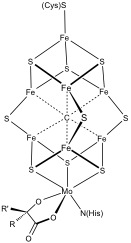
|
Iron–sulfur Cluster
Iron–sulfur clusters are molecular ensembles of iron and sulfide. They are most often discussed in the context of the biological role for iron–sulfur proteins, which are pervasive. Many Fe–S clusters are known in the area of organometallic chemistry and as precursors to synthetic analogues of the biological clusters. It is supposed that the last universal common ancestor had many iron-sulfur clusters. In biology Iron–sulfur clusters occur in many biological systems, often as components of electron transfer proteins. The ferredoxin proteins are the most common Fe–S proteins in nature. They feature either 2Fe–2S or 4Fe–4S centers. They occur in all branches of life. Fe–S clusters can be classified according to their Fe:S stoichiometry Fe–2S Fe–3S Fe–4S and Fe–4S The Fe–4Sclusters occur in two forms: normal ferredoxins and high potential iron proteins (HiPIP). Both adopt cuboidal structures, but they utilize different oxidation states. They are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iron–sulfur Protein
Iron–sulfur proteins are proteins characterized by the presence of iron–sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers in variable oxidation states. Iron–sulfur clusters are found in a variety of metalloproteins, such as the ferredoxins, as well as NADH dehydrogenase, hydrogenases, coenzyme Q – cytochrome c reductase, succinate – coenzyme Q reductase and nitrogenase. Iron–sulfur clusters are best known for their role in the oxidation-reduction reactions of electron transport in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Both Complex I and Complex II of oxidative phosphorylation have multiple Fe–S clusters. They have many other functions including catalysis as illustrated by aconitase, generation of radicals as illustrated by SAM-dependent enzymes, and as sulfur donors in the biosynthesis of lipoic acid and biotin. Additionally, some Fe–S proteins regulate gene expression. Fe–S proteins are vulnerable to attack by biogenic nitric oxide, formin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cluster Chemistry
Nanoclusters are atomically precise, crystalline materials most often existing on the 0-2 nanometer scale. They are often considered kinetically stable intermediates that form during the synthesis of comparatively larger materials such as semiconductor and metallic nanocrystals. The majority of research conducted to study nanoclusters has focused on characterizing their crystal structures and understanding their role in the nucleation and growth mechanisms of larger materials. Materials can be categorized into three different regimes, namely bulk, nanoparticles and nanoclusters. Bulk metals are electrical conductors and good optical reflectors and metal nanoparticles display intense colors due to surface plasmon resonance. However, when the size of metal nanoclusters is further reduced to form a nanocluster, the band structure becomes discontinuous and breaks down into discrete energy levels, somewhat similar to the energy levels of molecules. This gives nanoclusters similar q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Biometal (biology)
Biometals (also called biocompatible metals, bioactive metals, metallic biomaterials) are metals normally present, in small but important and measurable amounts, in biology, biochemistry, and medicine. The metals copper, zinc, iron, and manganese are examples of metals that are essential for the normal functioning of most plants and the bodies of most animals, such as the human body. A few ( calcium, potassium, sodium) are present in relatively larger amounts, whereas most others are trace metals, present in smaller but important amounts (the image shows the percentages for humans). Approximately 2/3 of the existing periodic table is composed of metals with varying properties, accounting for the diverse ways in which metals (usually in ionic form) have been utilized in nature and medicine. History At first, the study of biometals was referred to as bioinorganic chemistry. Each branch of bioinorganic chemistry studied separate, particular sub-fields of the subject. However, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iron-binding Proteins
Iron-binding proteins are carrier proteins and metalloproteins that are important in iron metabolism and the immune response. Iron is required for life. Iron-dependent enzymes catalyze a variety of biochemical reactions and can be divided into three broad classes depending on the structure of their active site: non-heme mono-iron, non-heme diiron , or heme centers. A well-known family of iron-dependent enzymes include oxygenases that facilitate hydroxyl group addition of one or both atoms from o2. Notable enzymes include tryptophan dioxygenase, ferredoxin, and 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase. Heme proteins Heme proteins are proteins that contain a heme prosthetic group. The heme group consists of a porphyrin ring coordinated with an iron ion. Four nitrogen atoms in the porphyrin ring act as a ligand for the iron in the center. In many cases, the equatorial porphyrin is complemented by one or two axial ligands. An example of this is in hemoglobin, where the porphyrin works together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bioinorganic Chemistry
Bioinorganic chemistry is a field that examines the role of metals in biology. Bioinorganic chemistry includes the study of both natural phenomena such as the behavior of metalloproteins as well as artificially introduced metals, including those that are non-essential, in medicine and toxicology. Many biological processes such as respiration depend upon molecules that fall within the realm of inorganic chemistry. The discipline also includes the study of inorganic models or mimics that imitate the behaviour of metalloproteins. As a mix of biochemistry and inorganic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry is important in elucidating the implications of electron-transfer proteins, substrate bindings and activation, atom and group transfer chemistry as well as metal properties in biological chemistry. The successful development of truly interdisciplinary work is necessary to advance bioinorganic chemistry. Composition of living organisms About 99% of mammals' mass are the elements carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from Latin ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cyclopentadienyl
Cyclopentadienyl can refer to * Cyclopentadienyl anion, or cyclopentadienide, ** Cyclopentadienyl ligand * Cyclopentadienyl radical, • * Cyclopentadienyl cation, See also * Pentadienyl {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cubane-type Cluster
A cubane-type cluster is an arrangement of atoms in a molecular structure that forms a cube. In the simplest case, the eight vertices are symmetry equivalent and the species has Oh symmetry group, symmetry. Such structure occurs in the hydrocarbon cubane (chemical formula ), which has carbon atoms at the corners of a cube and covalent bonds forming the edges. : Other compounds in the class have different elements in the corners, and various atoms or groups bonded to the corners. Most cubanes have more complicated structures, usually with nonequivalent vertices. They may be simple covalent compounds or macromolecular or supramolecular cluster compounds. Examples Heavier adamantogen cubanes with all vertices identical are all known, and exhibit only about half as much strain energy as cubane per molecule. The inert pair effect is believed to drive stability in cubanes with heavy main group elements: the bonding orbitals are almost entirely orbital hybridization, unhybridized ''p' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cations
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ ( potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− ( chloride ion) and OH− (hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron transfer, Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one Substrate (chemistry), substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |