origins of many of these superstitions are based in the inherent risks of sailing, and luck, either good or bad, as well as portents and omens that would be given associative meaning in relation to the life of a mariner, sailor, fisherman, or a crew in general. Even in the 21st century, "fishers and related fishing workers" in the U.S. have the second-most dangerous occupation, trailing only lumberjack, loggers. Bad luck By far the best known sailors' superstitions involve bad luck. Red sunrise Sailors are taught if the sunrise is red to take warning. The day ahead will be dangerous. "Red Sky at night, Sailors delight; Red Sky in the morning, Sailors take warning." It may also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
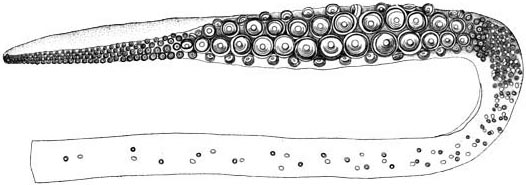
Giant Squid
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ... in the family (biology), family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of deep-sea gigantism, abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum body size at around for females, with males slightly shorter, from the cephalopod fin, posterior fins to the tip of its long cephalopod limb, arms. This makes it longer than the colossal squid at an estimated , but substantially lighter, as it is less robust and its arms make up much of the length. The Mantle (mollusc), mantle of the giant squid is about long (longer for females, shorter for males), and the feeding tentacles of the giant squid, concealed in life, are . Clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Pontoppidan
Erik Ludvigsen Pontoppidan (24 August 1698 – 20 December 1764) was a Danish author, a Lutheran bishop of the Church of Norway, a historian, and an antiquarian. His Catechism of the Church of Denmark heavily influenced Danish and Norwegian religious thought and practice for roughly the next 200 years after its 1737 publication. Early life and education Pontoppidan was born in Aarhus to provost Ludvig Henriksen Pontoppidan (1648–1706) and his second wife Else Sophie Spend (1673–1707). His younger brother Christian Ludvigsen Pontoppidan (1696–1765) was a provist (''stiftsprovst'') in Aarhus. His father's first wife was Barbara Backer (1646–1689). Orphaned at an early age, Erik Pontoppidan was placed in the house of a distant relative, Justice Councilor D.C. Braes to Kokkedal in Torslev parish and was mistreated by the home teacher, so in 1709, through the family's intervention, he first came to Aarhus Latin School and in 1710 to Fredericia Latin School, where he lived wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symmetry, bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of cephalopod arm, arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt Cephalopod ink, ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, Extant taxon, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus (genus), Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Latham Mitchill
Samuel Latham Mitchill (August 20, 1764September 7, 1831) was an American physician, naturalist, and politician who lived in Plandome, New York. Early life Samuel Mitchill was born in Hempstead in the Province of New York, the son of Robert Mitchill and his wife, Mary Latham, both Quakers. He was sent to Scotland and graduated in 1786 from the University of Edinburgh Medical School with an M.D., his education being paid for by a wealthy uncle. Returning to the United States after medical school, Mitchill also completed law school. As a lawyer, he oversaw the purchase of lands in western New York from the Iroquois Indians in 1788. Career Mitchill taught chemistry, botany, and natural history at Columbia College from 1792 to 1801 and was a founding editor of '' The Medical Repository'', the first medical journal in the United States. In 1793, he was elected a Foreign Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposers were James Gregory, Dugald Stewart, and John Rother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the ''Voyages extraordinaires'', a series of bestselling adventure novels including ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'' (1864), ''Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas'' (1870), and ''Around the World in Eighty Days'' (1872). His novels are generally set in the second half of the 19th century, taking into account contemporary scientific knowledge and the technological advances of the time. In addition to his novels, he wrote numerous plays, short stories, autobiographical accounts, poetry, songs, and scientific, artistic and literary studies. His work has been adapted for film and television since the beginning of cinema, as well as for comic books, theater, opera, music and video games. Verne is considered to be an important author in France and most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Bartholin
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Idaho * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts and entertainment * ''Thomas'' (Burton novel), a 1969 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Franz Paullini
Christian Franz Paullini (25 February 1643 – 10 June 1712) was a German physician, theologian, and writer. Biography Paullini was born in Eisenach to a family of merchants and scholars. His parents wanted him to become a priest and his initial education was designed with this in mind, but Paullini was attracted to the medicinal arts and studied both theology and medicine. He attended middle school and secondary school in Thuringia and graduated from Coburg. Paullini studied theology and medicine in Gdańsk, Königsberg, Rostock, Lübeck, Kiel and Copenhagen, was Magister Artium in Wittenberg and received his MD in Leiden. Meanwhile, he accomplished study stays and courses in Cambridge, Oxford, Sweden, Norway and Iceland.Pauliini was the personal physician of the Prince-Bishop of Munster Christoph Bernhard von Galen and later of the Duke of Brunswick in Wolfenbüttel. Paullini returned to Eisenach in 1685 and 1689 where he assumed the position of "Ducal Stadtphysicus" i.e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the Orthographic ligature, ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Sweden, Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomenclature, was partially developed by the Bauhin brothers, Gaspard Bauhin, Gaspard and Johann Bauhin, Johann, Linnaeus was the first to use it consistently throughout his book. The first edition was published in 1735. The full title of the 10th edition (1758), which was the most important one, was ', which appeared in English in 1806 with the title: "A General System of Nature, Through the Three Grand Kingdoms of Animals, Vegetables, and Minerals, Systematically Divided Into their Several Classes, Orders, Genera, Species, and Varieties, with their Habitations, Manners, Economy, Structure and Peculiarities". The 10th edition of Systema Naturae, tenth edition of this book (1758) is considered the starting point of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |