|
Ivšić's Law
Ivšić's law, also Stang's law or Stang–Ivšić's law, is a Common Slavic accent law named after Stjepan Ivšić (1911) and Christian Schweigaard Stang (1957); the two linguists independently discovered the law in those years. The law explains the origin of the Proto-Slavic accent, Proto-Slavic neoacute accent occurring in the accent paradigm ''b'' as retractive from the following syllable. Retraction from stressed weak yer During the Late Common Slavic period, the short vowels *''ь'' and *''ъ'' (known as yers, also written *''ĭ'' *''ŭ'') developed into "strong" and "weak" variants according to Havlík's law. The accented weak variants could no longer carry an accent, which was thus retracted onto the preceding syllable. That syllable gained a rising ''neoacute'' accent. It is denoted with a tilde diacritic ⟨◌̃⟩ on historically "long" syllables (*''a'', *''i'', *''u'', *''y'', *''ě'', *''ę'', *''ǫ'', *VR) and with a grave accent ⟨◌̀⟩ on historically "short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the Attested language, unattested, linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th century, 6th century AD. As with most other proto-languages, no attested writings have been found; scholars have reconstructed the language by applying the comparative method to all the attested Slavic languages and by taking into account other Indo-European languages. Rapid development of Slavic speech occurred during the Proto-Slavic period, coinciding with the massive expansion of the Slavic-speaking area. Dialectal differentiation occurred early on during this period, but overall linguistic unity and mutual intelligibility continued for several centuries, into the 10th century or later. During this period, many sound changes diffused across the entire area, often uniformly. This makes it incon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
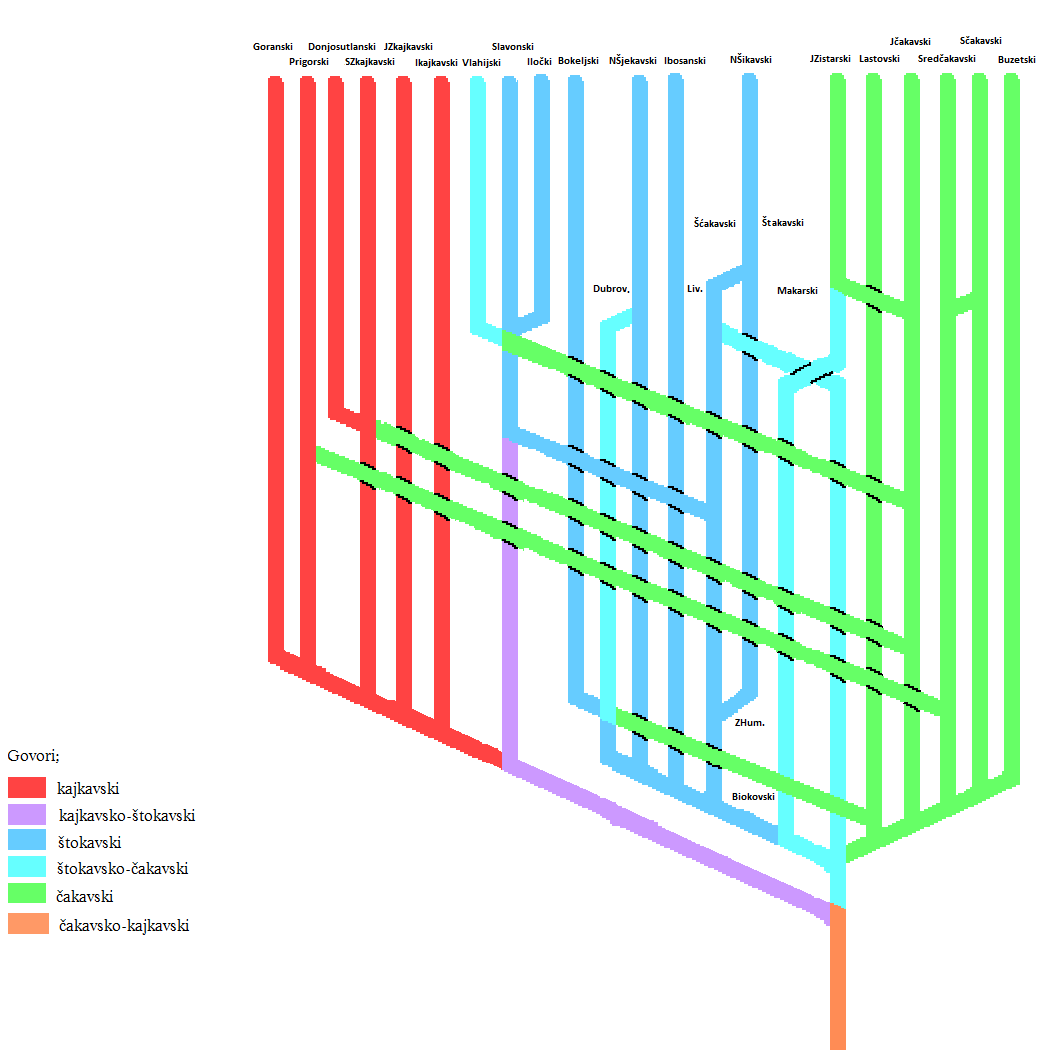
Čakavian
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic supradialect or language spoken by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia or Littoral Croatia), as well as by the Burgenland Croats as Burgenland Croatian in southeastern Austria, northwestern Hungary and southwestern Slovakia as well as few municipalities in southern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Chakavian represents the basis for early literary standards in Croatia, and until the modern age was simply known and understood, along with the Kajkavian and Shtokavian idioms in Croatia, as the Croatian language (''hrvatski jezik''). Legal and liturgical to literary texts until the 16th century, including literary work by "the father of Croatian literature" Marko Marulić and the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrvatska Akademija Znanosti I Umjetnosti
The Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts (; , HAZU) is the national academy of Croatia. HAZU was founded under the patronage of the Croatian bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer under the name Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts (, JAZU) since its founder wanted to make it the central scientific and artistic institution of all South Slavs. Today, its main goals are encouraging and organizing scientific work, applying the achieved results, developing of artistic and cultural activities, carrying about the Croatian cultural heritage and its affirmation in the world, publishing the results of scientific research and artistic creativity and giving suggestions and opinions for the advancement of science and art in areas of particular importance to Croatia. The academy is divided into nine classes; social sciences, mathematical, physical and chemical sciences, natural sciences, medical sciences, philological sciences, Literature, Fine Arts, Musical Arts and Musicology, technical sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rad JAZU
''Rad'' ( Croatian for ''proceedings'', ''work'') is an academic journal An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which Scholarly method, scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the ... published by the Yugoslav, now Croatian, Academy of Sciences and Arts. It was their only publication from 1867 until 1882, when each of the individual scientific sections of the academy started printing their own journals. , over five hundred issues have been published. External links * * * Croatian-language journals Publications established in 1867 Multidisciplinary academic journals Academic journals of Croatia Academic journals published by learned and professional societies {{academic-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matica Hrvatska
Matica hrvatska () is the oldest independent, non-profit and non-governmental Croatian national institution. It was founded on February 2, 1842 by the Croatian Count Janko Drašković and other prominent members of the Illyrian movement during the Croatian National Revival (1835–1874). Its main goals are to promote Croatian national and cultural identity in the fields of art, science, spiritual creativity, economy and public life as well as to care for social development of Croatia. Today, in the Palace of Matica hrvatska in the centre of Zagreb more than hundred book presentations, scientific symposia, round table discussions, professional and scientific lectures and concerts of classical music are being organized annually. Matica Hrvatska is also one of the largest and most important book and magazine publishers in Croatia. Magazines issued by Matica are '' Vijenac'', '' Hrvatska revija'' and '' Kolo''. Matica Hrvatska also publishes many books in one of its most famous edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagreb
Zagreb ( ) is the capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Croatia#List of cities and towns, largest city of Croatia. It is in the Northern Croatia, north of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slopes of the Medvednica mountain. Zagreb stands near the international border between Croatia and Slovenia at an elevation of approximately above mean sea level, above sea level. At the 2021 census, the city itself had a population of 767,131, while the population of Zagreb metropolitan area is 1,086,528. The oldest settlement in the vicinity of the city was the Roman Andautonia, in today's Šćitarjevo. The historical record of the name "Zagreb" dates from 1134, in reference to the foundation of the settlement at Kaptol, Zagreb, Kaptol in 1094. Zagreb became a free royal city in 1242. In 1851, Janko Kamauf became Zagreb's List of mayors of Zagreb, first mayor. Zagreb has special status as a Administrative divisions of Croatia, Croatian administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe, and was the first recognised emperor to rule from the west after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting influence on Europe throughout the Middle Ages. A member of the Frankish Carolingian dynasty, Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. With his brother, Carloman I, he became king of the Franks in 768 following Pepin's death and became the sole ruler three years later. Charlemagne continued his father's policy of protecting the papacy and became its chief defender, remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dybo's Law
Dybo's law, or Dybo–Illich-Svitych's law, is a Common Slavic accent law named after Soviet accentologists Vladimir Dybo and Vladislav Illich-Svitych. It was posited to explain the occurrence of nouns and verbs in Slavic languages which are invariantly accented on the inflectional ending. The latter is seen as an innovation from the original Proto-Balto-Slavic accent system, in which nouns and verbs either had invariable accent on the root, or "mobile" accent which could alternate between root and ending in the inflectional paradigm. Overview According to the law, the accent was shifted rightward from a non-acute syllable (i.e. a long circumflex syllable, or a short syllable) to the following syllable if the word belonged to the fixed accentual paradigm. This produced the difference between the later accent classes A and B. The length of the previously-accented syllable remains. The preservation of the original length is the primary source of pre-tonic length in the later S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a Feature (linguistics), feature of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement (linguistics), agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and many other languages present number categories of singular or plural. Some languages also have a Dual (grammatical number), dual, #Trial, trial and #Paucal, paucal number or other arrangements. The word "number" is also used in linguistics to describe the distinction between certain grammatical aspects that indicate the number of times an event occurs, such as the semelfactive aspect, the iterative aspect, etc. For that use of the term, see "Grammatical aspect". Overview Most languages of the world have formal means to express differences of number. One widespread distinction, found in English and many other languages, involves a simple two-way contrast between singular and plural number (''car''/''cars'', ''child''/''children'', etc.). Discussion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative Case
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case, or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb, or (in Latin and formal variants of English) a predicative nominal or adjective, as opposed to its object, or other verb arguments. Generally, the noun "that is doing something" is in the nominative, and the nominative is often the form listed in dictionaries. Etymology The English word ''nominative'' comes from Latin ''cāsus nominātīvus'' "case for naming", which was translated from Ancient Greek ὀνομαστικὴ πτῶσις, ''onomastikḗ ptôsis'' "inflection for naming", from ''onomázō'' "call by name", from ''ónoma'' "name". Dionysius Thrax in his The Art of Grammar refers to it as ''orthḗ'' or ''eutheîa'' "straight", in contrast to the oblique case, oblique or "bent" cases. Characteristics The reference form (more technically, the ''lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th century AD. As with most other proto-languages, no attested writings have been found; scholars have reconstructed the language by applying the comparative method to all the attested Slavic languages and by taking into account other Indo-European languages. Rapid development of Slavic speech occurred during the Proto-Slavic period, coinciding with the massive expansion of the Slavic-speaking area. Dialectal differentiation occurred early on during this period, but overall linguistic unity and mutual intelligibility continued for several centuries, into the 10th century or later. During this period, many sound changes diffused across the entire area, often uniformly. This makes it inconvenient to maintain the traditional definition of a prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stjepan Ivšić
Stjepan Ivšić (; 13 August 1884 – 14 January 1962) was a Croatian linguist, Slavicist, and accentologist. Biography Ivšić was born on 13 August 1884 in Orahovica. After finishing primary school in Orahovica, he attended secondary school in Osijek and Požega. At the Faculty of Philosophy at the University of Zagreb he studied Croatian and classical philology, and later specialized at the universities in Kraków, Prague, Saint Petersburg, Moscow, and Kyiv. He received his Ph.D. in 1913 with the thesis ''Prilog za slavenski akcenat'' (A Contribution on the Slavic Accent). He served as a professor at the secondary school in Gornji Grad in Zagreb from 1909 to 1915, and thenceforth as a professor of Slavic Studies at the Faculty of Philosophy in Zagreb. The focal point of Ivšić's research was Croatian Štokavian subdialects, on which he published several very important studies (''Šaptinovačko narječje'', 1907; ''Današnji posavski govor'', 1913). He was especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |