|
Kennedy's Disease
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA), popularly known as Kennedy's disease, is a rare, adult-onset, X-linked recessive lower motor neuron disease caused by trinucleotide CAG repeat expansions in exon 1 of the androgen receptor (AR) gene, which results in both loss of AR function and toxic gain of function. In men, the disease slowly progresses over decades with bulbar and lower motor neuron loss, muscle denervation, and direct skeletal muscle involvement. The disease causes progressive muscle loss with weakness, fasciculations, and cramps. Weakness of the bulbar muscles follows causing difficulties in speech (dysarthria) and swallowing (dysphagia). Female carriers do not show symptoms. Although there is no cure, supportive intervention can improve mobility and reduce complications. The prevalence of SBMA has been estimated at 2.6:100,000 males. There is no known cure for SBMA. Supportive care is focused on preventing disease complications and maintaining independen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen Receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the Cell nucleus, nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor. The main function of the androgen receptor is as a DNA-binding protein, DNA-binding transcription factor that Gene expression regulation, regulates gene expression; however, the androgen receptor has other functions as well. Androgen-regulated genes are critical for the development and maintenance of the male sexual phenotype. Function Effect on development In some cell types, testosterone interacts directly with androgen receptors, whereas, in others, testosterone is converted by 5-alpha reductase, 5-alpha-reductase to dihydrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
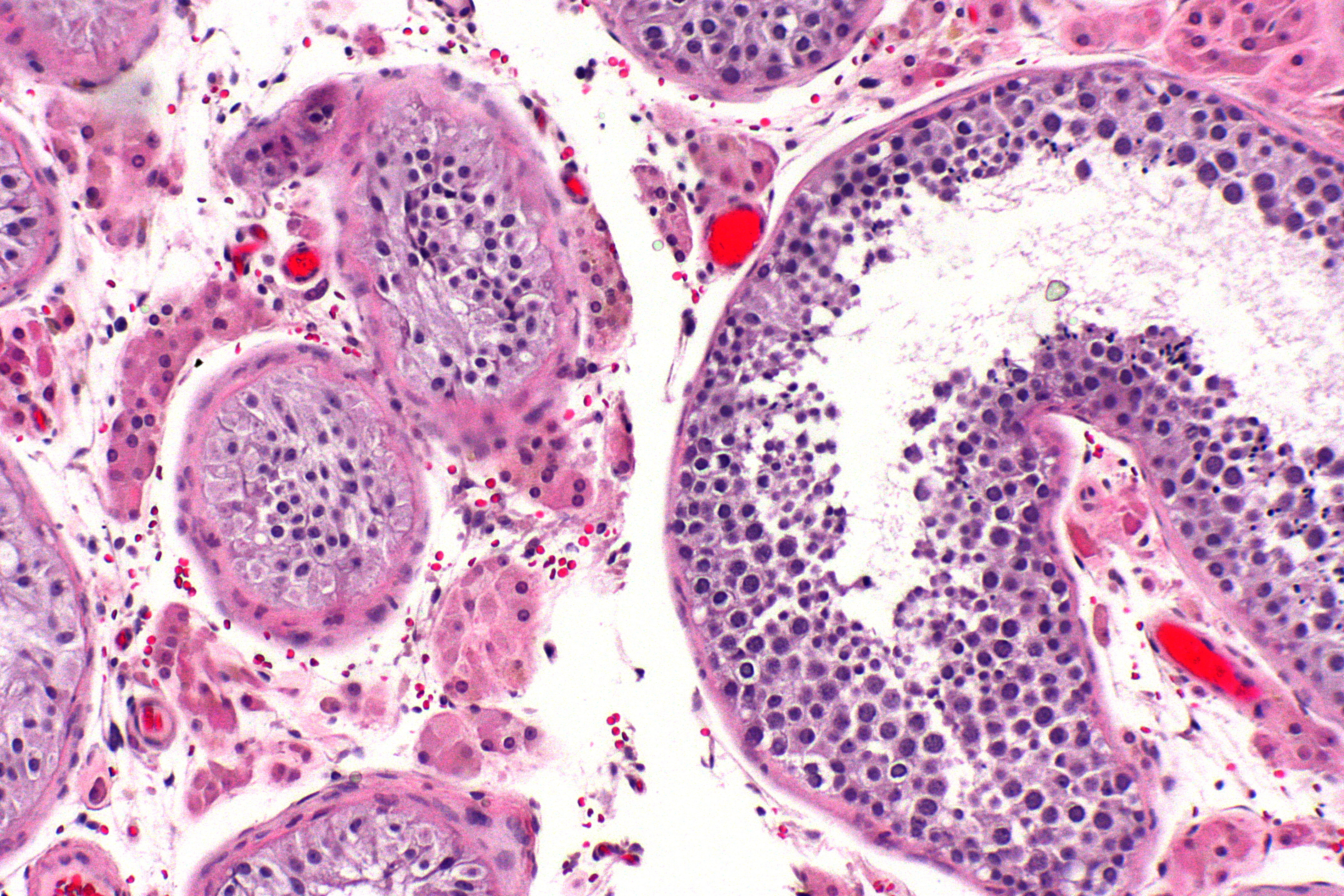
Testicular Atrophy
Testicular atrophy is a medical condition in which one or both testicles (or "testes") diminish in size and may be accompanied by reduced testicular function. Testicular atrophy is not related to the temporary shrinkage of the surrounding scrotum, which might occur in response to cold temperature. As the testicles are involved in testosterone and sperm production, the signs and symptoms of testicular atrophy overlap with those related to infertility or low testosterone levels. In a prepubescent person with testicular atrophy, there may be underdevelopment of secondary sex characteristics (e.g. lack of penis growth). In sexually developed individuals, testicular atrophy may be accompanied with lower sex drive and increased breast tissue. Additional signs and symptoms vary and can depend on the specific cause of the testicle shrinkage. Some causes include age, alcohol use, anabolic steroid use, testosterone replacement therapy, direct damage to the testicles, and infection. Diagnosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome. History The term ''exon'' is a shortening of the phrase ''expressed region'' and was coined by American biochemist Walter Gilbert in 1978: "The notion of the cistron... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messengerwhich I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions)alternating with regions which will be expressedexons." This definition was originally made for protein-coding transcripts that are spliced before b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion
A trinucleotide repeat expansion, also known as a triplet repeat expansion, is the DNA mutation responsible for causing any type of disorder categorized as a trinucleotide repeat disorder. These are labelled in dynamical genetics as dynamic mutations. Triplet expansion is caused by slippage during DNA replication, also known as "copy choice" DNA replication. Due to the repetitive nature of the DNA sequence in these regions, 'loop out' structures may form during DNA replication while maintaining complementary base pairing between the parent strand and daughter strand being synthesized. If the loop out structure is formed from the sequence on the daughter strand this will result in an increase in the number of repeats. However, if the loop out structure is formed on the parent strand, a decrease in the number of repeats occurs. It appears that expansion of these repeats is more common than reduction. Generally, the larger the expansion the more likely they are to cause disease or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2AM9
(UGA) was a subsidiary of Sega headquartered in Shibuya, Tokyo, Japan. Established in 2000, UGA was headed by Tetsuya Mizuguchi, who had previously worked at the Sega AM3 division. It is known for developing the ''Space Channel 5'' series and ''Rez (video game), Rez''. In 1996, Mizuguchi and ''Sega Rally Championship'' director Kenji Sasaki left AM3 to form AM Annex, and would go on to develop arcade games such as ''Sega Touring Car Championship'' and ''Sega Rally 2''. Mizuguchi later left Sasaki's team to form another division briefly known as Sega Consumer Development 4 (CS4), later becoming Research and Development #9 (R&D #9, or AM9). In 2000, the division was spun off into United Game Artists, a wholly owned subsidiary of Sega, with Mizuguchi acting as CEO. In 2003, due to financial issues, UGA was merged into Sonic Team, another of Sega's subsidiary companies. Mizuguchi subsequently left Sega in October of that year. Several games developed by United Game Artists are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally high levels of any or all lipids (e.g. fats, triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids) or lipoproteins in the blood. citing: and The term ''hyperlipidemia'' refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbrella term covering any of various acquired or genetic disorders that result in that finding. Hyperlipidemia represents a subset of dyslipidemia and a superset of hypercholesterolemia. Hyperlipidemia is usually chronic and requires ongoing medication to control blood lipid levels. Lipids (water-insoluble molecules) are transported in a Apolipoprotein, protein Lipoprotein, capsule. The size of that capsule, or lipoprotein, determines its density. The lipoprotein density and type of apolipoproteins it contains determines the fate of the particle and its influence on metabolism. Hyperlipidemias are divided into primary and secondary subtypes. Primary hyperlipidemia is usually due to genetic causes (such as a mutation in a recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis and steatotic liver disease (SLD), is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complications may include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and esophageal varices. The main subtypes of fatty liver disease are metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD, formerly "non-alcoholic fatty liver disease" (NAFLD)) and alcoholic liver disease (ALD), with the category "metabolic and alcohol associated liver disease" (metALD) describing an overlap of the two. The primary risks include alcohol, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. Other risk factors include certain medications such as glucocorticoids, and hepatitis C. It is unclear why some people with NAFLD develop simple fatty liver and others develop nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is associated with poorer outcomes. Diagnosis is ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological response in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance can be improved or reversed with lifestyle approaches, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocrine Gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types. Classification Structure Exocrine glands contain a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland. * The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland, thyroid, parathyroid gland, parathyroid, pituitary gland, pituitary, pineal gland, pineal, and adrenal glands, and the (male) testis and (female) ovaries. The hypothalamus, pancreas, and thymus also function as endocrine glands, among other functions. (The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are organs of the Neuroendocrinology#Neuroendocrine system, neuroendocrine system. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamusit is located in the brain adjacent to the pituitary glandis to link the endocrine system to the nervous system via the pituitary gland.) Other organs, such as the kidneys, also have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass, and the growth of androgenic hair, body hair. It is associated with increased aggression, sex drive, Dominance hierarchy, dominance, courtship display, and a wide range of behavioral characteristics. In addition, testosterone in both sexes is involved in health and well-being, where it has a significant effect on overall mood, cognition, social and sexual behavior, metabolism and energy output, the cardiovascular system, and in the prevention of osteoporosis. Insufficient levels of testosterone in men may lead to abnormalities including frailty, accumulation of adipose fat tissue within the body, anxiety and depression, sexual performance issues, and bone loss. Excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |