|
Key Deer
The Key deer (''Odocoileus virginianus clavium'') is an endangered subspecies of the white-tailed deer that lives only in the Florida Keys. It is the smallest extant North American deer species. Description This deer can be recognized by its characteristic size, smaller than all other white-tailed deer. Adult males (known as bucks) usually weigh and stand about tall at the shoulder. Adult females (does) usually weigh between and have an average height of at the shoulders. The deer is a reddish-brown to grey-brown in color. Antlers are grown by males and shed between February and March and regrown by June. When the antlers are growing, they have a white velvet coating. The subspecies otherwise generally resembles other white-tailed deer in appearance. Behavior Key deer easily swim between islands. Living close to humans, they have little of the natural fear of humans shown by most of their larger mainland relatives (an example of island tameness). The deer are often found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No Name Key
No Name Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys in the United States. It is from US 1 and sparsely populated, with only 43 homes. It is only about in comparison to its larger neighbor, Big Pine Key, which lies about half a mile (800 m) to its west. It is accessible by a concrete bridge from Big Pine Key and was the terminus of a car ferry that existed before the present Overseas Highway was built on the remains of Flagler's Overseas Railroad. Electricity No Name Key was known for not being connected to the commercial power grid, for a local county ordinance prohibited this. Residents mostly used a combination of solar energy and diesel or gas generators. This prohibition of commercial electricity sparked a lawsuit between Monroe County and the No Name Key property owners. In May 2013, the Florida Public Service Commission exercised its jurisdiction over public utilities and issued Order PSC-13-0207-PAA-EM declaring the residents had a right to commercial electrical po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernando De Escalante Fontaneda
Hernando de Escalante Fontaneda ( – after 1575, dates uncertain) was a Spanish shipwreck survivor who lived among the Native Americans of Florida for 17 years. His ''circa'' 1575 memoir, ''Memoria de las cosas y costa y indios de la Florida'', is one of the most valuable contemporary accounts of American Indian life from that period. The manuscript can be found in the General Archive of the Indies. In all, he produced five documents describing the peoples of Native Florida. Biography Escalante Fontaneda was the second son of Garcia de Escalante and Ana de Aldana. His father was a Spanish official in South America. Escalante Fontaneda was born in Cartagena, Colombia, around 1536. In 1549, when Escalante Fontaneda was 13, his brother and he were sailing to Spain, to study in Salamanca, when their ship was wrecked on the coast of Florida. The surviving crew and passengers were captured by the Calusa, who enslaved them and eventually sacrificed most of them, including Escalante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
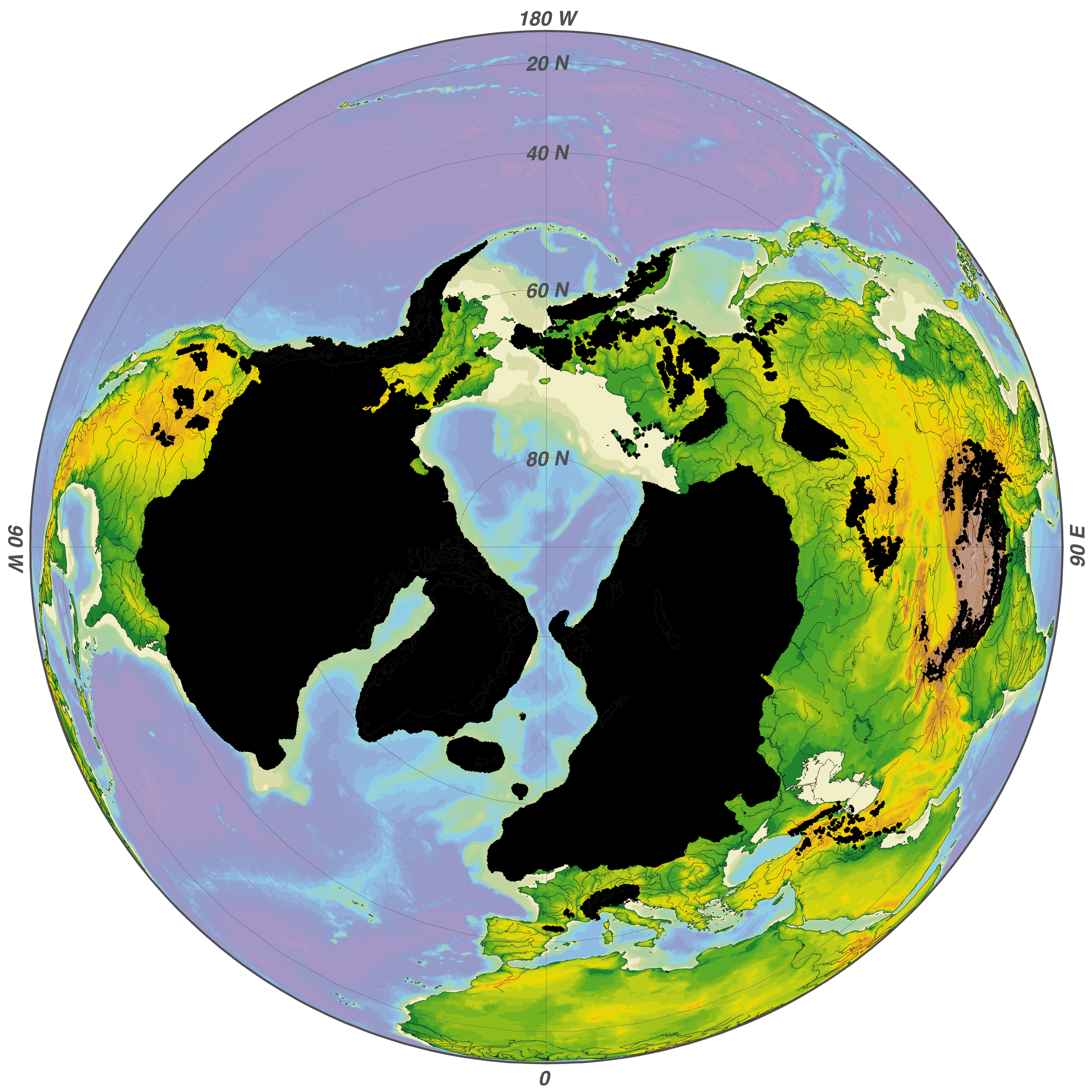
Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin glaciation, also called the Wisconsin glacial episode, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American Glacier#Classification_by_size,_shape_and_behavior, alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from about 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred about 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the ''Late W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea levels fall, exposing shallow, previously submerged sections of continental shelf; or when new land is created by plate tectonics; or occasionally when the sea floor rises due to post-glacial rebound after an ice age. Prominent examples Former land bridges * The Bassian Plain, which linked Australia to Tasmania * The Antarctic Land Bridge, which connected South America, Antarctica, and Australia during the Late Cretaceous and Early Paleogene * The Bering Land Bridge (aka Beringia), which intermittently connected Alaska (Northern America) with Siberia (North Asia) as sea levels rose and fell under the effect of ice ages * GAARlandia, a hypothesized land bridge which potentially connected the Greater Antilles with South America d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornamental Plant
Ornamental plants or ''garden plants'' are plants that are primarily grown for their beauty but also for qualities such as scent or how they shape physical space. Many flowering plants and garden varieties tend to be specially bred cultivars that improve on the original species in qualities such as color, shape, scent, and long-lasting blooms. There are many examples of fine ornamental plants that can provide height, privacy, and beauty for any garden. These ornamental perennial plants have seeds that allow them to reproduce. One of the beauties of ornamental grasses is that they are very versatile and low maintenance. Almost all types of plant have ornamental varieties: trees, shrubs, climbers, grasses, succulents, aquatic plants, herbaceous perennials and annual plants. Non-botanical classifications include houseplants, bedding plants, hedges, plants for cut flowers and ''foliage plants''. The cultivation of ornamental plants comes under floriculture and tree nurseries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and species numbers. Habitat destruction is in fact the leading cause of biodiversity loss and species extinction worldwide. Humans contribute to habitat destruction through the use of natural resources, agriculture, industrial production and urbanization (urban sprawl). Other activities include mining, logging and trawling. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, introduction of invasive species, ecosystem nutrient depletion, water and noise pollution are some examples. Loss of habitat can be preceded by an initial habitat fragmentation. Fragmentation and loss of habitat have become one of the most important topics of research in ecology as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '' brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it can be damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more often expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (‰), which is a spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples of berries in the culinary sense are strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries, white currants, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. In Britain, soft fruit is a horticultural term for such fruits. The common usage of the term "berry" is different from the scientific or botanical definition of a berry, which refers to a fleshy fruit produced from the ovary of a single flower where the outer layer of the ovary wall develops into an edible fleshy portion( pericarp). The botanical definition includes many fruits that are not commonly known or referred to as berries, such as grapes, tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, bananas, and chili peppers. Fruits commonly considered berries but excluded by the botanical definition include strawberries, raspber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thatch Palm
Thatch palm is a common name for several different species of palm trees that are used for thatching, and may refer to: *'' Coccothrinax'', many species native to the Caribbean *'' Howea'', two species native to Lord Howe Island, Australia *'' Thrinax'', three species native to the Caribbean *''Cocos nucifera The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the f ...'', the coconut tree, used in Makuti thatching {{Plant common name Arecaceae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccothrinax Argentata
''Coccothrinax argentata'', commonly called the Florida silver palm, is a species of Arecaceae, palm tree. It is native to south Florida, southeast Mexico, Colombia and to the West Indies, where it is found in the Bahamas, the southwest Caribbean and the Turks and Caicos Islands. Its natural habitat is rocky, calcareous soil in coastal scrubland and Tropical hardwood hammock, hammock communities. Description It is a small (2–6 m tall), slow-growing fan palm with leaves that are dark blue-green above and silver-coloured below. Measurements in Fairchild Tropical Garden showed an average growth rate of per year. Flowers are white and small on light orange branches. The fruits are globose and half an inch in diameter. They are initially green and turn purple or black when ripe. Silver palms in their natural habitat often grow among saw palmetto (''Serenoa repens'') and cabbage palmetto (''Sabal palmetto'') which have similar fronds. Silver Palms can be distinguished by its smooth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicennia Germinans
''Avicennia germinans'', the black mangrove, is a shrub or small tree growing up to 12 meters (39 feet) in the acanthus family, Acanthaceae. It grows in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, on both the Atlantic and Pacific Coasts, and on the Atlantic Coast of tropical Africa, where it thrives on the sandy and muddy shores where seawater reaches. It is common throughout coastal areas of Texas and Florida, and ranges as far north as southern Louisiana and northern Florida in the United States. Like many other mangrove species, it reproduces by vivipary. Seeds are encased in a fruit, which reveals the germinated seedling when it falls into the water. Unlike other mangrove species, it does not grow on prop roots, but possesses pneumatophores that allow its roots to breathe even when submerged. It is a hardy species and expels absorbed salt mainly from its leathery leaves. The name "black mangrove" refers to the color of the trunk and heartwood. The leaves oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |