|
Iraqi Dinar
The Iraqi dinar (ISO 4217, code: IQD; ), ) is the currency of Iraq. The Iraqi dinar is issued by the Central Bank of Iraq (CBI). On 7 February 2023, the exchange rate with the US dollar was US$1 = 1300 dinars. History The Iraqi dinar entered circulation on 1 April 1932, replacing the Indian rupee, which had been the official currency since the Mesopotamian campaign, British occupation of the country in World War I, at a rate of 1 dinar = 11 rupees. The dinar was pegged at par with Pound sterling, sterling until 1959 when, without changing its value, the peg was switched to the United States dollar at the rate of IQD 1 = US$2.80. By not following the US devaluations in 1971 and 1973, the official rate rose to US$3.3778, before a 5% devaluation reduced its rate to US$3.2169, a rate which remained until the Gulf War in 1990, although in late 1989 the black market rate was reported at five to six times higher than the official rate. Post-1990 developments After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fils (currency)
The fils (Arabic: فلس) is a subdivision of currency used in some Arab countries, such as Iraq and Bahrain. The term is a modern retranscription of ''fals'', an early medieval Arab coin. "Fils" is the singular form in Arabic, not plural (as its final consonant might indicate to an English speaker). The plural form of fils is ''fulūs'' (فلوس); the latter term can also refer to small amounts of money or to money in general in Egyptian Arabic, Egyptian and Mesopotamian Arabic, Iraqi and many other varieties of Arabic. * 1 Bahraini dinar = 1000 fulūs (or 1 fils = Bahraini dinar) * 1 Emirati dirham = 100 fulus * 1 Iraqi dinar = 1000 fulūs * 1 Jordanian dinar = 1000 fulūs * 1 Kuwaiti dinar = 1000 fulūs * 1 Yemeni rial = 100 fulūs See also * Falus References {{DEFAULTSORT:Fils (Currency) Denominations (currency) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Iraq, U.S. invasion of Iraq. He previously served as the Vice President of Iraq, vice president from 1968 to 1979 and also as the prime minister of Iraq, prime minister from 1979 to 1991 and later from 1994 to 2003. A leading member of the Ba'ath Party, Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, he espoused Ba'athism, a mix of Arab nationalism and Arab socialism, while the policies and political ideas he championed are collectively known as Saddamism. Born near the city of Tikrit to a Sunni Islam, Sunni Arabs, Arab family, Saddam joined the revolutionary Ba'ath Party in 1957. He played a key role in the 17 July Revolution that brought the Ba'athists to power and made him Vice President of Iraq, vice president under Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr. During his tenure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable in a brief amount of time. It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value. Many speculators pay little attention to the fundamental value of a security and instead focus purely on price movements. In principle, speculation can involve any tradable good or financial instrument. Speculators are particularly common in the markets for stocks, bonds, commodity futures, currencies, cryptocurrency, fine art, collectibles, real estate, and financial derivatives. Speculators play one of four primary roles in financial markets, along with hedgers, who engage in transactions to offset some other pre-existing risk, arbitrageurs who seek to profit from situations where fungible instruments trade at different prices in different market segments, and investors who seek profit through long-term ownership of an inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redenomination
In monetary economics, redenomination is the process of changing the face value of banknotes and coins in circulation. It may be done because inflation has made the currency unit so small that only large denominations of the currency are in circulation. In such cases the name of the currency may change or the original name may be used with a temporary qualifier such as "new". Redenomination may be done for other reasons such as changing over to a new currency such as the Euro or during decimalisation. Redenomination itself is considered symbolic as it does not have any impact on a country's exchange rate in relation to other currencies. It may, however, have a psychological impact on the population by suggesting that a period of hyperinflation is over, and is not a reminder of how much inflation has impacted them. The reduction in the number of zeros also improves the image of the country abroad. Inflation over time is the main cause for the purchasing power of the monetary un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
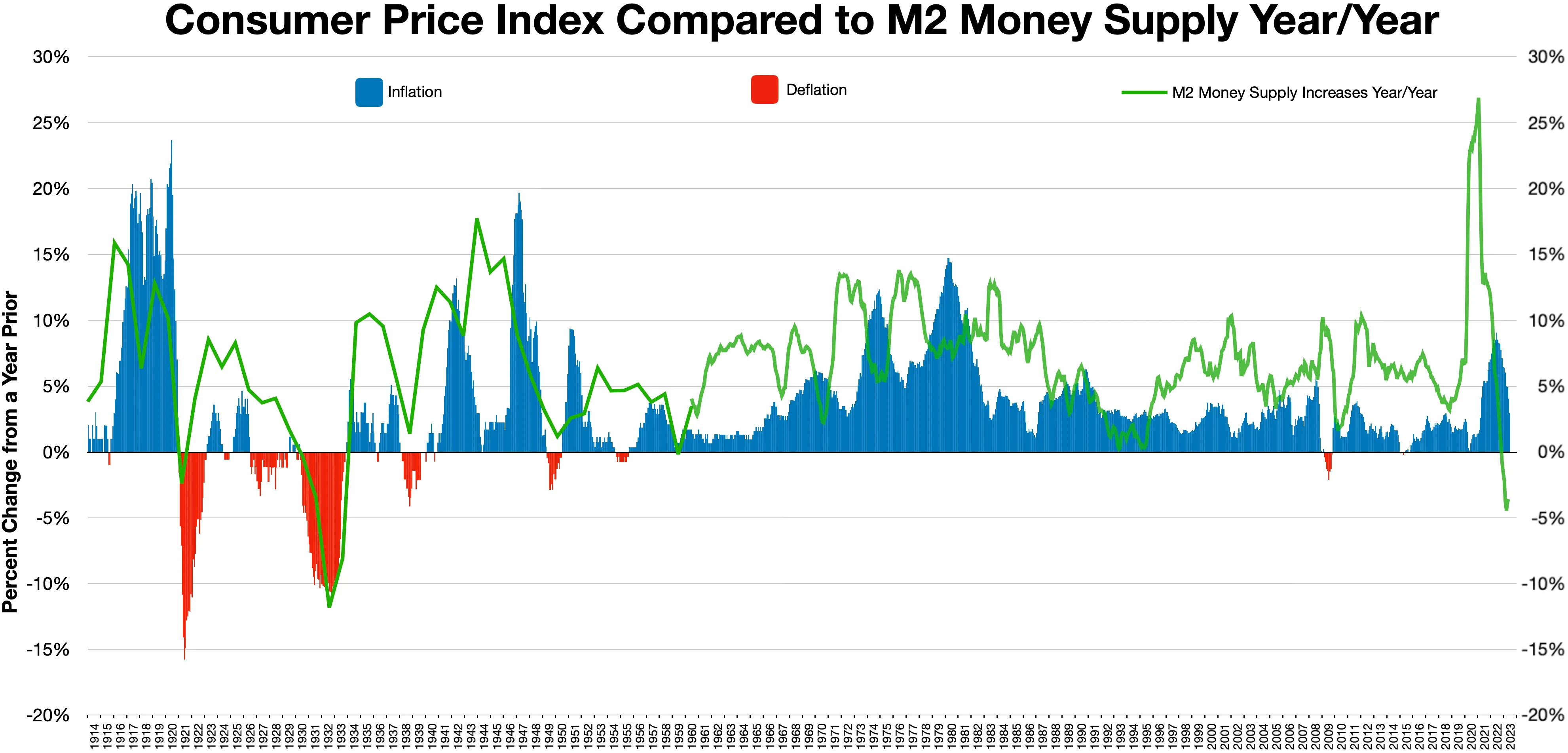
Deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from '' disinflation'', a slowdown in the inflation rate; i.e., when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral . Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supply is hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau De Change
A bureau de change (plural bureaux de change, both ; British English) or currency exchange (Comparison of American and British English, American English) is a business where people can exchange one currency for another. Nomenclature Originally French language, French, the term () is widely used throughout Europe and French-speaking Canada, where it is common to find a sign saying "exchange" or "change". Since the adoption of the euro, many exchange offices have started incorporating its logotype prominently on their signage. In the United States and English-speaking Canada the business is described as "currency exchange" and sometimes "money exchange", sometimes with various additions such as "foreign", "desk", "office", "counter", "service", etc.; for example, "foreign currency exchange office". Location A bureau de change is often located at a bank, at a travel agent, airport, main railway station, large supermarket branches, and anywhere else where there is likely to be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exchange Rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of the euro. The exchange rate is also regarded as the value of one country's currency in relation to another currency. For example, an Interbank lending market, interbank exchange rate of 141 Japanese yen to the United States dollar means that ¥141 will be exchanged for or that will be exchanged for ¥141. In this case it is said that the price of a dollar in relation to yen is ¥141, or equivalently that the price of a yen in relation to dollars is $1/141. Each country determines the exchange rate regime that will apply to its currency. For example, a currency may be floating exchange rate, floating, fixed exchange rate, pegged (fixed), or a hybrid. Governments can impose certain limits and controls on exchange rates. Countries can als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrodollar
Petrocurrency (or petrodollar) is a word used with three distinct meanings, often confused: #Dollars paid to oil-producing nations (petrodollar recycling)—a term invented in the 1970s meaning trading surpluses of oil-producing nations. #Currencies of oil-producing nations which tend to rise in value against other currencies when the price of oil rises (and fall when it falls). #Pricing of oil in US dollars: currencies used as a unit of account to price oil in the international market. Oil-producers' trading surpluses "Petrocurrency" or (more commonly) "petrodollars" are popular shorthand for revenues from petroleum exports, mainly from the OPEC members plus Russia and Norway. Especially during periods of historically expensive oil, the associated financial flows can reach a scale of hundreds of billions of US dollar-equivalents per year – including a wide range of transactions in a variety of currencies, some pegged to the US dollar and some not. Currencies correlated wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Currency In The Middle East
British involvement in the Middle East began with the General Maritime Treaty of 1820. This established the Trucial States and the nearby island of Bahrain as a base for suppressing sea piracy in the Persian Gulf. Meanwhile, in 1839 the British East India Company established an anti-piracy station in Aden to protect British shipping that was sailing to and from India. Involvement in the region expanded to Egypt in 1875 because of British interests in the Suez Canal, with a full scale British invasion of Egypt taking place in 1882. Muscat and Oman became a British Protectorate in 1891, and meanwhile Kuwait was added to the British Empire in 1899 because of fears surrounding the proposed Berlin-Baghdad Railway. There was a growing concern in the United Kingdom that Germany was a rising power, and about the implications that the proposed railway would have as regards access to the Persian Gulf. Qatar became a British Protectorate in 1916, and after the First World War, the British i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of last resort to national governments, and a leading supporter of exchange-rate economic stability, stability. Its stated mission is "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and poverty reduction, reduce poverty around the world." Established in July 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference, primarily according to the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it started with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary systems, international monetary system after World War II. In its early years, the IMF primarily focused on facilitating fixed exchange rates across the developed worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Soon after, it spread to other areas of Asia, and COVID-19 pandemic by country and territory, then worldwide in early 2020. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) on 30 January 2020, and assessed the outbreak as having become a pandemic on 11 March. COVID-19 symptoms range from asymptomatic to deadly, but most commonly include fever, sore throat, nocturnal cough, and fatigue. Transmission of COVID-19, Transmission of the virus is often airborne transmission, through airborne particles. Mutations have variants of SARS-CoV-2, produced many strains (variants) with varying degrees of infectivity and virulence. COVID-19 vaccines were developed rapidly and deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coalition Provisional Authority
The Coalition Provisional Authority (; , CPA) was a Provisional government, transitional government of Iraq established following the 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasion of the country on 19 March 2003 by Multi-National Force – Iraq, U.S.-led Coalition forces. The invasion marked the fall of the Ba'athist Iraq, Ba'athist regime led by Saddam Hussein. Citing United Nations Security Council Resolution 1483 (2003) and the Law of war, laws of war, the CPA was established in May 2003 and vested itself with executive (government), executive, Legislature, legislative, and judiciary authority over the Iraqi government from the period of the CPA's inception on 21 April 2003 until its dissolution on 28 June 2004. The CPA was admonished for its mismanagement of funds allocated to the Investment in post-invasion Iraq, reconstruction of post-invasion Iraq, with over $8 billion of these unaccounted for, including over $1.6 billion in cash that emerged in a basement in Lebanon. History of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |