|
Index Of Phonetics Topics
A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar ejective affricate () * Alveolar ejective () * Alveolar ejective fricative () * Alveolar flap () * Alveolar lateral approximant (, ) * Alveolar lateral ejective affricate () * Alveolar lateral ejective fricative () * Alveolar lateral flap () * Alveolar nasal () * Alveolar ridge * Alveolar trill (, ) * Alveolo-palatal consonant * Alveolo-palatal ejective fricative () * Apical consonant * Approximant consonant * Articulatory phonetics * Aspirated consonant (◌ʰ) * Auditory phonetics B * Back vowel * Basis of articulation * Bernd J. Kröger * Bilabial click () * Bilabial consonant * Bilabial ejective () * Bilabial flap () * Bilabial nasal () * Bilabial trill () * Breathy voice C * Cardinal vowel * Central consonant * Central vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Phonetics
Acoustic phonetics is a subfield of phonetics, which deals with acoustic aspects of speech sounds. Acoustic phonetics investigates time domain features such as the mean squared amplitude of a waveform, its duration, its fundamental frequency, or frequency domain features such as the frequency spectrum, or even combined spectrotemporal features and the relationship of these properties to other branches of phonetics (e.g. articulatory or auditory phonetics), and to abstract linguistic concepts such as phonemes, phrases, or utterances. The study of acoustic phonetics was greatly enhanced in the late 19th century by the invention of the Edison phonograph. The phonograph allowed the speech signal to be recorded and then later processed and analyzed. By replaying the same speech signal from the phonograph several times, filtering it each time with a different band-pass filter, a spectrogram of the speech utterance could be built up. A series of papers by Ludimar Hermann published i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Lateral Ejective Fricative
The alveolar lateral ejective fricative is a type of consonantal sound, reported in the Northwest Caucasian languages and in Modern South Arabian languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . Features Features of the alveolar lateral ejective fricative: Occurrence occurs in the reconstructed Proto-Semitic language. See also * Index of phonetics articles A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar ejecti ... References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Alveolar Lateral Ejective Fricative Fricative consonants Alveolar consonants Lateral consonants Ejectives Oral consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
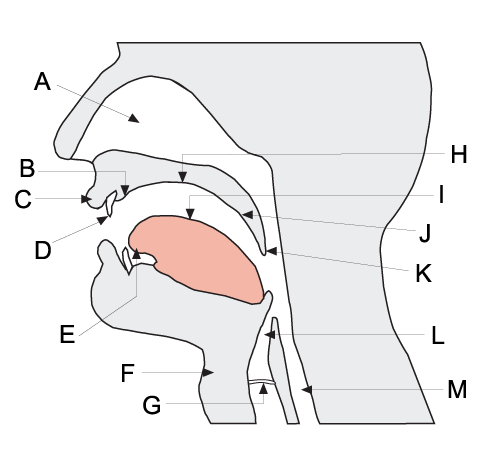
Basis Of Articulation
In phonetics, the basis of articulation, also known as articulatory setting, is the default position or standard settings of a speaker's organs of articulation when ready to speak. Different languages each have their own basis of articulation, which means that native speakers will share a certain position of tongue, lips, jaw, possibly even uvula or larynx, when preparing to speak. These standard settings enable them to produce the sounds and prosody of their native language more efficiently. Beatrice Honikman suggests thinking of it in terms of having a "gear" for English, another for French, and so on depending on which language is being learned; in the classroom, when working on pronunciation, the first thing the learner must do is to think themselves into the right gear before starting on pronunciation exercises. Jenner (2001) gives a detailed account of how this idea arose and how Honikman has been credited with its invention despite a considerable history of prior study. Diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Vowel
A back vowel is any in a class of vowel sound used in spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a back vowel is that the highest point of the tongue is positioned relatively back in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Back vowels are sometimes also called dark vowels because they are perceived as sounding darker than the front vowels. Near-back vowels are essentially a type of back vowels; no language is known to contrast back and near-back vowels based on backness alone. The category "back vowel" comprises both raised vowels and retracted vowels. Articulation In their articulation, back vowels do not form a single category, but may be either raised vowels such as or retracted vowels such as .Scott Moisik, Ewa Czaykowska-Higgins, & John H. Esling (2012"The Epilaryngeal Articulator: A New Conceptual Tool for Understanding Lingual-Laryngeal Contrasts"/ref> Partial list The back vowels that have dedicated symbols in the Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Phonetics
Auditory phonetics is the branch of phonetics concerned with the hearing of speech sounds and with speech perception. It thus entails the study of the relationships between speech stimuli and a listener's responses to such stimuli as mediated by mechanisms of the peripheral and central auditory systems, including certain areas of the brain. It is said to compose one of the three main branches of phonetics along with acoustic and articulatory phonetics, though with overlapping methods and questions. Physical scales and auditory sensations There is no direct connection between auditory sensations and the physical properties of sound that give rise to them. While the physical (acoustic) properties are objectively measurable, auditory sensations are subjective and can only be studied by asking listeners to report on their perceptions. The table below shows some correspondences between physical properties and auditory sensations. Segmental and suprasegmental Auditory phonetics is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspirated Consonant
In phonetics, aspiration is the strong burst of breath that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. In English, aspirated consonants are allophones in complementary distribution with their unaspirated counterparts, but in some other languages, notably most South Asian languages (including Indian) and East Asian languages, the difference is contrastive. In dialects with aspiration, to feel or see the difference between aspirated and unaspirated sounds, one can put a hand or a lit candle in front of one's mouth, and say ''spin'' and then ''pin'' . One should either feel a puff of air or see a flicker of the candle flame with ''pin'' that one does not get with ''spin''. Transcription In the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), aspirated consonants are written using the symbols for voiceless consonants followed by the aspiration modifier letter , a superscript form of the symbol for the voiceless glottal fricative . Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articulatory Phonetics
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures. Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound. Respiratory sounds can be produced by expelling air from the lungs. However, to vary the sound quality in a way useful for speaking, two speech organs normally move towards each other to contact each other to create an obstruction that shapes the air in a particular fashion. The point of maximum obstruction is called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximant Consonant
Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough nor with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no turbulence. This class is composed of sounds like (as in ''rest'') and semivowels like and (as in ''yes'' and ''west'', respectively), as well as lateral approximants like (as in ''less''). Terminology Before Peter Ladefoged coined the term "approximant" in the 1960s, the terms "frictionless continuant" and "semivowel" were used to refer to non-lateral approximants. In phonology, "approximant" is also a distinctive feature that encompasses all sonorants except nasals, including vowels, taps and trills. Semivowels Some approximants resemble vowels in acoustic and articulatory properties and the terms ''semivowel'' and ''glide'' are often used for these non-syllabic vowel-like segme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Consonant
An apical consonant is a phone (speech sound) produced by obstructing the air passage with the tip of the tongue (apex) in conjunction with upper articulators from lips to postalveolar, and possibly prepalatal. It contrasts with laminal consonants, which are produced by creating an obstruction with the blade of the tongue, just behind the tip. Sometimes ''apical'' is used exclusively for an articulation that involves only the tip of the tongue and ''apicolaminal'' for an articulation that involves both the tip and the blade of the tongue. However, the distinction is not always made and the latter one may be called simply ''apical'', especially when describing an apical dental articulation. As there is some laminal contact in the alveolar region, the apicolaminal dental consonants are also labelled as ''denti-alveolar''. It is not a very common distinction and is typically applied only to fricatives and affricates. Thus, many varieties of English have either apical or laminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolo-palatal Ejective Fricative
The alveolo-palatal ejective fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation ... that represents this sound is . Features Features of the alveolo-palatal ejective fricative: Occurrence See also * Index of phonetics articles External links * {{IPA navigation Fricative consonants Alveolar consonants Palatal consonants Ejectives Oral consonants Central consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolo-palatal Consonant
In phonetics, alveolo-palatal (or alveopalatal) consonants, sometimes synonymous with pre-palatal consonants, are intermediate in articulation between the coronal and dorsal consonants, or which have simultaneous alveolar and palatal articulation. In the official IPA chart, alveolo-palatals would appear between the retroflex and palatal consonants but for "lack of space".John Esling, 2010, "Phonetic Notation". In Hardcastle, Laver, & Gibbon, eds, ''The Handbook of Phonetic Sciences'', p 693 Ladefoged and Maddieson characterize the alveolo-palatals as palatalized postalveolars ( palato-alveolars), articulated with the blade of the tongue behind the alveolar ridge and the body of the tongue raised toward the palate, whereas Esling describes them as advanced palatals (pre-palatals), the furthest front of the dorsal consonants, articulated with the body of the tongue approaching the alveolar ridge. These descriptions are essentially equivalent, since the contact includes both t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Trill
The voiced alveolar trill is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar trills is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r. It is commonly called the rolled R, rolling R, or trilled R. Quite often, is used in phonemic transcriptions (especially those found in dictionaries) of languages like English and German that have rhotic consonants that are not an alveolar trill. That is partly for ease of typesetting and partly because is the letter used in the orthographies of such languages. In many Indo-European languages, a trill may often be reduced to a single vibration in unstressed positions. In Italian, a simple trill typically displays only one or two vibrations, while a geminate trill will have three or more. Languages where trills always have multiple vibrations include Albanian, Spanish, Cypriot Greek, and a number of Armenian and Portuguese dialects. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |