|
Joachim Ernst, Margrave Of Brandenburg-Ansbach
Joachim Ernst, Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach (22 June 1583 in Cölln an der Spree – 7 March 1625 in Ansbach) was a German nobleman. He ruled as margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach from 1603 to 1625, succeeding his cousin George Frederick and succeeded by his son Frederick III. Life Youth Joachim Ernst was the son of the elector John George of Brandenburg and his third wife, Elisabeth of Anhalt-Zerbst. He travelled in England and Scotland in 1599.''HMC Salisbury Hatfield'', vol. 15 (London, 1930), p. 236. He took over in 1603, the government of the Margraviate of Brandenburg-Ansbach, after the old line of Franconian Hohenzollerns died out with the death of George Fredrick the Elder of the Ansbach-Jägerndorf branch. Joachim Ernst founded the younger branch of Ansbach line of the Franconian Hohenzollerns. Succession rules His predecessor, George Frederick had settled the succession of his two Franconian possessions (Brandenburg-Ansbach and Brandenburg-Kulmbach) in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margrave Of Brandenburg-Ansbach
The Principality or Margraviate of (Brandenburg) Ansbach ( or ) was a principality in the Holy Roman Empire centered on the Franconian city of Ansbach. The ruling Hohenzollern princes of the land were known as margraves, as their ancestors were margraves (so the principality was a margraviate but not a march). History The principality was established following the death of Frederick V, Burgrave of Nuremberg, on 21 January 1398. By agreement, his lands were partitioned between his two sons, a process that took more than two years. The younger son, Frederick VI, received Ansbach and the elder, John III, received Bayreuth. After John III's death on 11 June 1420, the two principalities were reunited under Frederick VI, who had become Elector Frederick I of Brandenburg in 1415. On 21 September 1440, almost three years after Frederick's death his territories were divided between his sons; John received the principality of Bayreuth (Brandenburg-Kulmbach), Frederick received Branden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Treaty Of Gera
The House Treaty of Gera was a house law of the House of Hohenzollern on the succession in Brandenburg and in the Franconian territories at the end of the sixteenth century binding rules. The Treaty and came about because Elector John George of Brandenburg had violated the requirements made in Dispositio Achillea in his will. In these provisions, the indivisibility of the Mark of Brandenburg has been prescribed as a mandatory principle of succession. John George, however, had stipulated his will that part of the Neumark and Krosno Odrzańskie should be separated from the Mark and given to his two younger sons. History Immediately after John George's death in 1598, his eldest son and successor, Elector Joachim Frederick contested the will and consulted with Margrave George Frederick I. He was the last descendant of the elder branch of the Franconian Hohenzollerns and ruled the two margraviates of Brandenburg-Ansbach and Brandenburg-Kulmbach. George Frederick had no of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in starting the war. However, its scope and extent wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Dortmund (1609)
The Treaty of Dortmund, or Dortmund Recess, was an agreement that was concluded on 10 June 1609 between representatives of Elector Johann Sigismund of Brandenburg and Wolfgang Wilhelm of Palatinate-Neuburg with regard to the succession of the United Duchies of Julich-Cleves-Berg through the mediation of Landgrave Maurice of Hesse-Kassel. It took place in the city of Dortmund. Background The Duchy of Julich-Cleves-Berg was one of the largest and wealthiest states in the Holy Roman Empire. It was also in a key location, as it was close to the Spanish Road and the ongoing 80 Years War. In addition, with the Protestant Reformation occurring throughout Germany, tension between princes of the Holy Roman Empire were high. Its duke, Johann William, had no children, and thus his inheritance was in dispute. The two main candidates to the Julich inheritance were the Lutheran Wolfgang Wilhelm of Palatinate-Neuburg and the also Lutheran Johann Sigismund of Brandenburg. There were many a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Jülich Succession
The War of the Jülich Succession, also known as the Jülich War or the Jülich-Cleves Succession Crises (German language, German: ''Jülich-Klevischer Erbfolgestreit''), was a war of succession in the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg. The first phase of the war lasted between 10 June 1609 and 24 October 1610, with the second phase starting in May 1614 and finally ending on 13 October 1614. At first, the war pitted Catholic Church, Catholic Archduke Leopold V, Archduke of Austria, Leopold V against the combined forces of the Protestantism, Protestant claimants, John Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg, Johann Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg and Wolfgang Wilhelm, Count Palatine of Neuburg, Wolfgang Wilhelm of Palatinate-Neuburg, ending in the former's military defeat. The representatives of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg and Palatinate-Neuburg, Neuburg later entered conflict amongst themselves, partly due to religious conversions, which led to the resumption of hostilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Sigismund, Elector Of Brandenburg
John Sigismund (; 8 November 1572 – 23 December 1619) was a Prince-elector of the Margraviate of Brandenburg from the House of Hohenzollern. He became the Duke of Prussia through his marriage to Duchess Anna, the eldest daughter of Duke Albert Frederick of Prussia who died without sons. Their marriage resulted in the potential creation of Brandenburg-Prussia, which became a reality after Poland's leader appointed John Sigismund in charge of Prussia in regency and, shortly thereafter, Albert Frederick died without an able, direct male heir. Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia John Sigismund was born in Halle an der Saale to Joachim III Frederick, Elector of Brandenburg, and his first wife Catherine of Brandenburg-Küstrin. He succeeded his father as Margrave of Brandenburg in 1608. In 1611, John Sigismund traveled from Königsberg to Warsaw, where on 16 November 1611 he gave feudal homage to Sigismund III Vasa, King of Poland (the Duchy of Prussia was a Polish fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nördlingen
Nördlingen (; Swabian: ''Nearle'' or ''Nearleng'') is a town in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, with a population of approximately 20,674. It is located approximately east of Stuttgart, and northwest of Munich. It was built in an impact crater 15 million years old and in diameter—the Nördlinger Ries—of a meteorite which hit with an estimated speed of 70,000 km/h, and left the area riddled with an estimated 72,000 tons of micro-diamonds. Nördlingen was first mentioned in recorded history in 898. The town was the location of two battles during the Thirty Years' War, which took place between 1618 and 1648. Today it is one of very few towns in Germany that still have completely intact city walls—joining the ranks of Rothenburg ob der Tauber, Dinkelsbühl and Berching, all of them in Bavaria. Another attraction in the town is Saint George's Church's steeple, called "Daniel," which is made of a suevite impact breccia that contains shocked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auhausen
Auhausen is a municipality in the Swabian district Donau-Ries in Bavaria in Germany. The municipality is within the Oettingen central administrative body. Auhausen was the site of the 1608 meeting that formed the Protestant Union The Protestant Union (), also known as the Evangelical Union, Union of Auhausen, German Union or the Protestant Action Party, was a coalition of Protestant German states. It was formed on 14 May 1608 by Frederick IV, Elector Palatine in order t ..., also known as the ''Union of Auhausen''. Schloss Hirschbrunn, a castle owned by the House of Oettingen-Spielberg, is in Auhausen. References Donau-Ries {{DonauRies-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Union
The Protestant Union (), also known as the Evangelical Union, Union of Auhausen, German Union or the Protestant Action Party, was a coalition of Protestant German states. It was formed on 14 May 1608 by Frederick IV, Elector Palatine in order to defend the rights, land and safety of each member. It included both Calvinism, Calvinist and Lutheran states, and dissolved in 1621. Formation The union was formed following two events. Firstly, the Holy Roman Emperor Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II and Duchy of Bavaria, Bavarian Duke Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian I reestablished Catholic Church, Catholicism in Donauwörth in 1607. Secondly, by 1608, a majority of the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet had decided that the renewal of the 1555 Peace of Augsburg should be conditional upon the restoration of all church land appropriated since 1552. The Protestant princes met in Auhausen, and formed a coalition of Protestant states under the leadership of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the war included the Reformation, Centralised state, centralisation, excessive taxation, and the rights and privileges of the Dutch nobility and cities. After Eighty Years' War, 1566–1572, the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed Army of Flanders, his armies and Eighty Years' War, 1572–1576, regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, Spanish Fury, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent, but the Eighty Years' War, 1576–1579, general rebelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
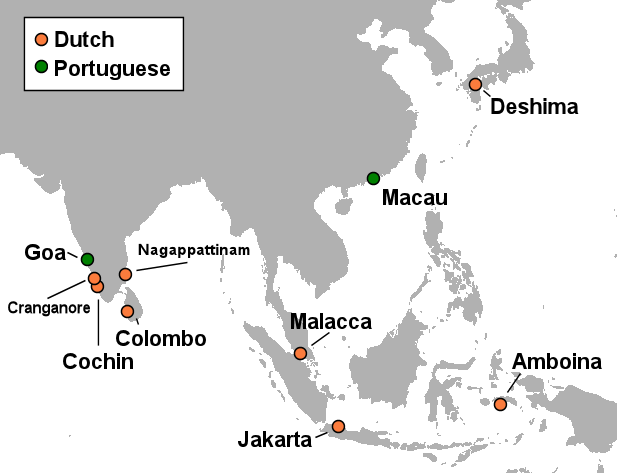
Dutch Empire
The Dutch colonial empire () comprised overseas territories and trading posts under some form of Dutch control from the early 17th to late 20th centuries, including those initially administered by Dutch chartered companies—primarily the Dutch East India Company (1602–1799) and Dutch West India Company (1621–1792)—and subsequently governed by the Dutch Republic (1581–1795) and modern Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1975). Following the ''de facto'' independence of the Dutch Republic from the Spanish Empire in the late 16th century, various trading companies known as '' voorcompagnie'' led maritime expeditions overseas in search of commercial opportunities. By 1600, Dutch traders and mariners had penetrated the lucrative Asian spice trade but lacked the capital or manpower to secure or expand their ventures; this prompted the States General in 1602 to consolidate several trading enterprises into the semi-state-owned Dutch East India Company (, VOC), which was g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |