|
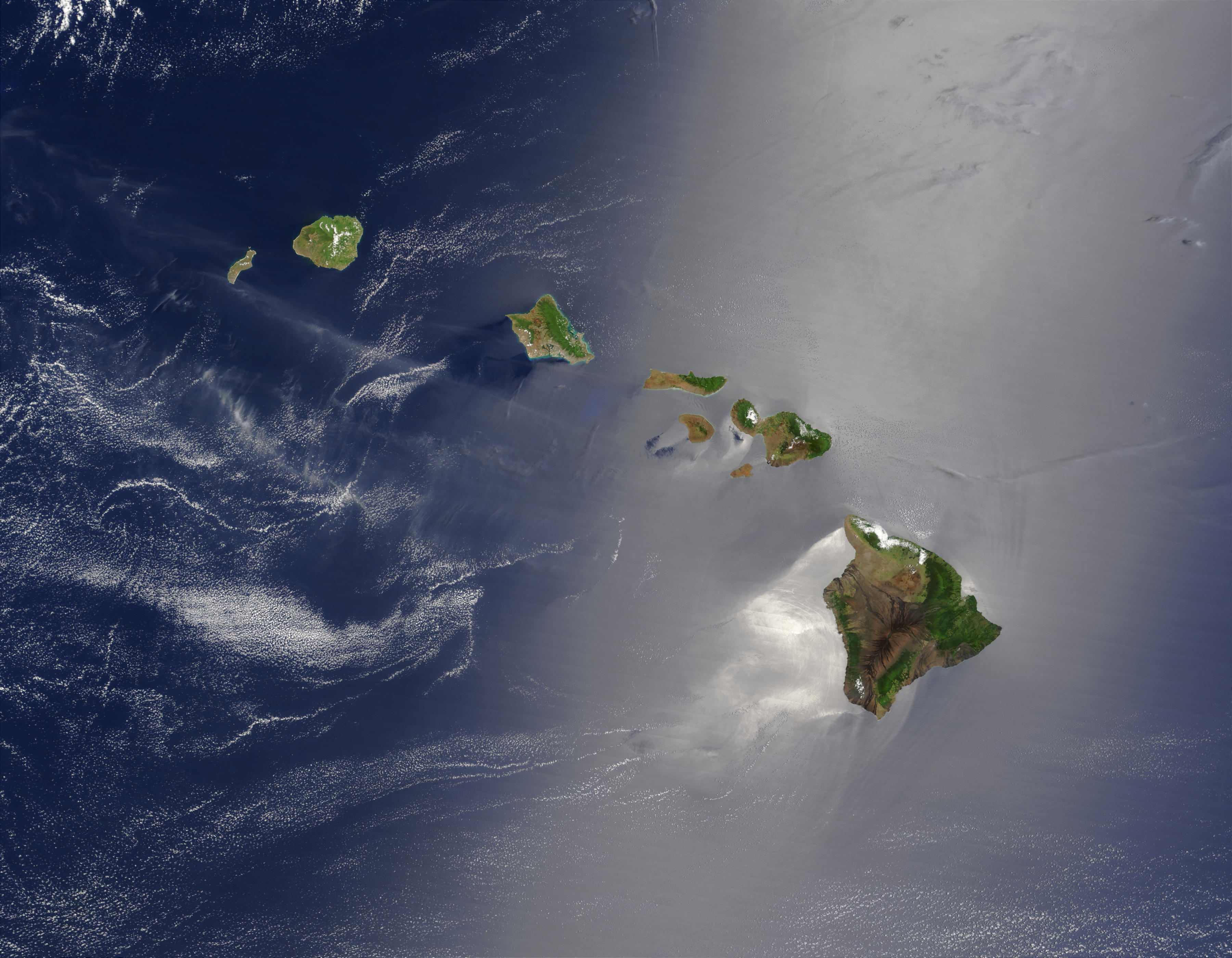
Island Restoration
The ecological restoration of islands, or island restoration, is the application of the principles of ecological restoration to islands and island groups. Islands, due to their isolation, are home to many of the world's endemic (ecology), endemic species, as well as important breeding grounds for seabirds and some marine mammals. Their ecosystems are also very vulnerable to human disturbance (ecology), disturbance and particularly to introduced species, due to their small size. Island groups, such as New Zealand and Hawaii, have undergone substantial extinctions and losses of Habitat (ecology), habitat. Since the 1950s several organisations and government agencies around the world have worked to restore islands to their original states; New Zealand has used them to hold natural populations of species that would otherwise be unable to survive in the wild. The principal components of island restoration are the removal of introduced species and the reintroduction of native species. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redonda By Sea 1, 2023
Redonda is an List of uninhabited regions, uninhabited Caribbean island which is a dependency of Saint John, Antigua and Barbuda, in the Leeward Islands, West Indies. The island is about long, wide, and is high at its highest point. It lies between the islands of Nevis and Montserrat, southwest of Antigua. Redonda is closer to Montserrat than to any other island; it is located northwest of Montserrat and southeast of Nevis. Redonda is home to vast numbers of sea birds, and the island was an important source of guano before artificial fertilisers started to be mass-produced. Guano-mining operations started in the 1860s and ceased after the start of World War I. During the mining operations a few buildings and other installations were put in place on the island, and some physical remnants of that phase in its history are still visible. "Redonda" is the feminine form of the Spanish language adjective meaning "round". In 1493, on his second voyage to the New World, Christop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
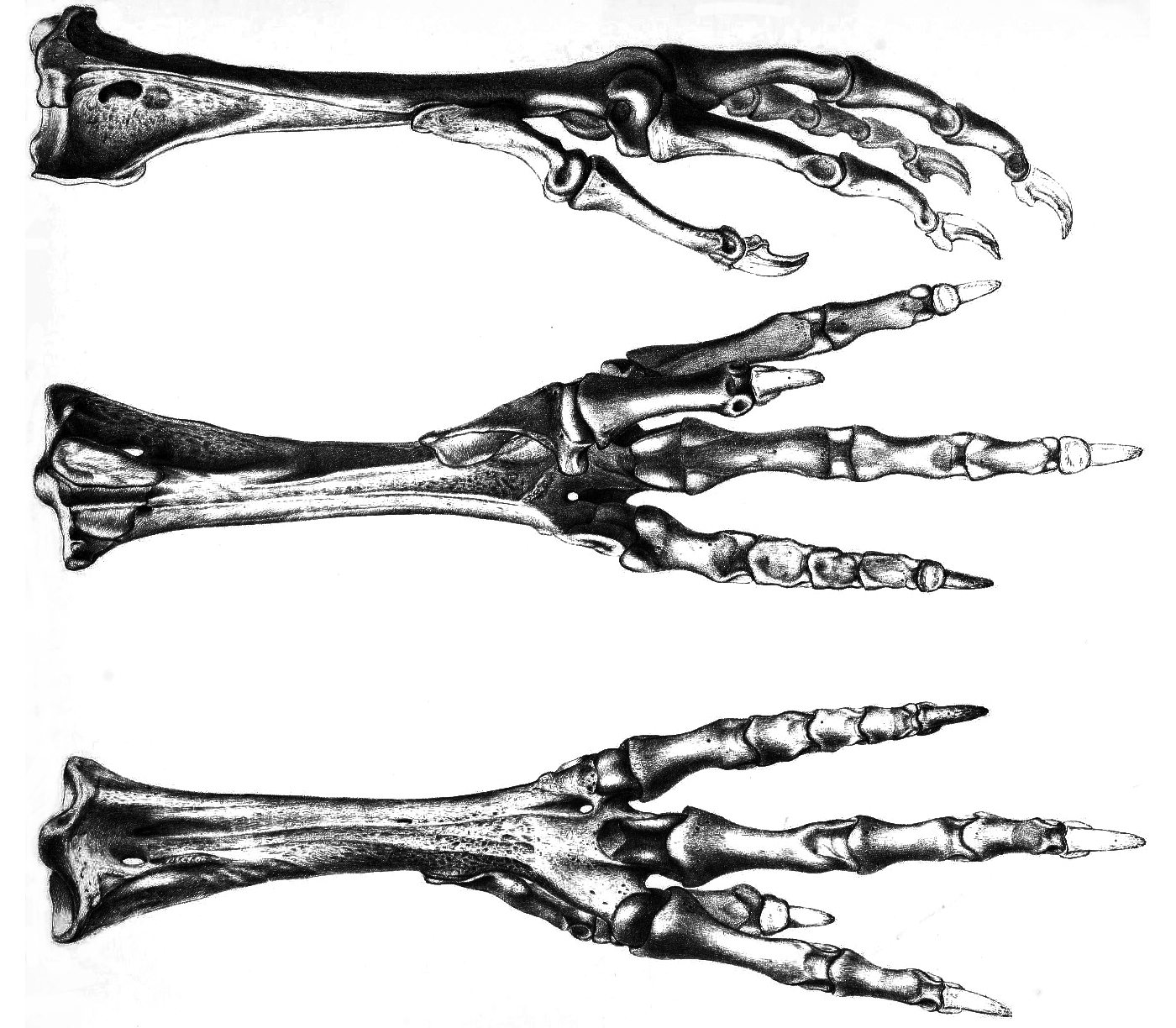
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinction, extinct flightless bird that was endemism, endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest relative was the also-extinct and flightless Rodrigues solitaire. The two formed the taxonomic rank, subtribe Raphina, a clade of extinct flightless birds that are a part of the group that includes Columbidae, pigeons and doves (the family Columbidae). The closest extant taxon, living relative of the dodo is the Nicobar pigeon. A white dodo was once thought to have existed on the nearby island of Réunion, but it is now believed that this assumption was merely confusion based on the also-extinct Réunion ibis and paintings of white dodos. Subfossil remains show the dodo measured about in height and may have weighed in the wild. The dodo's appearance in life is evidenced only by drawings, paintings, and written accounts from the 17th century. Since these portraits vary considerabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Conservation)
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been part of a continent. Oceanic islands can be formed from volcanic activity, grow into atolls from coral reefs, and form from sediment along shorelines, creating barrier islands. River islands can also form from sediment and debris in rivers. Artificial islands are those made by humans, including small rocky outcroppings built out of lagoons and large-scale land reclamation projects used for development. Islands are host to diverse plant and animal life. Oceanic islands have the sea as a natural barrier to the introduction of new species, causing the species that do reach the island to evolve in isolation. Continental islands share animal and plant life with the continent they split from. Depending on how long ago the continental island form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic, social, and environmental threats worldwide. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with the spread of international trade. Notable invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, giant hogweed (''Heracleum mantegazzianum''), Japanese knotw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takahē
The South Island takahē (''Porphyrio hochstetteri'') is a Flightless bird, flightless swamphen indigenous to New Zealand and the largest living member of the Rail (bird), rail family. It is often known by the abbreviated name takahē, which it shares with the Holocene extinction, recently extinct North Island takahē. The two takahē species are also known as notornis. Takahē were hunted extensively by both early European settlers and Māori people, Māori, and takahē bones have been found in middens in the South Island. Fossil remains have also been found across the South Island. They were not named and described by Europeans until 1847, and then only from fossil bones. In 1850 a living bird was captured, and three more collected in the 19th century. After another bird was captured in 1898, and no more were to be found, the species was presumed extinct. Fifty years later, however, after a carefully planned search, South Island takahē were dramatically rediscovered in No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magenta Petrel
The magenta petrel (''Pterodroma magentae''), or Chatham Island tāiko, is a small seabird in the gadfly petrel genus, ''Pterodroma''. Found exclusively on Chatham Island, New Zealand, it is one of the rarest birds in the world, believed to be extinct for over 100 years before its rediscovery in the 1970s. Description This medium-sized petrel has a brownish-grey head, neck, and upper breast, with white underparts. The undersides of the wings are brown. It has a black bill and pink legs. Adults weigh 400–580 g. The bird nests in 1–3 m long burrows under dense forest. They form long-term monogamous pair bonds, raising one egg at a time, and both partners incubate the egg and feed the chick. The breeding season is between September and May, during which time the birds forage over the open ocean. History Fossil records and historic records show that tāiko used to be the most abundant burrowing seabird on Chatham Island, though has not been found to have lived on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Rat
The Polynesian rat, Pacific rat or little rat (''Rattus exulans''), or , is the third most widespread species of rat in the world behind the brown rat and black rat. Contrary to its vernacular name, the Polynesian rat originated in Southeast Asia, and like its relatives has become widespread, migrating to most of Polynesia, including New Zealand, Easter Island, and Hawaii. It shares high adaptability with other rat species extending to many environments, from grasslands to forests. It is also closely associated with humans, who provide easy access to food. It has become a major pest in most areas of its distribution. Description The Polynesian rat is similar in appearance to other rats, such as the black rat and the brown rat. It has large, round ears, a pointed snout, black/brown hair with a lighter belly, and comparatively small feet. It has a thin, long body, reaching up to in length from the nose to the base of the tail, making it slightly smaller than other human-associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feral Cats
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact; it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens of generations and become a local apex predator in urban, savannah and bushland environments, and especially on islands where native animals did not evolve alongside predators. Some feral cats may become more comfortable with people who regularly feed them, but even with long-term attempts at socialization, they usually remain aloof and reject human touch. Of the 700 million cats in the world, an estimated 480 million are feral. Feral cats are devastating to wildlife, and conservation biologists consider them to be one of the worst invasive species on Earth. They are included in the list of the world's 100 worst invasive alien species. Attempts to control feral cat populations are widespread but generally of greatest impact within purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of Caprinae, goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the family Bovidae, meaning it is closely related to the sheep. It was one of the first animals to be domesticated, in Iran around 10,000 years ago. Goats have been used for milk, Goat meat, meat, Animal fur, wool, and Animal skin, skins across much of the world. Milk from goats is often turned into goat cheese, cheese. In 2022, there were more than 1.1 billion goats living in the world, of which 150 million were in India. Goats feature in mythology, folklore, and religion in many parts of the world, including in the classical myth of Amalthea (mythology), Amalthea, in Tanngrisnir and Tanngnjóstr, the goats that pulled the chariot of the Norse god Thor, in the Scandinavian Yule goat, and in Hinduism's goat-headed Daksha. In Christianity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuvier Island
Cuvier Island is a small uninhabited island off the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It lies on the seaward end of the Colville Channel, north of the Mercury Islands and approximately south-east of Great Barrier Island. The island is a wildlife sanctuary, managed by the Department of Conservation and is the subject of an ongoing island restoration project to eliminate non-native mammals and restore the original ecosystem.At one time in the 1920s the wife of the Lighthouse Keeper was the nominated Protector of Tuatara Lizards which were found in numbers at the rear of the housCuvier Island restoration (from the Department of Conservation website) It is also the location of the Cuvier Island Lighthouse which was constructed in 1889 and the wreck of the old '' HMNZS Philomel'' which was scuttled near the island on 6 August 1949 after decommissioning and being stripped of useful equipment. Geology The island is the remains of an igneous intrusion of the Coromand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Department Of Conservation
The Department of Conservation (DOC; Māori language, Māori: ''Te Papa Atawhai'') is the public service department of New Zealand charged with the conservation of New Zealand's natural and historical heritage. An advisory body, the New Zealand Conservation Authority, New Zealand Conservation Authority (NZCA) is provided to advise DOC and its ministers. In addition there are 15 conservation boards for different areas around the country that provide for interaction between DOC and the public. Functions and history Overview The department was formed on 1 April 1987, as one of several reforms of the public service, when the ''Conservation Act 1987'' was passed to integrate some functions of the Department of Lands and Survey, the New Zealand Forest Service, Forest Service and the New Zealand Wildlife Service, Wildlife Service. This act also set out the majority of the department's responsibilities and roles. As a consequence of Conservation Act all Crown land in New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest. Bermuda is an archipelago consisting of List of islands of Bermuda, 181 islands, although the most significant islands are connected by bridges and appear to form one landmass. It has a land area of . Bermuda has a tropical climate, with warm winters and hot summers. Its climate also exhibits Oceanic climate, oceanic features similar to other coastal areas in the Northern Hemisphere with warm, moist air from the ocean ensuring relatively high humidity and stabilising temperatures. Bermuda is prone to severe weather from Westerlies#Interaction with tropical cyclones, recurving tropical cyclones; however, it receives some protection from a coral reef and its position north of the Main Development Region, which limits the direction and severity of approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |