|
Italic Languages
The Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken on the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BC. The most important of the ancient Italic languages was Latin, the official language of ancient Rome, which conquered the other Italic peoples before the Common Era, common era. The other Italic languages became Extinct language, extinct in the first centuries AD as their speakers were assimilated into the Roman Empire and Language shift, shifted to some form of Latin. Between the third and eighth centuries AD, Vulgar Latin (perhaps influenced by Substratum (linguistics), substrata from the other Italic languages) diversified into the Romance languages, which are the only Italic languages natively spoken today, while Literary Latin also survived. Besides Latin, the known ancient Italic languages are Faliscan language, Faliscan (the closest to Latin), Umbrian language, Umbrian and Oscan lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
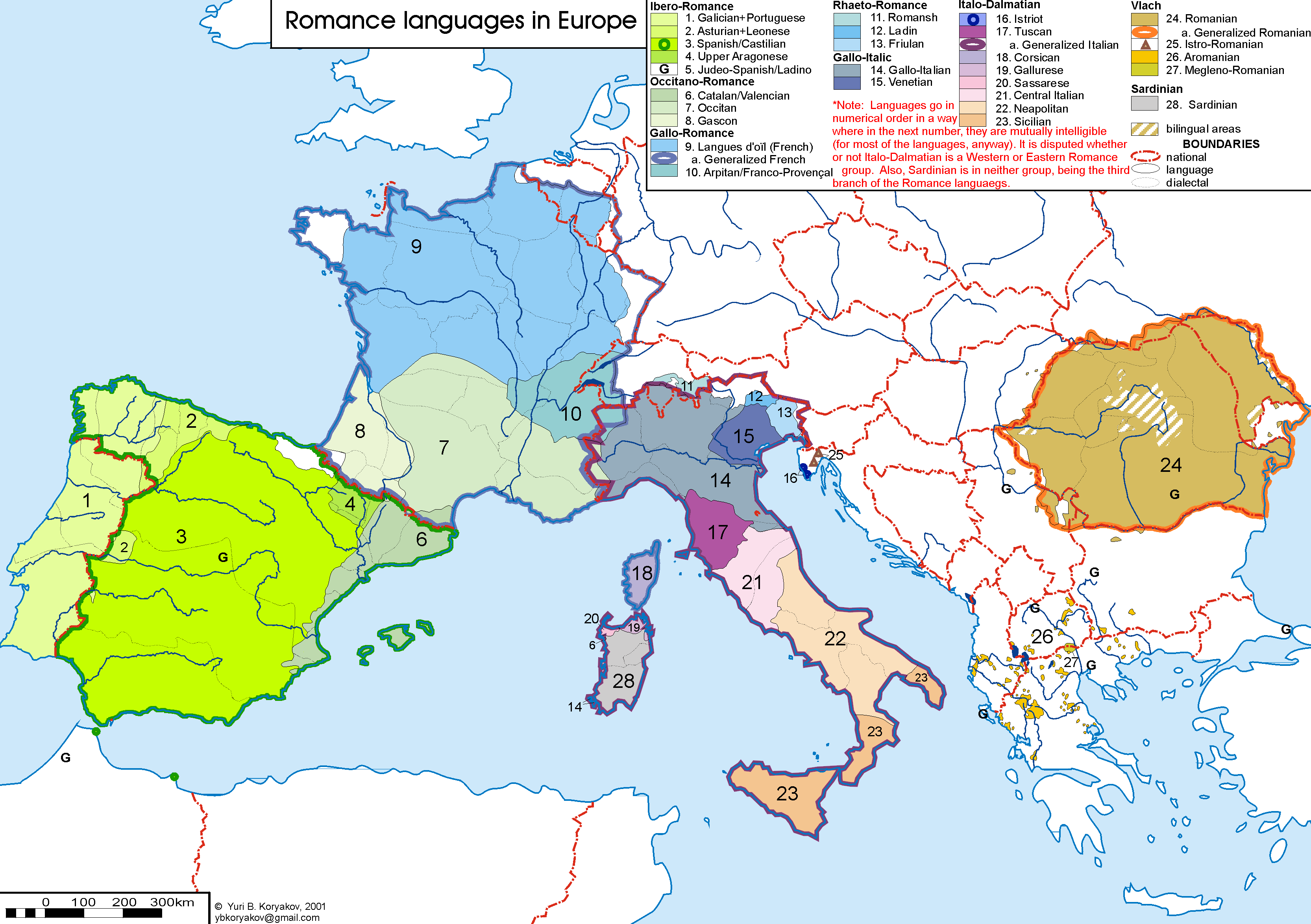
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siculian
Siculian (or Sicel) is an extinct Indo-European language spoken in central and eastern Sicily by the Sicels. It is attested in fewer than thirty inscriptions in eastern Sicily from the late 6th century to 4th century BCE, and in around twenty-five glosses from ancient writers. Classification Ancient sources state that Siculians entered Sicily from the Italian Peninsula either around the 13th century or the middle of the 11th century BCE (or in two waves), driving the prior inhabitants, the Sicanians and Elymians, to the west of the island. Due to its limited attestation, it is difficult to determine much about this language beyond that it was Indo-European. The prevalent modern view is that Siculian was an Italic language, although the scarcity of sources and the difficulties in interpreting inscriptions and glosses make it impossible to come to a definitive conclusion. Some inscriptions may reveal Italic elements, such as ''geped'' ('had'), which is comparable to the Oscan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Language
An extinct language or dead language is a language with no living native speakers. A dormant language is a dead language that still serves as a symbol of ethnic identity to an ethnic group; these languages are often undergoing a process of revitalisation. Languages that have first-language speakers are known as modern or living languages to contrast them with dead languages, especially in educational contexts. Languages have typically become extinct as a result of the process of cultural assimilation leading to language shift, and the gradual abandonment of a native language in favor of a foreign ''lingua franca''. As of the 2000s, a total of roughly 7,000 natively spoken languages existed worldwide. Most of these are minor languages in danger of extinction; one estimate published in 2004 expected that some 90% of the languages spoken at that time will have become extinct by 2050. Language death Normally the transition from a spoken to an extinct language occurs when a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression can be traced back to 1615, when it first appears in a book by Johannes Kepler as the (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the late 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications on the grounds that BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They have been promoted as more sensitive to non-Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age Italy
The prehistory of Italy began in the Paleolithic period, when members of the genus ''Homo species, Homo'' first inhabited what is now modern Italian territory, and ended in the Iron Age, when the first written records appeared in Insular Italy, Italy. Paleolithic In prehistoric times, the landscape of the Italian Peninsula was significantly different from its modern appearance. During glaciations, for example, the sea level was lower and the islands of Elba and Sicily were connected to the mainland. The Adriatic Sea began at what is now the Gargano, Gargano Peninsula, and what is now its surface up to Venice was a fertile plain with a humid climate. The arrival of the first known hominins was 850,000 years ago at Monte Poggiolo. The presence of ''Homo neanderthalensis'' has been demonstrated in archaeological findings dating to c. 50,000 years ago (late Pleistocene). There are about 20 unique sites, the most important being that of the Grotta Guattari at San Felice Circeo, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e.g., Tajikistan and Afghanistan), Armenia, and areas of southern India. Historically, Indo-European languages were also spoken in Anatolia. Some European languages of this family—English language, English, French language, French, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Russian language, Russian, Spanish language, Spanish, and Dutch language, Dutch—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, including Albanian language, Albanian, Armenian language, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic languages, Celtic, Germanic languages, Germanic, Hellenic languages, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian, and Italic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrsenian Languages
Tyrsenian (also Tyrrhenian or Common Tyrrhenic), named after the Tyrrhenians (Ancient Greek, Ionic: ''Tyrsenoi''), is an extinct family of closely related ancient languages put forward by linguist Helmut Rix in 1998, which consists of the Etruscan language of northern, central and south-western Italy, and eastern Corsica (France); the Raetic language of the Alps, in northern Italy and Austria, named after the Rhaetian people; and the Lemnian language attested in Lemnos in the northern Aegean Sea. Camunic in northern Lombardy, between Etruscan and Raetic, may belong to the family as well, but evidence of such is limited. The Tyrsenian languages are generally considered Pre-Indo-European, and more specifically Paleo-European. Classification In 1998 the German linguist Helmut Rix proposed that three then unclassified ancient languages belonged to a common linguistic family he called ''Tyrrhenian'': the Etruscan language spoken in Etruria, the Raetic language of the Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetian Language
Rhaetic or Raetic (), also known as Rhaetian, was a Tyrsenian language spoken in the ancient region of Rhaetia in the eastern Alps in pre-Roman and Roman times. It is documented by around 280 texts dated from the 5th through the 1st century BC, which were found through northern Italy, southern Germany, eastern Switzerland, Slovenia and western Austria, in two variants of the Old Italic scripts. Rhaetic is largely accepted as being closely related to Etruscan. The ancient Rhaetic language is not to be confused with the modern Romance languages of the same Alpine region, known as Rhaeto-Romance. Classification The German linguist Helmut Rix proposed in 1998 that Rhaetic, along with Etruscan, was a member of a language family he called Tyrrhenian, and which was possibly influenced by neighboring Indo-European languages. Robert S. P. Beekes likewise does not consider it Indo-European. Howard Hayes Scullard (1967), on the contrary, suggested it to be an Indo-European language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Language
Etruscan ( ) was the language of the Etruscan civilization in the ancient region of Etruria, in Etruria Padana and Etruria Campana in what is now Italy. Etruscan influenced Latin but was eventually superseded by it. Around 13,000 Etruscan epigraphy, inscriptions have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Ancient Greek, Greek, or Phoenician language, Phoenician; and a few dozen purported loanwords. Attested from 700 BC to AD 50, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study. Nowadays, it is generally agreed to be in the Tyrsenian language family, but before it gained currency as one of the Tyrsenian languages, it was commonly treated as an Language isolate, isolate, although there were also a number of other less well-known hypotheses. The consensus among linguists and Etruscologists is that Etruscan was a Pre-Indo-European languages, Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unclassified Language
An unclassified language is a language whose genetic affiliation to other languages has not been established. Languages can be unclassified for a variety of reasons, mostly due to a lack of reliable data but sometimes due to the confounding influence of language contact, if different layers of its vocabulary or morphology point in different directions and it is not clear which represents the ancestral form of the language. Some poorly known extinct languages, such as Gutian and Cacán, are simply unclassifiable, and it is unlikely the situation will ever change. A supposedly unclassified language may turn out not to be a language at all, or even a distinct dialect, but merely a family, tribal or village name, or an alternative name for a people or language that is classified. If a language's genetic relationship has not been established after significant documentation of the language and comparison with other languages and families, as in the case of Basque in Europe, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |