|
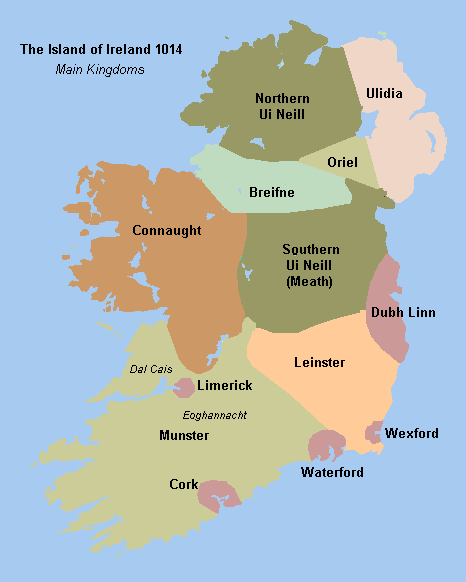
Kings Of Brega
The Kings of Brega were rulers of Brega, a petty kingdom north of Dublin in medieval Ireland. Overview Brega took its name from ' ('), meaning "fine plain", in modern County Meath, County Louth and County Dublin, Ireland. They formed part of the Uí Néill kindred, belonging to the Síl nÁedo Sláine branch of the southern Uí Néill. The kingdom of Brega included the Hill of Tara, the site where the High King of Ireland was proclaimed. Brega was bounded on the east by the Irish Sea and on the south by the River Liffey. It extended northwards across the River Boyne to include Sliabh Breagha the line of hills in southern County Louth. The western boundary, which separated it from the Kingdom of Mide, was probably quite fluid and is not accurately known. Brega was annexed in the 6th century by the Uí Néill. By the middle of the 8th century the Síl nÁedo Sláine had split into two hostile branches: Southern Brega, or the Kingdom of Loch Gabhair, which was ruled by the Uí ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petty Kingdom
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into the Kingdom of England in the 10th century, or the numerous Gaelic kingdoms of Ireland as the Kingdom of Ireland in the 16th century). Alternatively, a petty kingdom would be a minor kingdom in the immediate vicinity of larger kingdoms, such as the medieval Kingdom of Mann and the Isles relative to the kingdoms of Scotland or England or the Viking kingdoms of Scandinavia. In the parallel mainland Southeast Asian political model, petty kingdoms were known as ''mueang''. By the European High Middle Ages, many post-Roman Early Middle Ages petty kingdoms had evolved into principalities, grand duchies, or duchies. By the European Early Modern era, many of these principalities had been mediatized into larger monarchies, but the ruling fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Invasion Of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land in Ireland over which the monarchs of England then claimed sovereignty. The Anglo-Normans claimed the invasion was sanctioned by the papal bull '' Laudabiliter''. At the time, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King claiming lordship over most of the other kings. The Anglo-Norman invasion was a watershed in Ireland's history, marking the beginning of 800 years of British presence in Ireland. In May 1169, Anglo-Norman mercenaries landed in Ireland at the request of Diarmait mac Murchada (Dermot MacMurragh), the deposed King of Leinster, who sought their help in regaining his kingship. They achieved this within weeks and raided neighbouring kingdoms. This military intervention was sanctioned by King Henry II of England. In return, Diarmait had sworn loyalty to Henry and promised land to the Normans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarmait Mac Cerbaill
Diarmait mac Cerbaill (died ) was King of Tara or High King of Ireland. According to traditions, he was the last High King to follow the pagan rituals of inauguration, the ''ban-feis'' or marriage to goddess of the land. The last High King to observe the ancient pagan Feis Temrach or Assembly of Tara which took place on Samhain every three years to pass or renew laws, approve annals and records. While many later stories were attached to Diarmait, he was a historical ruler and his descendants were of great significance in Medieval Ireland. Sources It is believed that the earliest of the Irish annals which came to make up the lost ''Chronicle of Ireland'' were kept as a contemporary record from no later than the middle of the 7th century, and may be rather older as it has been argued that many late 6th century entries have the appearance of contemporary recording. There is general agreement that the annals are largely based, in their earliest contemporary records, on a chronicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
604 In Ireland
Events from the 7th century in Ireland. 600s ;601 *Probable year in which Colmán mac Cobthaig, Uí Fiachrach becomes king of Connacht.''The Oxford Illustrated History of Ireland.'' Foster, RF. Oxford University Press, Oxford. 1989 ;602 or 604 * Death of Áed mac Diarmato or Áed Sláine (Áed of Slane), the son of Diarmait mac Cerbaill. Legendary stories exist of Áed's birth. Killed his nephew and was in turn slain by his grandnephew. ;603 * Death of Brandub mac Echachall dates per ''The Chronology of the Irish Annals'', Daniel P. McCarthy an Irish king of the Uí Cheinnselaig of Leinster. His father, Echu mac Muiredaig had been a king of the Ui Cheinnselaig. They belonged to a branch known as the Uí Felmeda. Byrne, Francis John, ''Irish Kings and High-Kings.'' Batsford, London, 1973. . Table 10. ;605 * Birth of Colmán of Lindisfarne (died February 18, 675) also known as Saint Colmán, Bishop of Lindisfarne from 661 until 664. Colman resigned the Bishopric of Lindisfarn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Áed Sláine
Áed mac Diarmato (died 604), called Áed Sláine (Áed of Slane), was the son of Diarmait mac Cerbaill. Legendary stories exist of Áed's birth. Saint Columba is said to have prophesied his death. His descendants, the Síl nÁedo Sláine—the seed of Áed of Slane—were prominent in 7th and early 8th century Ireland. Origins Áed's mother is said to have been Mugain Mór, perhaps an euhemerisation of a Munster sovereignty goddess. This Mugain is called the daughter of Conchrad mac Duach, the king of Osraige. Mugain and Diarmait's marriage is barren, and Mugain is humiliated by Diarmait's chief wife until she is given blessed holy water to drink by Saint Finnian of Moville, after which she gives birth to a lamb, then to a salmon, and finally to Áed. The two great Southern Uí Néill dynasties of the midlands were the Síl nÁedo Sláine (the Seed of Áedo of Slane), kings of Brega in the east, and the Clann Cholmáin Máir (the Children of Colmán the Great) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mellifont Abbey
Mellifont Abbey (, literally 'the Big Monastery'), was a Cistercians, Cistercian abbey located close to Drogheda in County Louth, Ireland. It was the first abbey of the order to be built in Ireland. In 1152, it hosted the Synod of Kells-Mellifont. After its dissolution in 1539, the abbey became a private manor house. This saw the signing of the Treaty of Mellifont in 1603 and served as William III of England, William of Orange's headquarters in 1690 during the Battle of the Boyne. Today, the ruined abbey is a national monument (Ireland), national monument of Ireland and accessible to the public. The English language name for the monastery, 'Mellifont', comes from the Latin phrase '' Melli-fons'', meaning 'Font of Honey'. Location Mellifont Abbey sits on the banks of the River Mattock, some 10 km (6 miles) north-west of Drogheda. History Origins The abbey was founded in 1142 on the orders of Saint Malachy, Archbishop of Armagh. By 1170, Mellifont had one hundred monks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrard
Ferrard () is a barony in County Louth, Ireland. Etymology Ferrard derives its name from ''Fera Arda Ciannachta'', "men of the high Ciannachta", referring to the uplands around Mount Oriel. Location Ferrard is found in south County Louth, between the White River, River Boyne and Mattock River. Ferrard barony is bordered to the north by Ardee; to the west by Lower Slane, Upper Slane, County Meath and to the south by Drogheda and Lower Duleek, County Meath. History Ferrard derives its name from ''Fera Arda'', or ''Fatharta'', the ancient home of the Fir Arda Ciannachta. List of settlements Below is a list of settlements in the historical Ferrard barony: * Baltray *Clogherhead * Collon * Dunleer *Termonfeckin Termonfeckin or Termonfechin () is a small village and townland in County Louth, Ireland. It is within a civil parish of the same name, and is north-east of Drogheda. The population of the village almost quadrupled in the period between the 199 ... * Tullyalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airgíalla
Airgíalla (; Modern Irish: Oirialla, English: Oriel, Latin: ''Ergallia'') was a medieval Irish over-kingdom and the collective name for the confederation of tribes that formed it. The confederation consisted of nine minor kingdoms, all independent of each other but paying nominal suzerainty to an overking, usually from the most powerful dynasty. Airgíalla at its peak roughly matched the modern dioceses of Armagh and Clogher, spanning parts of counties Armagh, Monaghan, Louth, Fermanagh, Tyrone and Londonderry. Its main towns were Armagh and Clogher. The name's usage survives as a cultural area of folk tradition in South East Ulster and adjoining areas of County Louth. According to legend, Airgíalla was founded by the Three Collas, who are said to have conquered what is now central Ulster from the Ulaid. The decisive victory was the battle of Achadh Leithdheirg, said to have been fought around the year 331. However, this tale is thought to be mostly fiction, and the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donnchad Ua Cerbaill
Donnchad Ua Cerbaill or Donnchadh Ó Cearbhaill, king of Airgíalla, fl. –1168. Ua Cerbaill was a supporter of the Irish religious reform movement of the 12th century. He was a close associate of Saint Malachy, and with him founded Mellifont Abbey, the first Cistercian abbey to be built in Ireland. He was also responsible for foundations by the Arrouaisian order at Louth, Knock Abbey and Termonfeckin. Saint Malachy's brother Christian (Gilla Críst Ua Morgair) served as Bishop of Clogher in the Ua Cerbhaill kingdom from 1126 to 1138 at the time Donnchad came to power. Donnchad was central to the successful overthrow and killing of Muirchertach Mac Lochlainn, High King of Ireland, who in violation of an oath had blinded Donnchad's foster-son Eochaid Mac Duinn Sléibe the king of Ulaid in 1166. Afterwards he placed Áed in Macáem Tóinlesc, ruler of Tulach Óc, on the throne of Ailech reviving the O'Neill lineage's control of Tír Eoghain and dividing the power of the Aile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarmaid Mac Murchadha
Diarmait Mac Murchada (Irish language, Modern Irish: ''Diarmaid Mac Murchadha''; Anglicisation, anglicised as Dermot MacMurrough or Dermot MacMurphy; – c. 1 May 1171), was Kings of Leinster, King of Leinster in Ireland from 1127 to 1171. In 1167, he was deposed by the High King of Ireland, Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair. To recover his kingdom, Mac Murchada solicited help from King Henry II of England. His issue unresolved, he gained the military support of the Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke (otherwise known as "Strongbow"), thus initiating the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. In exchange for his aid, Mac Murchada promised Strongbow the hand in marriage of his daughter Aoife MacMurrough, Aoife and the right to succeed to the List of kings of Leinster, Kingship of Leinster. Henry II then mounted a larger Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, second invasion in 1171 to ensure his control over Strongbow, resulting in the Norman Lordship of Ireland. Mac Murchada was later known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Breifne
The Kingdom of Breifne or Bréifne (), anglicized as Breffny, was a medieval overkingdom in Gaelic Ireland. It comprised what is now County Leitrim, County Cavan and parts of neighbouring counties, and corresponds roughly to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Kilmore. It had emerged by the 10th century, as a confederation of ' headed by an overking drawn from the Uí Briúin Bréifne. By the 11th century, Bréifne was ruled by the Ua Ruairc (O'Rourke) dynasty. The kingdom reached the height of its power in the 12th century, under Tigernán Ua Ruairc. During the latter part of his reign, Bréifne took part in campaigns against the Norman invasion of Ireland. His assassination by the Anglo-Normans in 1172 was followed by a succession dispute, and a conflict between the Ua Ruairc and Ua Raghallaigh (O'Reilly) dynasties. Following the Battle of Magh Slecht in 1256, Bréifne split into West Breifne (ruled by the Ua Ruairc) and East Breifne (ruled by the Ua Raghallaigh). Bréifn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |