|
Johnson's Criteria
Johnson's criteria, or the Johnson criteria, created by John Johnson, describe both spatial domain and frequency domain approaches to analyze the ability of observers to perform visual tasks using image intensifier technology. It was an important breakthrough in evaluating the performance of visual devices and guided the development of future systems. Using Johnson's criteria, many predictive models for sensor technology have been developed that predict the performance of sensor systems under different environmental and operational conditions. History Night vision systems enabled the measurement of visual thresholds following World War II. The 1950s also marked a time of notable development in the performance modeling of night vision imaging systems. From 1957 to 1958, Johnson, a United States Army Night Vision & Electronic Sensors Directorate (NVESD) scientist, was working to develop methods of predicting target detection, orientation, recognition, and identification. Working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal Processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a sequence of numbers that represent Sampling (signal processing), samples of a continuous variable in a domain such as time, space, or frequency. In digital electronics, a digital signal is represented as a pulse train, which is typically generated by the switching of a transistor. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing. DSP applications include Audio signal processing, audio and speech processing, sonar, radar and other sensor array processing, spectral density estimation, statistical signal processing, digital image processing, data compression, video coding, audio coding, image compression, signal processing for telecommunications, control systems, biomedical engineering, and seismology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time series. While a time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time, a frequency-domain graph shows how the signal is distributed within different frequency bands over a range of frequencies. A complex valued frequency-domain representation consists of both the magnitude and the phase of a set of sinusoids (or other basis waveforms) at the frequency components of the signal. Although it is common to refer to the magnitude portion (the real valued frequency-domain) as the frequency response of a signal, the phase portion is required to uniquely define the signal. A given function or signal can be converted between the time and frequency domains with a pair of mathematical operators called transforms. An example is the Fourier transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
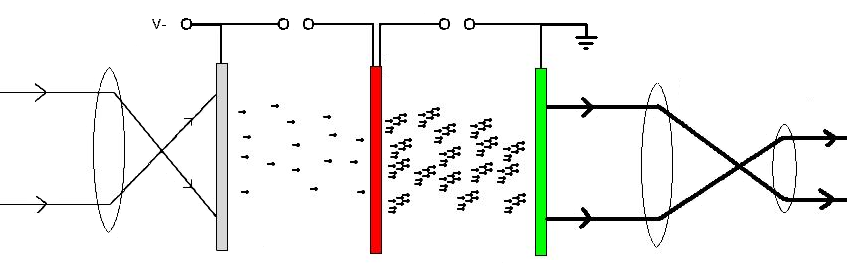
Image Intensifier
An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light processes, such as fluorescence of materials in X-rays or gamma rays ( X-ray image intensifier), or for conversion of non-visible light sources, such as near-infrared or short wave infrared to visible. They operate by converting photons of light into electrons, amplifying the electrons (usually with a microchannel plate), and then converting the amplified electrons back into photons for viewing. They are used in devices such as night-vision goggles. Introduction Image intensifier tubes (IITs) are optoelectronic devices that allow many devices, such as night vision devices and medical imaging devices, to function. They convert low levels of light from various wavelengths into visible quantities of light at a single wavelength. Operation Im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predictive Modelling
Predictive modelling uses statistics to Prediction, predict outcomes. Most often the event one wants to predict is in the future, but predictive modelling can be applied to any type of unknown event, regardless of when it occurred. For example, predictive models are often used to detect crimes and identify suspects, after the crime has taken place. In many cases, the model is chosen on the basis of detection theory to try to guess the probability of an outcome given a set amount of input data, for example given an email determining how likely that it is e-mail spam, spam. Models can use one or more classifier (mathematics), classifiers in trying to determine the probability of a set of data belonging to another set. For example, a model might be used to determine whether an email is spam or "ham" (non-spam). Depending on definitional boundaries, predictive modelling is synonymous with, or largely overlapping with, the field of machine learning, as it is more commonly referred to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operational
An operational definition specifies concrete, replicable procedures designed to represent a construct. In the words of American psychologist S.S. Stevens (1935), "An operation is the performance which we execute in order to make known a concept." For example, an operational definition of "fear" (the construct) often includes measurable physiologic responses that occur in response to a perceived threat. Thus, "fear" might be operationally defined as specified changes in heart rate, electrodermal activity, pupil dilation, and blood pressure. Overview An operational definition is designed to model or represent a concept or theoretical definition, also known as a construct. Scientists should describe the operations (procedures, actions, or processes) that define the concept with enough specificity such that other investigators can replicate their research. Operational definitions are also used to define system states in terms of a specific, publicly accessible process of preparatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night vision compared to many animals such as cats, dogs, foxes and rabbits, in part because the human eye lacks a tapetum lucidum, tissue behind the retina that reflects light back through the retina thus increasing the light available to the photoreceptors. Types of ranges Spectral range Night-useful spectral range techniques can sense radiation that is invisible to a human observer. Human vision is confined to a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum called visible light. Enhanced spectral range allows the viewer to take advantage of non-visible sources of electromagnetic radiation (such as near-infrared or ultraviolet radiation). Some animals such as the mantis shrimp and trout can see using much more of the infrared and/or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Communications-Electronics Research, Development And Engineering Center
The Combat Capabilities Development Command (CCDC) C5ISR Center, formerly the Communications-Electronics RD&E Center (CERDEC), is the United States Army information technologies and integrated systems center. CCDC C5ISR Center is headquartered at Aberdeen Proving Ground in Maryland, with activities at Fort Belvoir in Virginia and Joint Base McGuire-Dix-Lakehurst in New Jersey. As one of the 10 organizations that make up the Combat Capabilities Development Command, a subordinate organization of the Army Futures Command, CCDC C5ISR Centers supplies Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Cyber, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (C4ISTAR, C5ISR) capabilities, technologies and integrated solutions for the Soldier. Core competencies CCDC C5ISR Center's six directorates and Product Director (PD) aim to integrate Department of Defense Architecture Framework, C5ISR technologies in order to provide System of systems, systems-of-systems products for soldiers. "C5ISR" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale Model
A scale model is a physical model that is geometrically similar to an object (known as the ''prototype''). Scale models are generally smaller than large prototypes such as vehicles, buildings, or people; but may be larger than small prototypes such as anatomical structures or subatomic particles. Models built to the same scale as the prototype are called '' mockups''. Scale models are used as tools in engineering design and testing, promotion and sales, filmmaking special effects, military strategy, and hobbies such as rail transport modeling, wargaming and racing; and as toys. Model building is also pursued as a hobby for the sake of artisanship. Scale models are constructed of plastic, wood, or metal. They are usually painted with enamel, lacquer, or acrylics. Model prototypes include all types of vehicles (railroad trains, cars, trucks, military vehicles, aircraft, and spacecraft), buildings, people, and science fiction themes (spaceships and robots). Methods M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Pair (optics)
In philately, a line pair is a coil pair of postage stamp A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage (the cost involved in moving, insuring, or registering mail). Then the stamp is affixed to the f ...s bearing an inked line between the two stamps. There are at least two kinds of these: *A guide line pair has a guide line between the stamps. Since the guide lines are deliberately incised into the plate, they will generally be sharp and clear. *A joint line pair has a joint line between the stamps, deriving from the seam in the cylindrical plate used to print the stamps. These lines are somewhat smeared in appearance. Since line pairs tend to be rarer, collectors are often willing to pay more money for them. {{DEFAULTSORT:Line Pair Philatelic terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly ''resolved''. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes (e.g. lines per mm, lines per inch), to the overall size of a picture (lines per picture height, also known simply as lines, TV lines, or TVL), or to angular subtense. Instead of single lines, line pairs are often used, composed of a dark line and an adjacent light line; for example, a resolution of 10 lines per millimeter means 5 dark lines alternating with 5 light lines, or 5 line pairs per millimeter (5 LP/mm). Photographic lens are most often quoted in line pairs per millimeter. Types The resolution of digital cameras can be described in many different ways. Pixel count The term ''resolution'' is often considered eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an event is to occur."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th ed., (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', vol. 1, 3rd ed., (1968), Wiley, . This number is often expressed as a percentage (%), ranging from 0% to 100%. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%). These concepts have been given an axiomatic mathematical formaliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |