|
Italian Campaign Of 1796–1797
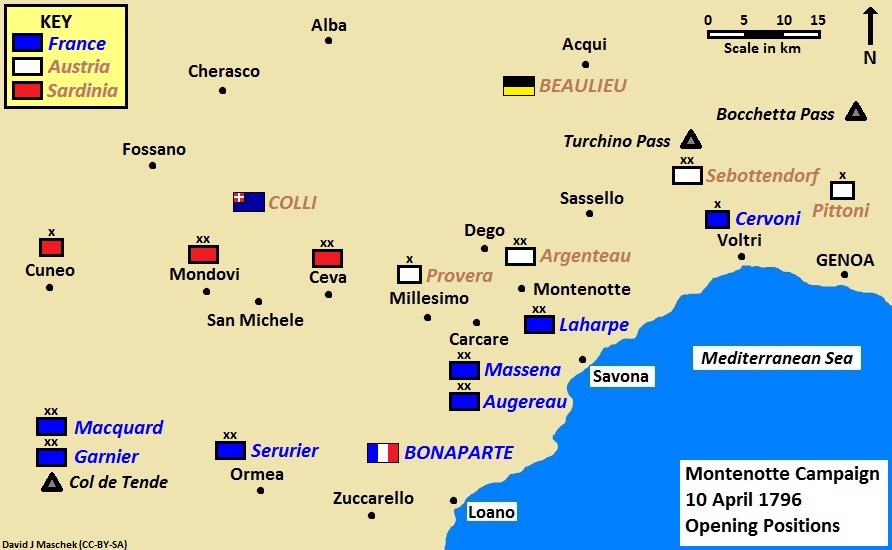
The Italian campaign of 1796–1797 (Italian language, Italian: ''Campagna d'Italia''), also known as the First Italian Campaign, was a series of military operations in Italy during the War of the First Coalition. Led by Napoleon Bonaparte, the First French Republic's Army of Italy (France), Army of Italy fought and defeated the armies of the Kingdom of Sardinia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Papal States, as well as various revolts, notably Veronese Easter, in the Republic of Venice. The campaign opened with the Montenotte campaign on 10 April 1796, where despite the limitations of his means, Bonaparte descended from the Alps into Italy and achieved a rapid series of victories that decisively knocked Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Piedmont-Sardinia Armistice of Cherasco, out of the First Coalition. Next, Napoleon chased the Austrian Army during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, Austrian army across Lombardy (historical region), Lombardy, culminating in Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The First Coalition
The War of the First Coalition () was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797, initially against the Constitutional Cabinet of Louis XVI, constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French First Republic, French Republic that succeeded it. They were only loosely allied and fought without much apparent coordination or agreement; each power had its eye on a different part of France it wanted to appropriate after a French defeat, which never occurred. Shusterman, Noah (2015). ''De Franse Revolutie (The French Revolution)''. Veen Media, Amsterdam. (Translation of: ''The French Revolution. Faith, Desire, and Politics''. Routledge, London/New York, 2014.) Chapter 7, pp. 271–312: The federalist revolts, the Vendée and the beginning of the Terror (summer–fall 1793). Relations between the French revolutionaries and neighbouring monarchies had deteriorated following the Declaration of Pillnitz in August 1791. Eight months later, Louis XVI and the Leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice was dissolved and dismembered by the French general Napoleon Bonaparte and the Habsburg monarchy on 12 May 1797, ending approximately 1,100 years of its existence. It was the final action of Napoleon's Italian campaign of 1796–1797 before the War of the First Coalition formally ended in October. In 1796, General Napoleon had been sent by the newly formed French Republic to confront Austria, as part of the Italian front of the French Revolutionary Wars. He chose to go through Venice, which was officially neutral. Reluctantly, the Venetians allowed the formidable French army to enter their country so that it might confront Austria. However, the French covertly began supporting Jacobin revolutionaries within Venice, and the Venetian Senate began quiet preparations for war. The Venetian armed forces were depleted and hardly a match for the battle-tested French or even a local uprising. After the capture of Mantua on 2 February 1797, the French dropped a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of Italy (France)
The Army of Italy () was a field army of the French Army stationed on the Italian border and used for operations in Italy itself. It is best known for its role during the French Revolutionary Wars (in which it was one of the early commands of Napoleon Bonaparte, during his Italian campaign) and Napoleonic Wars. History Bonaparte's reforms Poorly supplied (uniforms and shoes were rare), and only getting reinforcements irregularly, the Army of Italy was sometimes reduced to looting to survive. When Bonaparte arrived (he took up command on 27 March 1796), indiscipline was rife. Chouan songs were sung by the troops, and a company of the Dauphin was formed. All the while improving the supply system as much as possible, Bonaparte also reestablished discipline. He condemned officers who had cried ''Vive le roi !'', (English: "Live the king!"), dismissed the 13th regiment of hussards for indiscipline and dissolved an entire regiment when it revolted at the end of March. Purge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as List of islands of Italy, nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the List of European countries by area, tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and List of cities in Italy, largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous List of ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is spoken by about 68 million people, including 64 million native speakers as of 2024. Italian is an official language in Languages of Italy, Italy, Languages of San Marino, San Marino, Languages of Switzerland, Switzerland (Ticino and the Grisons), and Languages of Vatican City, Vatican City; it has official Minority language, minority status in Minority languages of Croatia, Croatia, Slovene Istria, Romania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the municipalities of Santa Teresa, Espírito Santo, Santa Tereza, Encantado, Rio Grande do Sul, Encantado, and Venda Nova do Imigrante in Languages of Brazil#Language co-officialization, Brazil. Italian is also spoken by large Italian diaspora, immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduke Charles, Duke Of Teschen
Archduke Charles Louis John Joseph Lawrence of Austria, Duke of Teschen (; 5 September 177130 April 1847) was an Austrian field marshal, the third son of Emperor Leopold II and his wife, Maria Luisa of Spain. He was also the younger brother of Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor. He was epileptic, but achieved respect both as a commander and as a reformer of the Austrian army. He was considered one of Napoleon's most formidable opponents and one of the greatest generals of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He began his career fighting the revolutionary armies of France. Early in the wars of the First Coalition, he saw victory at Neerwinden in 1793, before being defeated at Wattignies in 1793 and Fleurus in 1794. In 1796, as chief of all Austrian forces on the Rhine, Charles defeated Jean-Baptiste Jourdan at Amberg, Würzburg and Limburg, and then won victories at Wetzlar, Emmendingen and Schliengen that forced Jean Victor Marie Moreau to withdraw across the Rhine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
József Alvinczi
Freiherr Joseph Alvinczi von Borberek a.k.a. Baron József Alvinczi de Borberek (; 1 February 1735 – 25 September 1810) was a soldier in the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Army and a field marshal of the Austrian Empire. He is remembered for handing Napoleon his first two defeats, at the battles of Second Battle of Bassano, Bassano and Battle of Caldiero (1796), Caldiero, both in 1796 and just days apart. Napoleon would later remark that Alvinczi was the best general he had fought thus far. Early career An ethnic Magyars, Magyar, he was born in Transylvania in a place called Vințu de Jos, Alvinc (German: ''Alwintz''), and spent his boyhood in the household of ''Graf'' Franz Gyulai before joining his regiment as a ''Fähnrich'' aged 14. By 1753 he had risen to ''Hauptmann''. During the Seven Years' War, Alvinczi distinguished himself leading a Grenadier (soldier), grenadier company in the battles of Battle of Torgau, Torgau and Battle of Teplitz, Teplitz, where his courageous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagobert Sigmund Von Wurmser
Dagobert Sigmund, Count von Wurmser (7 May 1724 – 22 August 1797) was an Austrian field marshal during the French Revolutionary Wars. Although he fought in the Seven Years' War, the War of the Bavarian Succession, and mounted several successful campaigns in the Rhineland in the initial years of the French Revolutionary Wars, he is probably most remembered for his unsuccessful operations against Napoleon Bonaparte during the 1796 campaign in Italy. Although initially in the Army of France during the Seven Years' War, Wurmser left France after Louis reached a peace agreement with Britain, and joined the military of the House of Habsburg. He later took part in the short-lived War of the Bavarian Succession, also called the so-called ''Kartoffelkrieg'' (Potato War). During the French Revolutionary Wars, Wurmser commanded several imperial Habsburg armies on in the Rhine River valley between 1793 and 1795, and perhaps his most conspicuous achievement was the taking of the lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Peter Beaulieu
Johann Peter de Beaulieu, also Jean Pierre de Beaulieu (26 October 1725, in Lathuy, Brabant, Belgium – 22 December 1819), was a Walloon military officer. He joined the Habsburg army and fought against the Prussians during the Seven Years' War. A cultured man, he later battled Belgian rebels and earned promotion to general officer. During the French Revolutionary Wars he fought against the First French Republic and attained high command. In 1796, a young Napoleon Bonaparte won some of his first victories against an army led by Beaulieu. He retired and was the Proprietor (Inhaber) of an Austrian infantry regiment until his death. Early career Born in Lathuy Castle, Jodoigne in the Austrian Netherlands (now Walloon Brabant, Belgium) in 1725, Beaulieu joined the Habsburg army in 1743 and fought in the War of the Austrian Succession. During the Seven Years' War he served first as an infantry officer and later on the staff of Feldmarschall Leopold Joseph von Daun. Beaulieu was wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banner Of The Holy Roman Emperor Without Haloes (1400-1806)
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Also, a bar-shaped piece of non-cloth advertising material sporting a name, slogan, or other marketing message is also a banner. Banner-making is an ancient craft. Church banners commonly portray the saint to whom the church is dedicated. The word derives from Old French ''baniere'' (modern ), from Late Latin ''bandum'', which was borrowed from a Germanic source (compare ). Cognates include Italian language">Italian ''bandiera'', Portuguese ''bandeira'', and Spanish language">Spanish ''bandera''. Vexillum The vexillum was a flag-like object used as a military standard by units in the Ancient Roman army. The word ''vexillum'' itself is a diminutive of the Latin ''velum'', meaning a sail, which confirms the historical evidence (from coins a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelangelo Alessandro Colli-Marchi
Michelangelo Alessandro Colli-Marchi or Michelangelo da Vigevano or Michael Colli (1738 Milan – 22 December ,Florence 1808) entered the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Austrian army as a commissioned officer and became a general officer after fighting in the Seven Years' War, War of the Bavarian Succession, and Austro-Turkish War (1787-1791), Austro-Turkish War. During the War of the First Coalition, he was loaned to the Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont for three years. In 1796, his army was defeated by Napoleon Bonaparte in a swift campaign that knocked Sardinia-Piedmont out of the war. In early 1797, he was given command of the army of the Papal States, but his troops were defeated at Battle of Faenza, Faenza. Early career Michelangelo Alessandro Colli-Marchi was born in either Vigevano or Milan in 1738. His father Giuseppe Antonio Colli (1698–1766) had represented Vigevano with the Habsburg government in Milan and was granted a title of nobility. Well educated, Colli was commissione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Papal States (pre 1808)
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade in Arab countries. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |