|
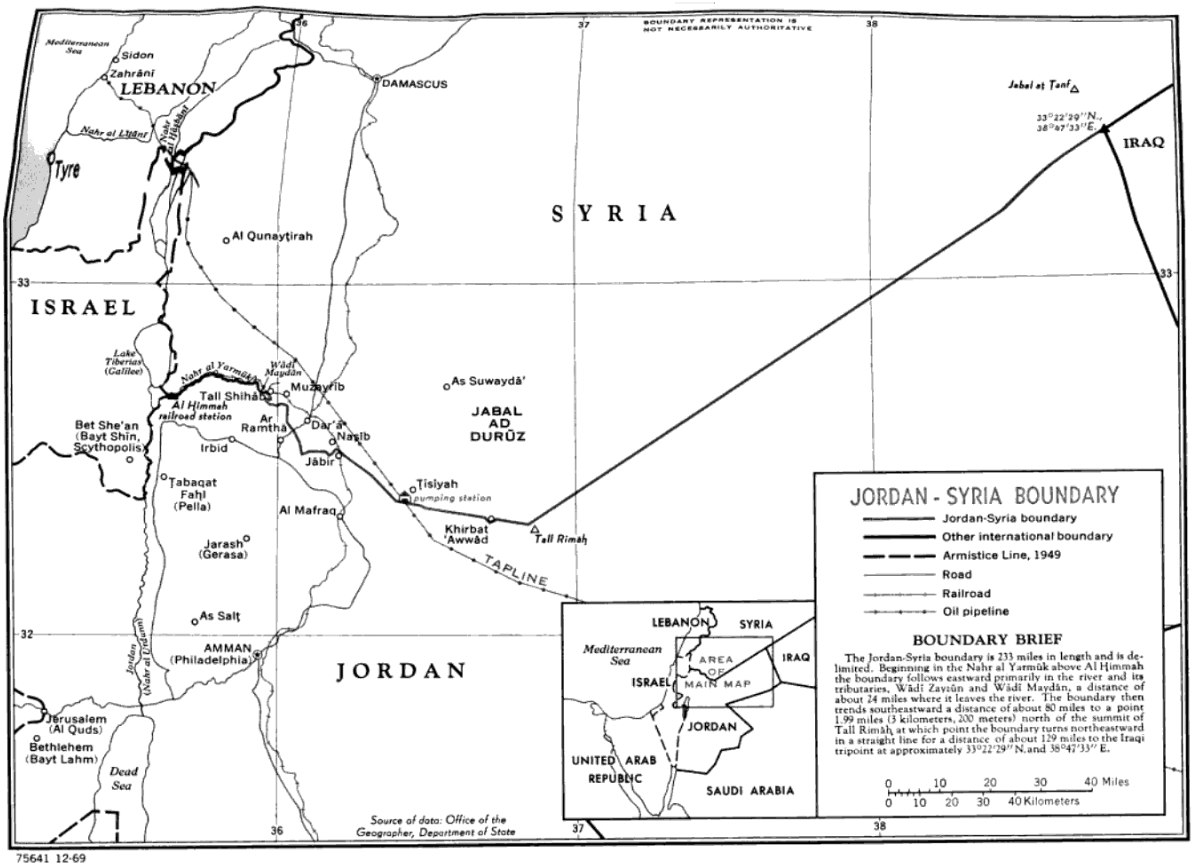
Jordan–Syria Border
The Jordan–Syria border is 362 km (225 m) in length and runs from the tripoint with Israel in the west to the tripoint with Iraq in the east. Description The border starts in the west at the tripoint with Israel, though the precise location of the tripoint is at present unclear owing to the Israeli occupation of the Golan Heights, which are claimed by Syria. The ''de jure'' tripoint lies immediately east of the Israeli town of Sha'ar HaGolan, whereas the ''de facto'' tripoint lies at the border's junction with the United Nations UNDOF Zone south-east of Metzar. The Jordan-Golan Heights border runs along the Yarmouk River, and this river then continues as the westernmost section of the Jordan–Syria border proper. The border leaves the river just east of Al-Turrah, and a series of irregular and short straight lines then proceeds to the south-east, passing between Ar Ramtha and Daraa across the Daraa Border Crossing and on to the Nasib Border Crossing on the Amman– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jordan Syria Border Map
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian territories to the west. The Jordan River, flowing into the Dead Sea, is located along the country's western border within the Jordan Rift Valley. Jordan has a small coastline along the Red Sea in its southwest, separated by the Gulf of Aqaba from Egypt. Amman is the country's capital and largest city, as well as the most populous city in the Levant. Inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period, three kingdoms developed in Transjordan during the Iron Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their kingdom centered in Petra. The Greco-Roman period saw the establishment of several cities in Transjordan that comprised the Decapolis. Later, after the end of Byzantine rule, the region became part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
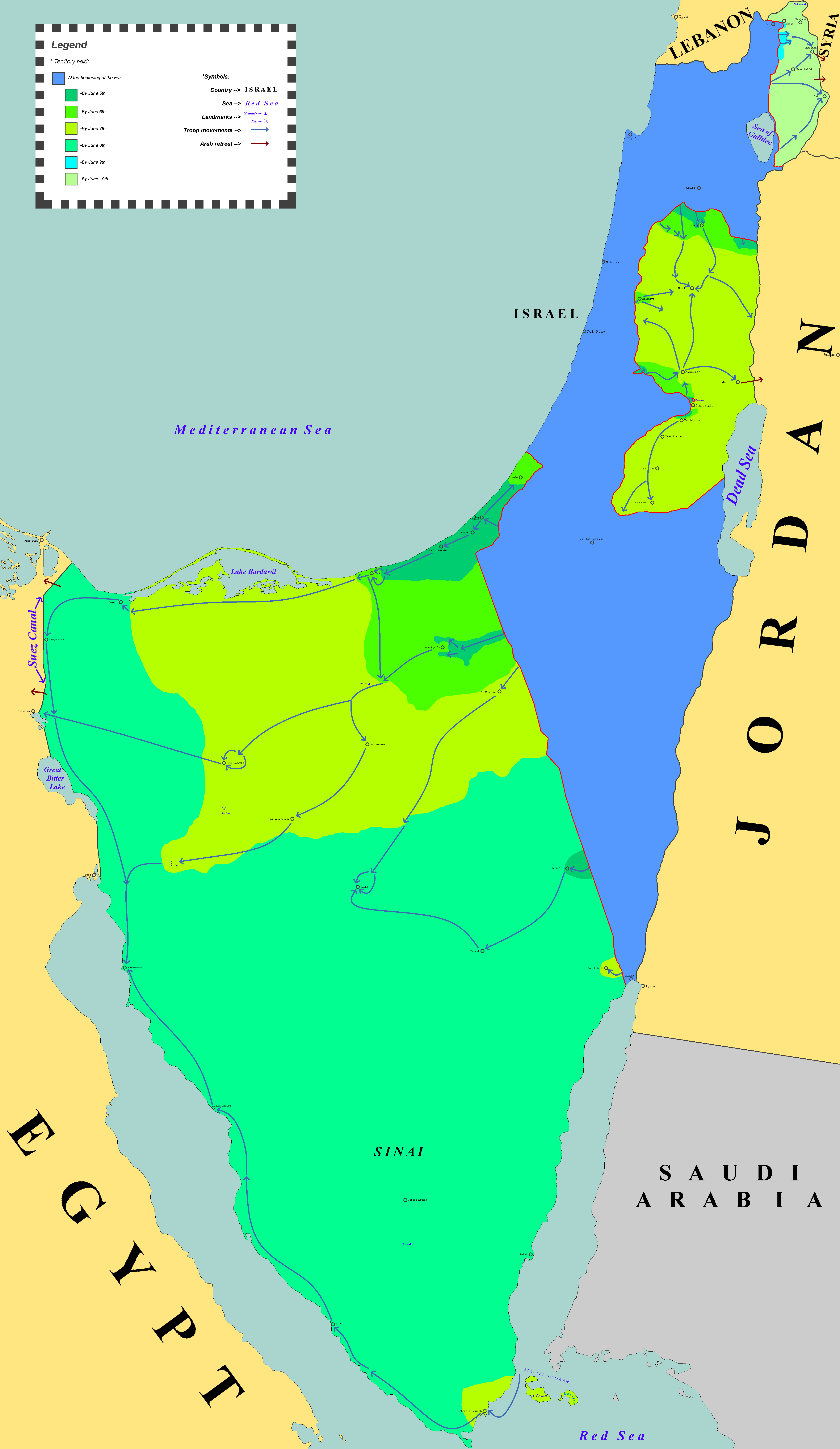
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June 1967. Military hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbors, which had been observing the 1949 Armistice Agreements signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. In 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran (giving access to Eilat, a port on the southeast tip of Israel) escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iraq–Syria Border
The Iraqi–Syrian border is the border between Syria and Iraq and runs for a total length of across Upper Mesopotamia and the Syrian desert, from the tripoint with Jordan in the south-west to the tripoint with Turkey in the north-east. Description The border starts in the west at the tripoint with Jordan at , with the initial section being a continuation of the long straight line that forms the eastern section of the Jordan–Syria border. The boundary then shifts in the vicinity of the Euphrates river and the Al-Qa'im border crossing, proceeding northwards via a series of short straight lines, and then north-eastwards to the Tigris river. The Tigris then forms a short 3-4 mile section of the border up to the Turkish tripoint at the confluence with the Khabur (Tigris), Khabur river at . History At the start of the 20th century, the Ottoman Empire controlled what is now Syria and Iraq. During the First World War, an Arab Revolt - supported by Britain - succeeded in removing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paulet–Newcombe Agreement
The Paulet–Newcombe Agreement or Paulet-Newcombe Line, was a 1923 agreement between the British and French governments regarding the position and nature of the boundary between the Mandates of Palestine and Iraq, attributed to Great Britain, and the Mandate of Syria and Lebanon, attributed to France. The 1923 line defined the border of Mandatory Palestine from the Mediterranean up to Al-Hamma, Tiberias. The 1920 line defined, in less detail, the border of the French Mandate for Syria and Lebanon from the Mediterranean up to Jeziret-ibn-Omar. The Agreement takes its name from the two Lieutenant colonels who were in charge of precisely mapping the border lines and drafting the Agreement, i.e. French Lieutenant colonel N. Paulet and British Lieutenant colonel S. F. Newcombe. Together with a preliminary 1920 agreement, these are known as the Franco-British Boundary Agreements. The Iraq-Syria border was subsequently finalized in 1932 following a League of Nations commission re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
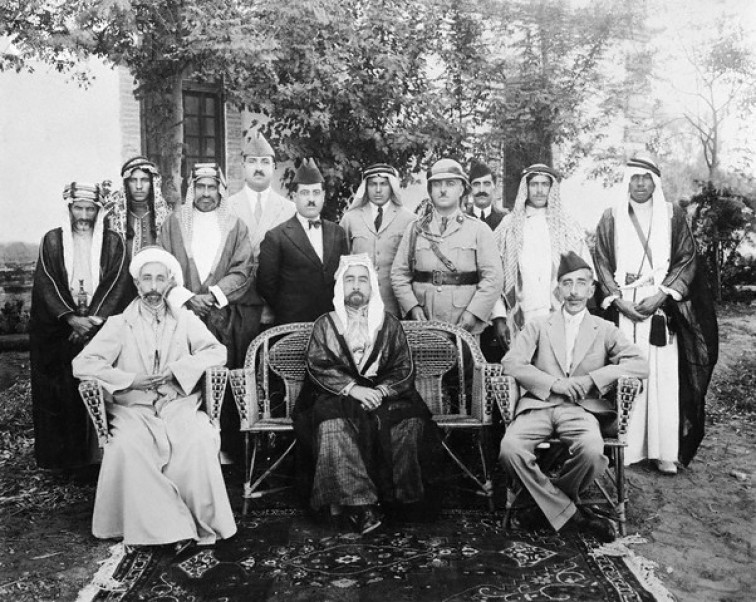
Abdullah I Of Jordan
Abdullah I (Abdullah bin Hussein; 2 February 188220 July 1951) was the ruler of Jordan and its predecessor state Transjordan from 1921 until his assassination in 1951. He was the Emir of Transjordan, a British protectorate, until 1946, when he became king of an independent Transjordan (shortened to Jordan in 1949). As a member of the Hashemite dynasty, the royal family of Jordan since 1921, Abdullah was a 38th-generation direct descendant of Muhammad. Born in Mecca, Hejaz, Ottoman Empire, Abdullah was the second of four sons of Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, and his first wife, Abdiyya bint Abdullah. He was educated in Istanbul and Hejaz. From 1909 to 1914, Abdullah sat in the Ottoman legislature, as deputy for Mecca, but allied with Britain during the First World War. During the war, he played a key role in secret negotiations with the United Kingdom that led to the Great Arab Revolt against Ottoman rule that was led by his father Sharif Hussein.Encyclopaedia Britannic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Emirate Of Transjordan
The Emirate of Transjordan (), officially the Amirate of Trans-Jordan, was a British protectorate established on 11 April 1921,Hashemite Monarchs of Jordan , "The Emirate of Transjordan was founded on April 11, 1921, and became the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan upon formal independence from Britain in 1946" which remained as such until achieving formal independence from Britain as the Kingdom of Transjordan in 1946. After the Ottoman defeat in World War I, the Transjordan region was administered within OETA East; after the British withdrawal in 1919, this regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Interregnum (Transjordan)
The Interregnum (between rulers) period in Transjordan was a short period during which Transjordan had no established ruler or occupying power that lasted from the end of the Franco-Syrian War on 25 July 1920 until the Establishment of the Emirate of Transjordan in April 1921. Transjordan was in the British sphere of influence, but the British did not send an army or administration, and the government of the Hashemite Arab Kingdom of Syria under Prince Faisal had collapsed after being defeated by the French during the Battle of Maysalun in July 1920. Norman Bentwich, England in Palestine, p. 51, "The High Commissioner had ... only been in office a few days when Emir Faisal ... had to flee his kingdom" and "The departure of Faisal and the breaking up of the Emirate of Syria left the territory on the east side of Jordan in a puzzling state of detachment ... His Majesty's Government were unwilling to embark on any definite commitment, and vetoed any entry into the territory by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia, the largest in the Middle East, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 12th-largest in the world. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Bahrain, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the south. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt and Israel. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of Geography of Saudi Arabia, its terrain consists of Arabian Desert, arid desert, lowland, steppe, and List of mountains in Saudi Arabia, mountains. The capital and List of cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandate For Palestine
The Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations mandate for British Empire, British administration of the territories of Mandatory Palestine, Palestine and Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordanwhich had been Ottoman Syria, part of the Ottoman Empire for four centuriesfollowing the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I. The mandate was assigned to Britain by the San Remo conference in April 1920, after France's concession in the 1918 Clemenceau–Lloyd George Agreement (Middle East), 1918 Clemenceau–Lloyd George Agreement of the previously agreed "international administration" of Palestine under the Sykes–Picot Agreement. Transjordan was added to the mandate after Arab Kingdom of Syria, the Arab Kingdom in Damascus was toppled by the French in the Franco-Syrian War. Civil administration began in Palestine and Transjordan in July 1920 and April 1921, respectively, and the mandate was in force from 29 September 1923 to 15 May 1948 and to 25 May 1946 respectively. The ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arab Kingdom Of Syria
The Syrian Arab Kingdom (, ') was a self-proclaimed, unrecognized monarchy existing briefly in the territory of Bilad al-Sham, historical Syria. It was announced on 5 October 1918 as a fully independent Arab constitutional government with the permission of the British military. It gained independence as an emirate after the withdrawal of the British forces from Occupied Enemy Territory Administration, OETA East on 26 November 1919, and was proclaimed as a kingdom on 8 March 1920. As a kingdom the state existed a little over four months, from 8 March to 25 July 1920. During its brief existence, the kingdom was led by Sharif Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, Hussein bin Ali's son Faisal bin Hussein. Despite its claims to the territory of the Syria (region), region of Syria, Faisal's government controlled a limited area and was dependent on Britain which, along with France, generally opposed the idea of a Greater Syria and refused to recognize the kingdom. After a Franco-Syrian War, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandate For Syria And The Lebanon
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (; , also referred to as the Levant States; 1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate founded in the aftermath of the First World War and the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, concerning the territories of Syria (region), Syria and Lebanon. The mandate system was supposed to differ from colonialism, with the governing country intended to act as a trustee until the inhabitants were considered eligible for self-government. At that point, the mandate would terminate and a sovereign state would be born. During the two years that followed the end of the war in 1918—and in accordance with the Sykes–Picot Agreement signed by the United Kingdom and France during the war—the British held control of most of Ottoman Iraq (now Iraq) and the southern part of Ottoman Syria (now Israel, Palestine (region), Palestine and Transjordan (region), Transjordan), while the French controlled the rest of Ottoman Syria (including History of Lebanon under Ott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |