|
Jean De Brébeuf
Jean de Brébeuf () (25 March 1593 16 March 1649) was a French Jesuit missionary who travelled to New France (Canada) in 1625. There he worked primarily with the Huron for the rest of his life, except for a few years in France from 1629 to 1633. He learned their language and customs, writing extensively about each to aid other missionaries. In 1649, Brébeuf and another missionary were captured when an Iroquois raid took over a Huron village (referred to in French as St. Louis). Together with Huron captives, the missionaries were ritually tortured and killed on 16 March 1649. Afterwards, his heart was eaten by Iroquois tribesmen. Brébeuf was beatified in 1925 and with eight Jesuit missionaries was canonized in the Catholic Church in 1930. Biography Early years Brébeuf was born 25 March 1593 in Condé-sur-Vire, Normandy, France (He was the uncle of poet Georges de Brébeuf.). He joined the Society of Jesus in 1617 at the age of 24, spending the next two years under the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denomination. In Anglican Communion, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheranism, Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but a selected few are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official Ecclesiastical polity, ecclesiastical recognition, and veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. In many Protestant denominations, and following from Pauline usage, ''saint'' refers broadly to any holy Christian, without special recognition or selection. While the English word ''saint'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Canonized
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of saints, or authorized list of that communion's recognized saints. Catholic Church Canonization is a papal declaration that the Catholic faithful may venerate a particular deceased member of the church. Popes began making such decrees in the tenth century. Up to that point, the local bishops governed the veneration of holy men and women within their own dioceses; and there may have been, for any particular saint, no formal decree at all. In subsequent centuries, the procedures became increasingly regularized and the Popes began restricting to themselves the right to declare someone a Catholic saint. In contemporary usage, the term is understood to refer to the act by which any Christian church declares that a person who has died is a sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
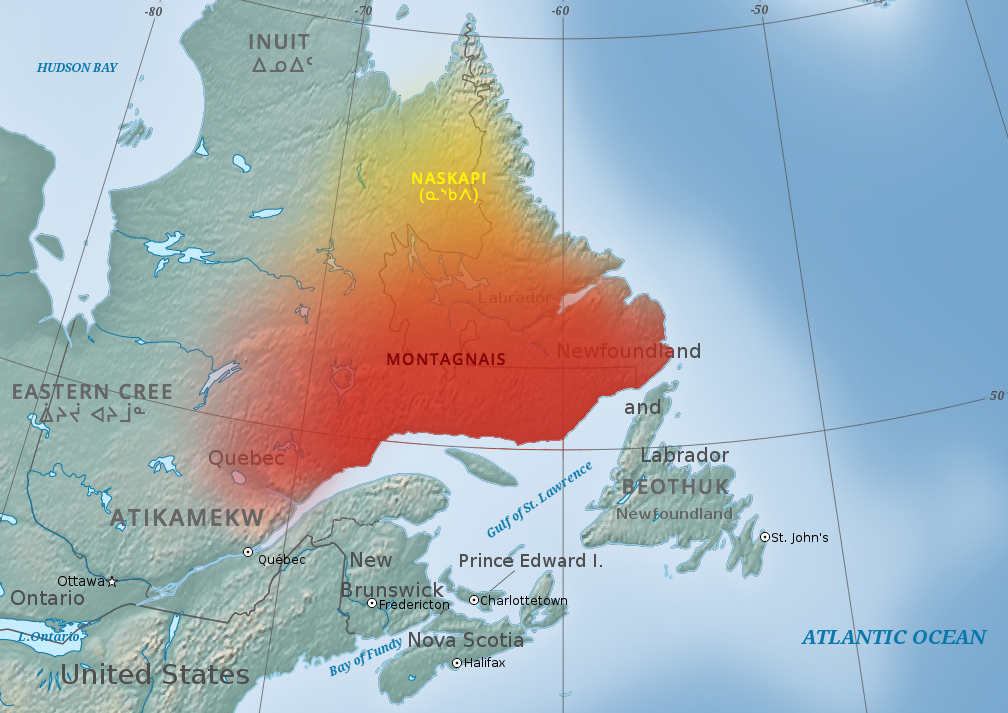
Innu People
The Innu/Ilnu ('man, person'), formerly called Montagnais (French for ' mountain people'; ), are the Indigenous Canadians who inhabit northeastern Labrador in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as '' Nitassinan'' ('Our Land', ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ('Innu Land'). The ancestors of the modern First Nations were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for many thousands of years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, which changed over time from Old Montagnais to Innu-aimun (popularly known since the French colonial era as Montagnais), is spoken throughout Nitassinan, with certain dialect differences. It is part of the Cree–Montagnais– Naskapi dialect continuum, and is unrelate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Énemond Massé
Énemond Massé, SJ (3 August 1575 – 12 May 1646) was a French Jesuit missionary, one of the first Jesuits sent to New France. Life Nesmes Massé was born 3 August 1575 at Lyon. He was the eldest son of François and Philippe Bica Massé. His father was a baker. On 22 August 1595 he entered the novitiate of the Society of Jesus at Avignon, taking the name Énemond. After completing his novitiate he taught at the Collège of Tournon from 1597 to 1599, and was also assistant to the bursar. He completed his theological studies at the Collège of Dole in 1602. Sometime after his ordination to the priesthood in 1603, he went to the Collège in Lyon, to serve as minister or bursar. In 1609 he left the province of Lyon to join Father Pierre Coton, the confessor to Henri IV, at the court. In September 1610 Father Massé was selected to accompany Father Pierre Biard to New France. They left from Dieppe and arrived in Port-Royal (Acadia) on 22 May 1611. Massé was seasick for much o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Lalemant
Charles Lallemant, SJ (; or Lalemant; November 17, 1587 – November 18, 1674) was a French Jesuit missionary. He was born in Paris in 1587 and later became the first superior of the Jesuit Missions amongst the Huron in Canada. His letter to his brother, dated August 1, 1626, inaugurated the series '' Relations des Jésuites de la Nouvelle-France'' about the missionary work in the North American colonies of New France. Biography Born in Paris to an official of the criminal court, Lalemant entered the novitiate of the Society of Jesus at Rouen on July 29, 1607. Following this period, he studied philosophy at the Jesuit college in La Flèche (1609–12). For the subsequent formation period of his regency, he taught the lower classes at the college in Nevers (1612–15), then studied theology at La Flèche (1615–19). After this, his spent his period of tertianship, a third probationary year, in Paris (1619–20). He then served as a teacher of logic and physics at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |