|
Kaikadi Language
The Kaikadi language is a Dravidian language related to Tamil, spoken by about 23,000 people of the formerly nomad Kaikadi tribe primarily in Maharashtra Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th .... References Tamil languages {{Dr-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tamiloid Languages
The Tamiloid languages, also known as the Tamil languages, are the group of Dravidian languages The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian l ... most closely related to Tamil. In addition to Tamil itself, they are Eravallan, Kaikadi, Mala Malasar, Malasar, Malapandaram, Mannan, Muthuvan, Paliyan, Pattapu, Bugandi and Yerukala. Arwi is not a separate language but a register of Tamil used by Muslims. It is written in the Arabic alphabet and contains many loans from Arabic. Kakkala may be either a Tamil language or one of the Malayalam languages. Internal classification Glottolog classifies the Tamiloid languages as follows: References Tamil languages {{Dr-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
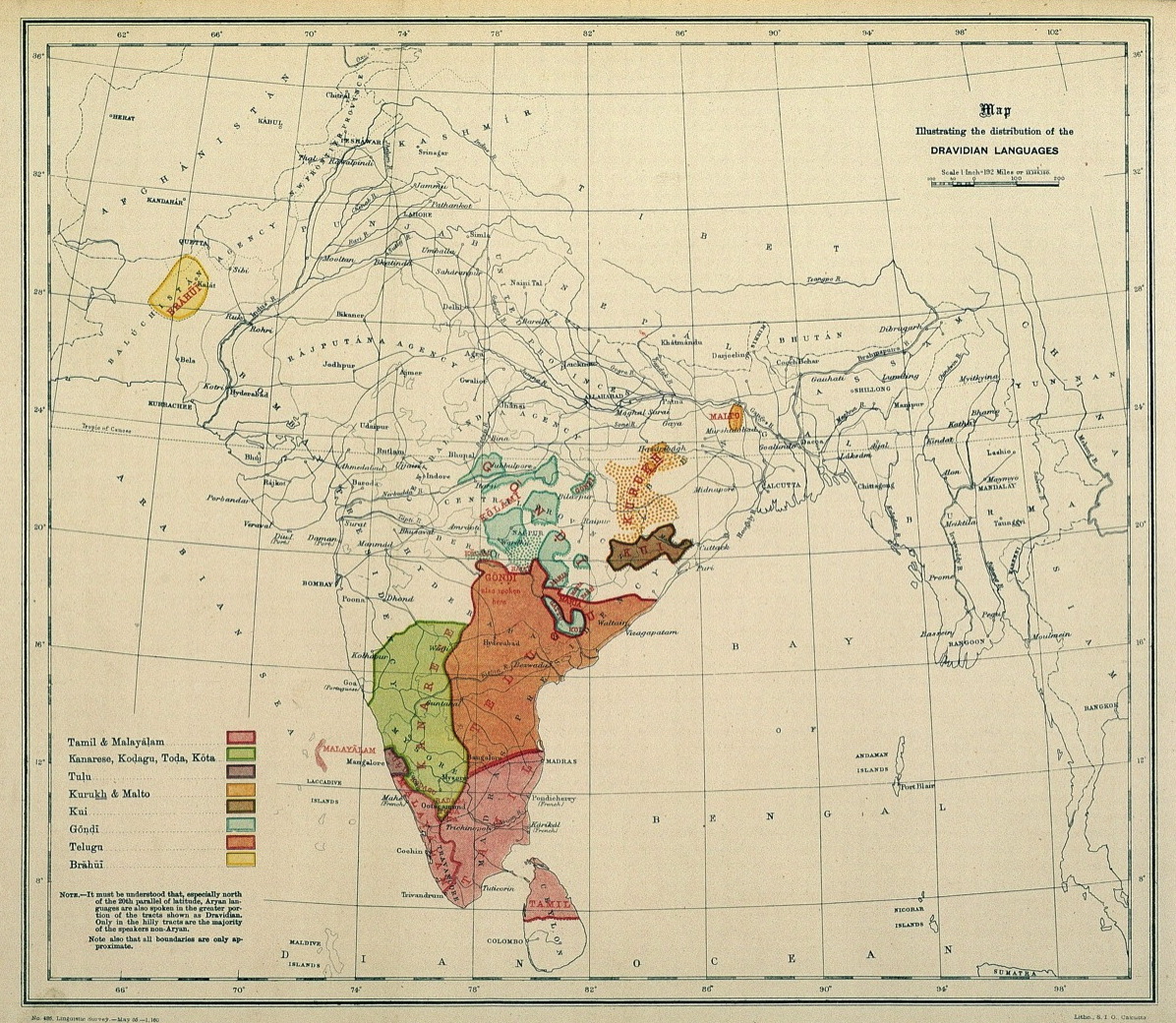
Dravidian Language
The Dravidian languages are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto and Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Iranian Balochistan, Afghanistan and around the Marw oasis in Turkmenistan. During the British colonial period, Dravidian speakers were sent as indentured labourers to Southeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middle Tamil Language
Middle Tamil is the form of the Tamil language that existed from the 8th to the 15th century. The development of Old Tamil into Middle Tamil, which is generally taken to have been completed by the 8th century, was characterised by a number of phonological and grammatical changes despite maintaining grammatical and structural continuity with the previous form of the language. In phonological terms, the most important shifts were the virtual disappearance of the aytam (ஃ), an old phoneme, the coalescence of the alveolar and dental nasals, and the transformation of the alveolar plosive into a rhotic. In grammar, the most important change was the emergence of the present tense. The present tense evolved out of the verb ' (), meaning "to be possible" or "to befall". In Old Tamil, this verb was used as an aspect marker to indicate that an action was micro-durative, non-sustained or non-lasting, usually in combination with a time marker such as ' (). In Middle Tamil, this us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old Tamil Language
Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning from the 3rd century BCE to the seventh century CE. Prior to Old Tamil, the period of Tamil linguistic development is termed as Proto-Tamil. After the Old Tamil period, Tamil becomes Middle Tamil. The earliest records in Old Tamil are inscriptions from between the 3rd and 1st century BCE in caves and on pottery. These inscriptions are written in a variant of the Brahmi script called Tamil-Brahmi. The earliest long text in Old Tamil is the '' Tolkāppiyam'', an early work on Tamil grammar and poetics, whose oldest layers could be as old as the mid-2nd century BCE.Zvelebil, K. ''The Smile of Murugan: On Tamil Literature of South '' p. xx Old Tamil preserved many features of Proto-Dravidian, the reconstructed common ancestor of the Dravidian languages, including inventory of consonants, the syllable structure, and various grammatical features. History According to Bhadriraju Krishnamurti, Tamil, as a Dravidian language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pattapu Language
Pattapu is a described Dravidian language of Andhra Pradesh. Pattapu was a coastal community in Southern Andhra Pradesh, India. They are listed as an Other Backward Class. They mostly live in the coastal areas of Nellore, Prakasam and Bapatla districts. The people that speak the language belong to 146 different villages. The language is closely related to Tamil but also has influences of Telugu Telugu may refer to: * Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of South India ** Telugu literature, is the body of works written in the Telugu language. * Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India * Telugu script, used to write the Tel .... Most of their villages have a temple dedicated to Lord Sriram. According to Ramayana: one person from this caste was helped by Lord Sri Ram to the cross the river in search of Ma Site Devi. Lord Sri Ram promised that person that he will worshipped by that person's caste (pattapu kapu). They are mostly depends on hunting and cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yerukala Language
Yerukula is a Dravidian language mainly spoken by the Yerukala tribe. This language is also called ''Kurru basha'' or ''Kulavatha''. Yerukala is linguistically close to South Dravidian languages such as Ravula and Irula. Lexical similarity among these languages ranges from 53% to 81%; in the case of Irula, it varies from 33% to 38%; in case of Ravula, it varies from 28% to 45%; in case of modern Tamil, it varies from 27% to 45%. Sathupati Prasanna Sree has developed a unique script for use with the language. Some of the language terms, mostly relations. References External linksYerukalas Home Page Tamil languages {{Dr-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Malayalamoid Languages
The Malayalamoid languages, also known as the Malayalam languages, are the group of Dravidian languages most closely related to Malayalam Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of .... In addition to Malayalam itself, they are: * Paniya, Ravula, Aranadan, Judeo-Malayalam, Arabi Malayalam, Suriyani Malayalam, Kadar, Malaryan, Malavedan, Mannan, Jeseri, Mullu Kurumba. Unclassified Kumbaran and Kakkala may be Malayalam languages as well. Internal classification Glottolog classifies the Malayalam languages as follows: References * {{Dr-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Urali Language
Urali is a southern Dravidian language. It is spoken by the Urali tribe in the hills around Idukki in Kerala, and Bargur Bargur is a selection-grade town panchayat in the Krishnagiri district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, that serves as the headquarters of Bargur taluk, one of the seven taluks in Krishnagiri district. History The town panchayat of Bargur was ... in Tamil Nadu. It is still commonly spoken among the community. References Dravidian languages {{Dravidian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the northwest. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India, the third most populous country subdivision in South Asia and the fourth-most populous in the world. The state is divided into 6 divisions and 36 districts. Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra due to its historical significance as a major trading port and its status as India's financial hub, housing key institutions and a diverse economy. Additionally, Mumbai's well-developed infrastructure and cultural diversity make it a suitable administrative center for the state, and the most populous urban are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kodava Language
The Kodava (, natively: ''Koḍava takkï'', , meaning 'speech of Kodavas', Angloid name: Codava, Coorgi) is a Dravidian language spoken in Kodagu district (Coorg) in Southern Karnataka, India. It is an endangered language. The term Kodava has two related usages. Firstly, it is the name of the Kodava language and culture followed by a number of communities from Kodagu. Secondly, within the Kodava-speaking communities and region (Kodagu), it is a demonym for the dominant Kodava people. Hence, the Kodava language is not only the primary language of the Kodavas but also of many other castes and tribes in Kodagu. The language has two dialects: Mendele (spoken in Northern and Central Kodagu, i.e. outside Kodagu's Kiggat naadu) and Kiggat (spoken in Kiggat naadu, in Southern Kodagu). Historically, it has been associated to Old Canarese or Hale Kannada However, it has been re-analysed as a language by early 20th century academics. Now it is considered as an intermediate language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Toda Language
Toda is a indigenous Dravidian language noted for its many fricatives and trills. It is spoken by the Toda people, a population of about one thousand who live in the Nilgiri Hills of southern India. The Toda language is considered to have originated from the Toda-Kota subgroup of South Dravidian. Krishnamurti (2003) does not consider the existence of a single Toda-Kota branch and says Kota split first and later Toda did as Kota doesn't have the centralized vowels of other Tamil-Toda languages. Phonology Vowels For a Dravidian language, Toda's sixteen vowels is an unusually large number. There are eight vowel qualities, each of which may occur long or short. There is little difference in quality between the long and short vowels, except for , which occurs as when short and as when long. Consonants Toda has an unusually large number of fricatives and trills. Its seven places of articulation are the most for any Dravidian language. The voiceless laterals are true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |