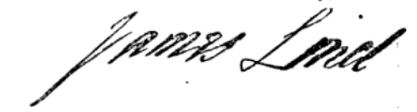|
James Lind
James Lind (4 October 1716 – 13 July 1794) was a Scottish physician. He was a pioneer of naval hygiene in the Royal Navy. By conducting one of the first ever clinical trials, he developed the theory that citrus fruits cured scurvy. Lind argued for the health benefits of better ventilation aboard naval ships, the improved cleanliness of sailors' bodies, clothing and bedding, and below-deck fumigation with sulphur and arsenic. He also proposed that fresh water could be obtained by distillation, distilling sea water. His work advanced the practice of preventive medicine and improved nutrition. Early life Lind was born in Edinburgh, Scotland, in 1716 into a family of merchants, then headed by his father, James Lind. He had an elder sister. He was educated at the Royal High School, Edinburgh. In 1731 he began his medical studies as an apprentice of George Langlands, a fellow of the Incorporation of Surgeons which preceded the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh. In 1739, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Lind (physician, Born 1736)
James Lind Royal Society of London, FRS FRSE FRCPE (May 17, 1736 – October 17, 1812) was a Scottish natural philosopher and physician. Life James Lind was born in Gorgie, Edinburgh on 17 May 1736. He studied medicine at Edinburgh University under William Cullen and Joseph Black, and graduated in 1768. In 1766, he then joined the East India Company as surgeon. In 1768 he received his doctorate (MD) from Edinburgh upon completing a dissertation on marsh fever (malaria) in Bengal. On 6 November 1770 he was admitted a Fellow of the College of Physicians, Edinburgh, College of Physicians, Edinburgh. In 1773 he was a founding member of the Aesculapian Club. Lind was also a corresponding member of the Lunar Society of Birmingham, Lunar Society. Personality Lind is widely regarded as having an eccentric personality, and considered to be reckless with spending money as captured by the following dialogue: "Why, Dr. Lind, you spend a whole seas of gold", to which Lind replied, "Madam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh had a population of in , making it the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city in Scotland and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous in the United Kingdom. The Functional urban area, wider metropolitan area had a population of 912,490 in the same year. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament, the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland, and the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarch in Scotland. It is also the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. The city has long been a cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Water
Seawater, or sea water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts (predominantly sodium () and chloride () ions). The average density at the surface is 1.025 kg/L. Seawater is denser than both fresh water and pure water (density 1.0 kg/L at ) because the dissolved salts increase the mass by a larger proportion than the volume. The freezing point of seawater decreases as salt concentration increases. At typical salinity, it freezes at about . The coldest seawater still in the liquid state ever recorded was found in 2010, in a stream under an Antarctic glacier: the measured temperature was . Seawater pH is typically limited to a range between 7.5 and 8.4. However, there is no universally accepted reference pH-scale for seawater and the difference between measurements b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Anson's Voyage Around The World
While Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain was fighting the War of Jenkins' Ear with Spain in 1740, Commodore (Royal Navy), Commodore George Anson, 1st Baron Anson, George Anson led a squadron of eight ships on a mission to disrupt or capture the Spanish possessions in the Pacific. He returned to Britain in 1744 by way of Qing dynasty, China, thereby completing a circumnavigation of the globe. The voyage was notable for the capture of the Manila galleon and for its horrific losses due to powerful storms and disease, with only 188 men of the original 1,854 crew and officers surviving. An account of the voyage was published in 1748. It was widely read by the general public and was a great commercial success. It has been described in 1899 as being "still esteemed as the story of a remarkable voyage extremely well told." Background In 1739, the riches that Spain derived from the New World were well known throughout Europe. Huge quantities of silver were shipped from Peru, carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Anson, 1st Baron Anson
Admiral of the Fleet George Anson, 1st Baron Anson, PC, FRS (23 April 1697 – 6 June 1762) was a Royal Navy officer and politician from the Anson family. He served as a junior officer during the War of the Spanish Succession and then saw active service against Spain at the Battle of Cape Passaro, off the south tip of Sicily, during the War of the Quadruple Alliance. He then undertook a circumnavigation of the globe during the War of Jenkins' Ear. Anson commanded the fleet that defeated the French Admiral de la Jonquière at the First Battle of Cape Finisterre in 1747, during the War of the Austrian Succession. Anson went on to be First Lord of the Admiralty during the Seven Years' War. Among his reforms were the removal of corrupt defence contractors, improved medical care, submitting a revision of the Articles of War to Parliament to tighten discipline throughout the Navy, uniforms for commissioned officers, the transfer of the Marines from Army to Navy authority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesoderm, the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord, are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leukocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ) was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, Essential nutrients cannot be biosynthesis, synthesized in the organism in sufficient quantities for survival, and therefore must be obtained through the Diet (nutrition), diet. For example, vitamin C can be synthesized by some species but not by others; it is not considered a vitamin in the first instance but is in the second. Most vitamins are not single molecules, but groups of related molecules called vitamers. For example, there are eight vitamers of vitamin E: four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The term ''vitamin'' does not include the three other groups of essential nutrients: mineral (nutrient), minerals, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids. Major health organizations list thirteen vitamins: * Vitamin A (all-' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Vitamin C may be taken by mouth or by intramuscular, subcutaneous or intravenous injection. Various health claims exist on the basis that moderate vitamin C deficiency increases disease risk, such as for the common cold, cancer or COVID-19. There are also claims of benefits from vitamin C supplementation in excess of the recommended d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh Medical School
The University of Edinburgh Medical School (also known as Edinburgh Medical School) is the medical school of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland and the United Kingdom and part of the University of Edinburgh College of Medicine and Veterinary Medicine, College of Medicine and Veterinary Medicine. It was established in 1726, during the Scottish Enlightenment, making it the oldest medical school in the United Kingdom and the oldest medical school in the English-speaking world. The medical school in 2025 was ranked 5th by the Complete University Guide, 6th in the UK by The Guardian University Guide, and 7th by The Times University Guide. It also ranked 21st in the world by both the Times Higher Education World University Rankings and the QS World University Rankings in the same year. According to a Healthcare Survey run by Saga in 2006, the medical school's main teaching hospital, the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, was considered the best hospital in Scotland. The medical school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venereal Diseases
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, oral sex, or sometimes manual sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of transmitting them to others. The term ''sexually transmitted infection'' is generally preferred over ''sexually transmitted disease'' or ''venereal disease'', as it includes cases with no symptomatic disease. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital warts, genital herpes, and HIV/AIDS. Parasitic STIs include trichomoniasis. Most STIs are treatable and curable; of the most common infections, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Medicine
A Doctor of Medicine (abbreviated MD, from the Latin language, Latin ) is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the ''MD'' denotes a professional degree of physician. This generally arose because many in 18th-century medical professions trained in Scotland, which used the MD degree nomenclature. In England, however, Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) was used: in the 19th century, it became the standard in Scotland too. Thus, in the United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Ireland and other countries, the MD is a research doctorate, honorary degree, honorary doctorate or applied clinical degree restricted to those who already hold a professional degree (Bachelor's/Master's/Doctoral) in medicine. In those countries, the equivalent professional degree to the North American, and some others' usage of MD is still typically titled Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery. History The fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Fleet
The Channel Fleet and originally known as the Channel Squadron was the Royal Navy formation of warships that defended the waters of the English Channel from 1854 to 1909 and 1914 to 1915. History Throughout the course of Royal Navy's history there had been different squadrons stationed in home waters. One of the earliest known naval formations to be based at Plymouth was called the Western Squadron which was the forerunner of the Channel Squadron that was later known as the Channel Fleet. In 1650 Captain William Penn, Commander-in-Chief, was charged with guarding the Channel from Beachy Head to Lands End with six ships. This system continued following the Restoration. It was the start of what was to become a Western Squadron. From 1690 the squadron operated out of Plymouth Dockyard during wartime periods, which was for most of the 18th century and early 19th century. In 1854 The Channel Squadron, sometimes known as the Particular Service Squadron, was established. The Channel Sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |