|
Illusory Palinopsia
Illusory palinopsia is a subtype of palinopsia, a visual disturbance defined as the persistence or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is a broad term describing a heterogeneous group of symptoms, which is divided into hallucinatory palinopsia and illusory palinopsia. Illusory palinopsia is likely due to sustained awareness of a stimulus and is similar to a visual illusion: the distorted perception of a real external stimulus. Illusory palinopsia is caused by migraines, hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), prescription drugs, and head trauma, but is also sometimes idiopathic. Illusory palinopsia consists of afterimages that are short-lived or unformed, occur at the same location in the visual field as the original stimulus, and are often exposed or exacerbated based on environmental parameters such as stimulus intensity, background contrast, fixation, and movement. Illusory palinopsia symptoms occur continuously or predi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropsia
Micropsia is a condition affecting human visual perception in which objects are perceived to be smaller than they actually are. Micropsia can be caused by optical factors (such as wearing glasses), by distortion of images in the eye (such as optically, via swelling of the cornea or from changes in the shape of the retina such as from retinal edema, macular degeneration, or central serous retinopathy), by changes in the brain (such as from traumatic brain injury, epilepsy, migraines, prescription drugs, and illicit drugs), and from psychological factors. Dissociative phenomena are linked with micropsia, which may be the result of brain-lateralization disturbance. Micropsia is also commonly reported when the eyes are fixating at ( convergence), or focusing at (accommodation), a distance closer than that of the object in accord with Emmert's law. Specific types of micropsia include hemimicropsia, a form of micropsia that is localized to one half of the visual field and can be cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucinatory Palinopsia
Hallucinatory palinopsia is a subtype of palinopsia, a visual disturbance defined as the persistent or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is a broad term describing a group of symptoms which is divided into hallucinatory palinopsia and illusory palinopsia. Hallucinatory palinopsia refers to the projection of an already-encoded visual memory and is similar to a complex visual hallucination: the creation of a formed visual image where none exists. Hallucinatory palinopsia usually arises from posterior cortical lesions or seizures and can be the presenting symptom of a serious neurological disease. Hallucinatory palinopsia describes afterimages or scenes that are formed, long-lasting, high resolution, and isochromatic. The palinoptic images are not typically reliant on environmental parameters and often present with homonymous visual field deficits. Hallucinatory palinopsia occurs unpredictably and the persistent images can appear anywhere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucinatory Palinopsia
Hallucinatory palinopsia is a subtype of palinopsia, a visual disturbance defined as the persistent or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed. Palinopsia is a broad term describing a group of symptoms which is divided into hallucinatory palinopsia and illusory palinopsia. Hallucinatory palinopsia refers to the projection of an already-encoded visual memory and is similar to a complex visual hallucination: the creation of a formed visual image where none exists. Hallucinatory palinopsia usually arises from posterior cortical lesions or seizures and can be the presenting symptom of a serious neurological disease. Hallucinatory palinopsia describes afterimages or scenes that are formed, long-lasting, high resolution, and isochromatic. The palinoptic images are not typically reliant on environmental parameters and often present with homonymous visual field deficits. Hallucinatory palinopsia occurs unpredictably and the persistent images can appear anywhere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akinetopsia
Akinetopsia (Greek: a for "without", kine for "to move" and opsia for "seeing"), also known as cerebral akinetopsia or motion blindness, is a term introduced by Semir Zeki to describe an extremely rare neuropsychological disorder, having only been documented in a handful of medical cases, in which a patient cannot perceive motion in their visual field, despite being able to see stationary objects without issue. There are varying degrees of akinetopsia: from seeing motion as frames of a cinema reel to an inability to discriminate any motion. There is currently no effective treatment or cure for akinetopsia. Signs and symptoms Akinetopsia can be separated into two categories, "inconspicuous akinetopsia" or "gross akinetopsia", based on symptom severity and the amount the akinetopsia affects the patient's quality of life. Inconspicuous akinetopsia Inconspicuous akinetopsia is often described by seeing motion as a cinema reel or a multiple exposure photograph. This is the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
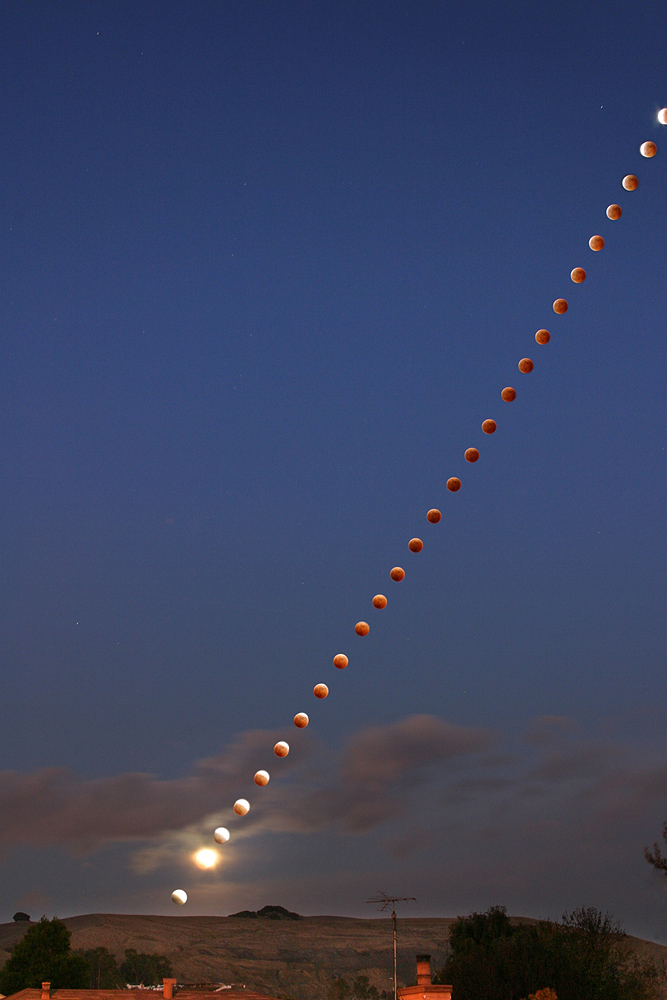
Long-exposure Photography
Long-exposure, time-exposure, or slow-shutter photography involves using a long-duration shutter speed to sharply capture the stationary elements of images while blurring, smearing, or obscuring the moving elements. Long-exposure photography captures one element that conventional photography does not: an extended period of time. The paths of bright moving objects become clearly visible—clouds form broad bands, vehicle lights draw bright streaks, stars leave trails in the sky, and water waves appear smooth. Only bright objects leave visible trails, whereas dark objects usually disappear. Boats in long exposures disappear during the daytime, but draw bright trails from their lights at night. Technique While there is no fixed definition of what constitutes "long", the intent is to create a photo that somehow shows the effect of passing time, be it smoother waters or light trails. A 30-minute photo of a static object and surrounding cannot be distinguished from a short expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Exposure
In photography and cinematography, a multiple exposure is the superimposition of two or more exposures to create a single image, and double exposure has a corresponding meaning in respect of two images. The exposure values may or may not be identical to each other. Overview Ordinarily, cameras have a sensitivity to light that is a function of time. For example, a one-second exposure is an exposure in which the camera image is equally responsive to light over the exposure time of one second. The criterion for determining that something is a double exposure is that the sensitivity goes up and then back down. The simplest example of a multiple exposure is a double exposure without flash, i.e. two partial exposures are made and then combined into one complete exposure. Some single exposures, such as "flash and blur" use a combination of electronic flash and ambient exposure. This effect can be approximated by a Dirac delta measure (flash) and a constant finite rectangular window, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterimage
AfterImage is a Filipino rock band formed in 1986, best known for their songs "Habang May Buhay", "Next in Line", and "Mangarap Ka". They disbanded in 1997 and became active again in 2008 after they reunited and released their fourth studio album. After disbanding in 1997, Wency Cornejo, the band's vocalist, pursued a solo career. In January 1992, the band signed with Dyna Records, The band's first album, entitled ''Touch the Sun'', was released in July 1992. Among the eight songs that the album contained, four were released as singles: "Next in Line", "Bai (Sa Langit ang Ating Tagpuan)", "Only You", and "Pagtawid". The title of the album, which was the concluding part of the lyric to "Next in Line", was said to have just been a spontaneous utter of phrase which Cornejo made during the recording session for the said song. History The band was composed of five members: Bobit Uson on bass guitar, Chuck Isidro on lead guitar, Rogie Callejo on drums, Arnold Cabalza on keyboards an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical sensitivity of the eyes, though the term is sometimes additionally applied to abnormal or irrational fear of light such as heliophobia. The term ''photophobia'' comes from the Greek φῶς (''phōs''), meaning "light", and φόβος (''phóbos''), meaning "fear". Causes Patients may develop photophobia as a result of several different medical conditions, related to the eye, the nervous system, genetic, or other causes. Photophobia may manifest itself in an increased response to light starting at any step in the visual system, such as: *Too much light entering the eye. Too much light can enter the eye if it is damaged, such as with corneal abrasion and retinal damage, or if its pupil(s) is unable to normally constrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillopsia
Oscillopsia is a visual disturbance in which objects in the visual field appear to oscillate. The severity of the effect may range from a mild blurring to rapid and periodic jumping. Oscillopsia is an incapacitating condition experienced by many patients with neurological disorders. It may be the result of ocular instability occurring after the oculomotor system is affected, no longer holding images steady on the retina. A change in the magnitude of the vestibulo-ocular reflex due to vestibular disease can also lead to oscillopsia during rapid head movements. Oscillopsia may also be caused by involuntary eye movements such as nystagmus, or impaired coordination in the visual cortex (especially due to toxins) and is one of the symptoms of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Those affected may experience dizziness and nausea. Oscillopsia can also be used as a quantitative test to document aminoglycoside toxicity. Permanent oscillopsia can arise from an impairment of the ocular syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
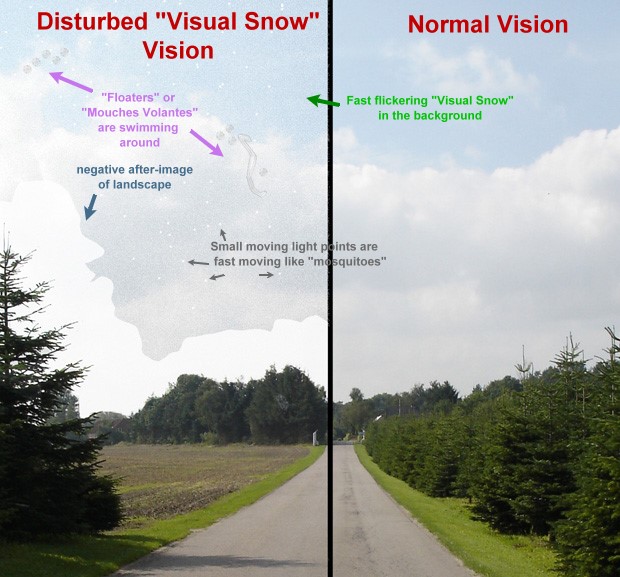
Visual Snow
Visual snow syndrome (VSS) is an uncommon neurological condition in which the primary symptom is that affected individuals see persistent flickering white, black, transparent, or coloured dots across the whole visual field. Other common symptoms are palinopsia, enhanced entoptic phenomena, photophobia, and headaches. The condition is typically always present and has no known cure, as viable treatments are still under research. Migraine and tinnitus are common comorbidities and are both associated with a more severe presentation of the syndrome. The cause of the syndrome is unclear. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve excessive excitability of neurons in the right lingual gyrus and left anterior lobe of cerebellum. Another hypothesis proposes that visual snow syndrome could be a type of thalamocortical dysrhythmia and may involve the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN). A failure of inhibitory action from the TRN to the thalamus may be the underlying cause for inabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alice In Wonderland Syndrome
Alice in Wonderland syndrome (AIWS), also known as Todd's syndrome or dysmetropsia, is a neuropsychological condition that causes a distortion of perception. People may experience distortions in visual perception of objects, such as appearing smaller (micropsia) or larger (macropsia), or appearing to be closer ( pelopsia) or farther ( teleopsia) than they actually are. Distortion may also occur for senses other than vision. The cause of Alice in Wonderland syndrome is currently unknown, but it has often been associated with migraines, head trauma, or viral encephalitis caused by Epstein–Barr virus infection. It is also theorized that it can be caused by abnormal amounts of electrical activity, resulting in abnormal blood flow in those parts of the brain which process visual perception and texture. Although there are cases of Alice in Wonderland syndrome in both adolescents and adults, it is most commonly seen in children. Classification Though not agreed upon in literature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |