|
Kadam Rao Padam Rao
Kadam Rao Padam Rao is the earliest available manuscript in Dakhini ''masnavi'' of 4000 lines, written during 1421-1434 AD, by Fakhruddin Nizami of Bidar Bidar ( ) is a city and headquarters of the Bidar district in Karnataka state of India. Bidar is a prominent place on the archaeological map of India, it is well known for architectural, historical religious and rich heritage sites. Pictures .... It contains a Sufi tale designed to describe the soul's present state and its liberation, in the form of an exciting story: King Kadam Rao wants to learn yoga. But the shrewd yogi bans the king's soul into a parrot, slips into the king's body and rules in his place. The vizier Padam Rao notices it, searches the King and finally finds and frees him. References {{reflist Urdu-language literature Indian non-fiction literature Deccani language books 15th-century Indian books Indian manuscripts Sufi literature Sufism in India Urdu in India Urdu-language poetry Works about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccan Urdu
Deccani ( ''dakanī'' or ''dakhanī''; also known as Deccani Urdu, Deccani Hindi, and Deccani Hindustani) is an Indo-Aryan language variety based on a form of Hindustani spoken in the Deccan region of south-central India and is the native language variety of the Deccani people. The historical form of Deccani sparked the development of Urdu literature during the late-Mughal period. Deccani arose as a ''lingua franca'' under the Delhi Sultanate and Bahmani Sultanates, as trade and migration from the north introduced Hindustani to the Deccan. It later developed a literary tradition under the patronage of the Deccan Sultanates. Deccani itself came to influence modern standard Urdu and later Hindi. The Deccani language has an Indo-Aryan core vocabulary, though it incorporated loanwords from Persian, which was the official language of the Deccan Sultanates. Additionally, Deccani differs from northern Hindustani sociolects due to archaisms retained from the medieval era, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masnavi (poetic Form)
Mathnawi ( ), also spelled masnavi, mesnevi or masnawi, is a kind of poem written in rhyming couplets, or more specifically "a poem based on independent, internally rhyming lines". Most mathnawi poems follow a meter of eleven, or occasionally ten, syllables, but had no limit in their length. Typical mathnawi poems consist of an indefinite number of couplets, with the rhyme scheme aa/bb/cc. Mathnawi poems have been written in Persian, Arabic, Turkish, Kurdish and Urdu cultures. Certain Persian mathnawi poems, such as Rumi's '' Masnavi-e Ma’navi'', have had a special religious significance in Sufism. Other influential writings include the poems of Ghazali and ibn Arabi. Mathnawi's are closely tied to Islamic theology, philosophy, and legends, and cannot be understood properly without knowledge about it. Arabic mathnawi Arabic mathnawi poetry, also known as ''muzdawij'' ( – , referring to the internal rhyme scheme of the lines), was popularized during the Abbasid era. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidar
Bidar ( ) is a city and headquarters of the Bidar district in Karnataka state of India. Bidar is a prominent place on the archaeological map of India, it is well known for architectural, historical religious and rich heritage sites. Picturesquely perched on the Deccan plateau, the Bidar fort is more than 500 years old and still standing strong. According to the book "Bidar Heritage" published by the state ''Department of Archaeology, Museums and Heritage'', of the 61 monuments listed by the department, about 30 are tombs located in and around Bidar city., explaining its nickname, "City of Whispering Monuments". The heritage sites in and around Bidar have become the major attraction for film shooting in recent years, with Bollywood making visits apart from Kannada film industry Bidar is home for the second biggest Indian Air Force training centre in the country. The Bidar Airport, IAF Station Bidar is used for advanced jet training of prospective fighter pilots on BAe Hawk air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu-language Literature
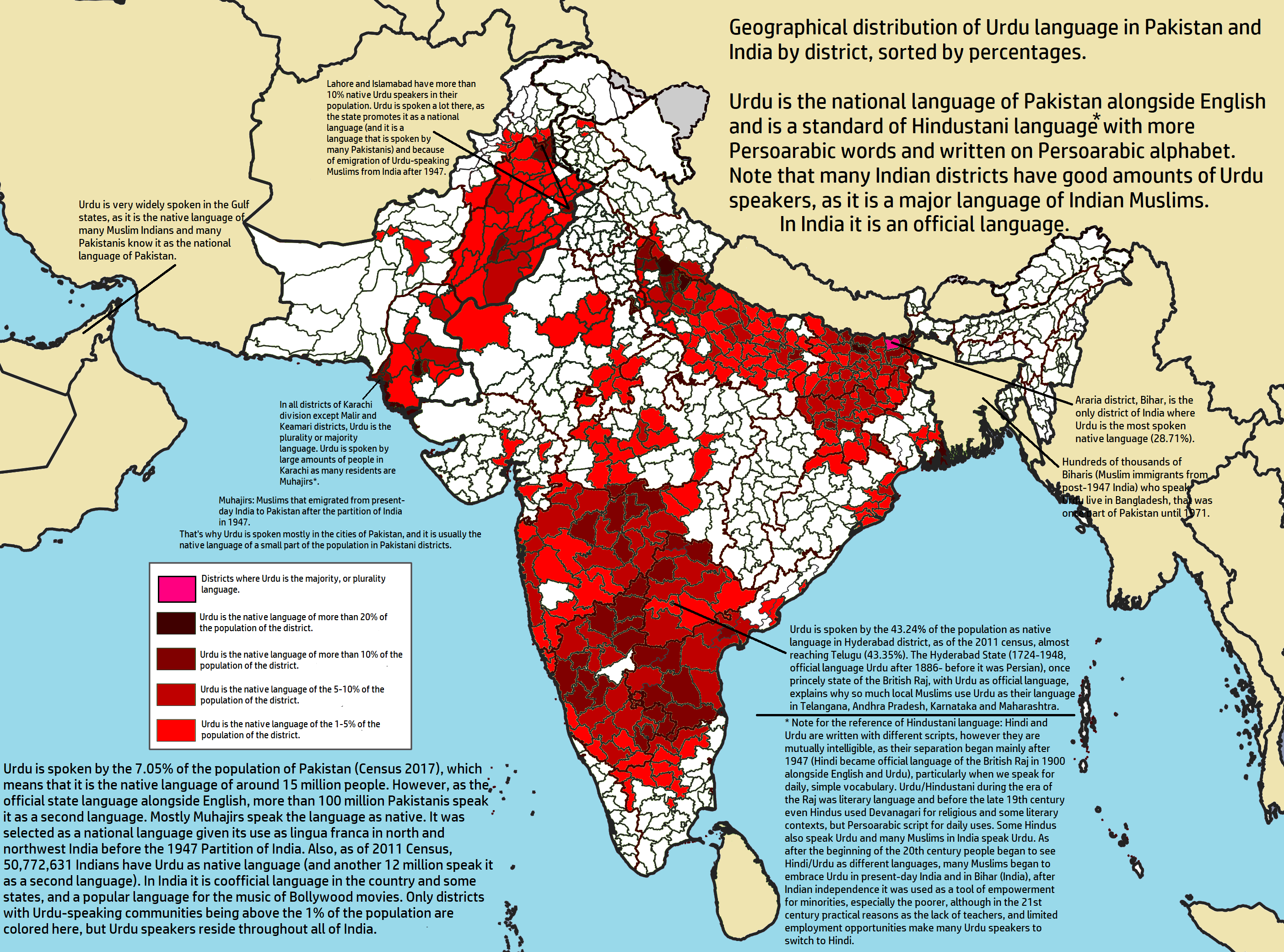
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Non-fiction Literature
Indian or Indians may refer to: Associated with India * of or related to India ** Indian people ** Indian diaspora ** Languages of India ** Indian English, a dialect of the English language ** Indian cuisine Associated with indigenous peoples of the Americas * Indigenous peoples of the Americas ** First Nations in Canada ** Native Americans in the United States ** Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean ** Indigenous languages of the Americas Places * Indian, West Virginia, U.S. * The Indians, an archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands Arts and entertainment Film * ''Indian'' (film series), a Tamil-language film series ** ''Indian'' (1996 film) * ''Indian'' (2001 film), a Hindi-language film Music * Indians (musician), Danish singer Søren Løkke Juul * "The Indian", an unreleased song by Basshunter * "Indian" (song), by Sturm und Drang, 2007 * "Indians" (song), by Anthrax, 1987 * Indians, a song by Gojira from the 2003 album '' The Link'' Other uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccani Language Books
Deccani (also Dakhini, Dakhni or Dekhani) is anything related to the Deccan region of India. Specifically, it may be: *Deccani language, an Indo-Aryan language spoken in southern India, closely related to Urdu **Deccani Muslims, speakers of Deccani **Deccani film industry, Deccani-language film industry based in Hyderabad, India **Deccani Masnavi, collection of poetry in Deccani *Deccani painting, a style of Indian painting *Deccani Marathi, a dialect of the Marathi language *Deccani architecture, Indian architectural style See also *Deccan (other) *Deccan sultanates, sultanates in medieval-India *Hyderabadi Muslims Hyderabadi Muslims, also referred to as Hyderabadis, are a community of Deccani people, from the area that used to be the princely state of Hyderabad in the regions of Marathwada, Telangana, and Kalyana-Karnataka. While the term "Hyderabad ..., Muslims from Hyderabad, India and surrounding regions, of which the Deccani Muslims form a sub-group {{disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th-century Indian Books
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian calendar dates from 1 January 1401 (represented by the Roman numerals MCDI) to 31 December 1500 (MD). In History of Europe, Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period. Many technological, social and cultural developments of the 15th century can in retrospect be seen as heralding the "European miracle" of the following centuries. The Perspective (graphical), architectural perspective, and the modern fields which are known today as banking and accounting were founded in Italy. The Hundred Years' War ended with a decisive Kingdom of France, French victory over the Kingdom of England, English in the Battle of Castillon. Financial troubles in England following the conflict resulted in the Wars of the Roses, a series of dynastic wars for the throne of England. The conflicts ended with the defeat of Richard III by Henry VII of England, Henry VII at the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Manuscripts
Indian or Indians may refer to: Associated with India * of or related to India ** Indian people ** Indian diaspora ** Languages of India ** Indian English, a dialect of the English language ** Indian cuisine Associated with indigenous peoples of the Americas * Indigenous peoples of the Americas ** First Nations in Canada ** Native Americans in the United States ** Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean ** Indigenous languages of the Americas Places * Indian, West Virginia, U.S. * The Indians, an archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands Arts and entertainment Film * ''Indian'' (film series), a Tamil-language film series ** ''Indian'' (1996 film) * ''Indian'' (2001 film), a Hindi-language film Music * Indians (musician), Danish singer Søren Løkke Juul * "The Indian", an unreleased song by Basshunter * "Indian" (song), by Sturm und Drang, 2007 * "Indians" (song), by Anthrax, 1987 * Indians, a song by Gojira from the 2003 album '' The Link'' Other uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi Literature
Sufi literature consists of works in various languages that express and advocate the ideas of Sufism. Sufism had an important influence on medieval literature, especially poetry, that was written in Arabic, Persian, Punjabi, Turkic, Sindhi and Urdu. Sufi doctrines and organizations provided more freedom to literature than did the court poetry of the period. The Sufis borrowed elements of folklore in their literature. The works of Nizami, Nava'i, Hafez, Sam'ani and Jami were more or less related to Sufism. The verse of such Sufi poets as Sanai (died c. 1140), Attar (born c. 1119), and Rumi (died 1273) protested against oppression with an emphasis on divine justice and criticized evil rulers, religious fanaticism and the greed and hypocrisy of the orthodox Muslim clergy. The poetic forms used by these writers were similar to the folk song, parable and fairy tale. Authors of Sufi folk literature particularly borrowed preexisting poetic forms, songs, and narrative structure to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufism In India
Sufism has a history in India that has been evolving for over 1,000 years. The presence of Sufism has been a leading entity increasing the reaches of Islam throughout South Asia.Schimmel, p.346 Following the entrance of Islam in the early 8th century, Sufi mystic traditions became more visible during the 10th and 11th centuries of the Delhi Sultanate and after it to the rest of India. A conglomeration of four chronologically separate dynasties, the early Delhi Sultanate consisted of rulers from Turkic and Afghan lands. This Persian influence flooded South Asia with Islam, Sufi thought, syncretic values, literature, education, and entertainment that has created an enduring impact on the presence of Islam in India today. Sufi preachers, merchants and missionaries also settled in coastal Gujarat through maritime voyages and trade. Various leaders of Sufi orders, Tariqa, chartered the first organized activities to introduce localities to Islam through Sufism. Saint figures and myth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu In India
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, however, has had significant relevance for a language's status and functions. It also has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |